Introduction
As we move further into the digital age, cybersecurity in 2025 stands at a crossroads. Threats are constantly changing at a breathtaking pace, with AI-powered attacks, more remote work, cloud dependency, and networked devices adding to the list. Organizations need to adopt Cybersecurity Best Practices 2025 not only to safeguard their assets but also to remain ahead of the ever-evolving sophisticated cyber threats.
Why Proactive Cybersecurity Is Non-Negotiable
Those days are gone when security was reactive. New businesses operate in an era where a single breach can result in millions of dollars in losses, reputational issues, and legal actions. Being proactive involves integrating cybersecurity into each process, system, and decision.
Let’s examine the top cybersecurity practices that all organizations should implement in 2025.
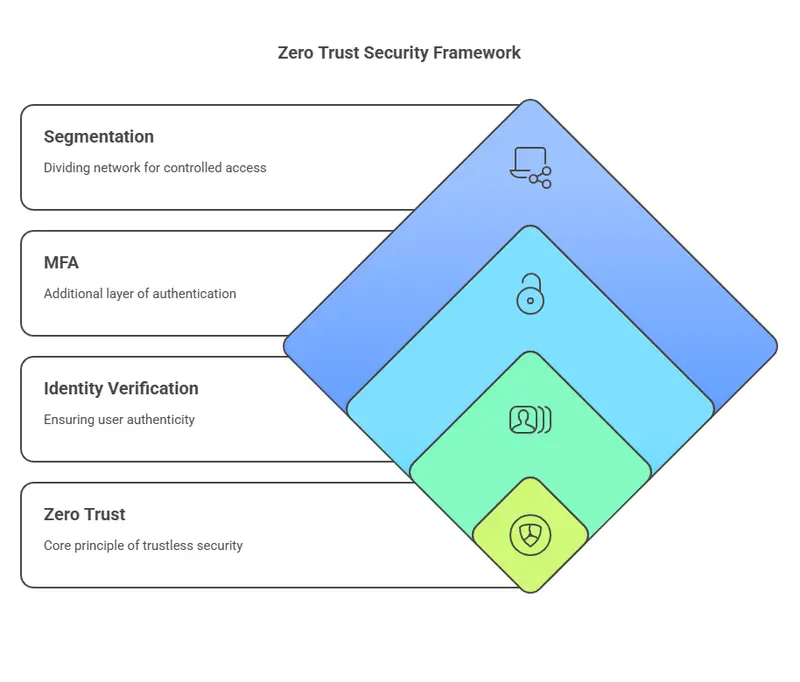
Implement a Zero Trust Architecture
As part of Cybersecurity Best Practices, implementing a Zero Trust framework is critical to reducing internal and external risks. Zero Trust is no longer a buzzword—it’s a requirement. Founded on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” Zero Trust ensures that no user or device is trusted by default, even if they are located within the corporate network.
How to Transition to Zero Trust:
- Divide your network into distinct areas and implement rigorous access controls.
- Enforce the application of multi-factor authentication (MFA) on all entry gateways.
- Keep a consistent watch for unusual patterns in user activity.
Benefits:
- Limits the side-to-side maneuvers of intruders.
- Enhances awareness of who is accessing specific information and when.
- Diminishes the effects of threats from within.
Real-world example:
Google has developed its own Zero Trust architecture through a project named BeyondCorp, which provides secure access to internal apps from untrusted networks without relying on VPNs.
Enhance Endpoint Security
Laptops, smartphones, servers & IoT devices are often the first targets in cyberattacks. They must be adequately secured.
Key Practices:
- Implement Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools for real-time monitoring.
- Keep all software and firmware up to date and patched regularly.
- Identify & priotitize protection for high-risk endpoints to manage possible threats.
Trend Watch 2025: The rise of XDR (Extended Detection and Response) is gaining popularity daily, as it combines endpoint, cloud, network, and identity data to provide a broader perspective of the threat environment.
Prioritize Employee Training and Awareness
Human mistakes and hackers are aware of this, which remains a leading risk in cybersecurity. A single careless click can jeopardize your whole system.
Effective Strategies:
- Hold monthly training sessions on cybersecurity.
- Conduct simulated phishing attacks to assess employees’ awareness and alertness.
- Foster a security-focused environment in which staff members can report any suspicious behavior they see.
Suggestion: Make training fun! Enhance cybersecurity training by incorporating elements such as rewards, leaderboards, and interactive features. Modules are effective in enhancing employee engagement and retention in the security sector.
Training staff regularly is one of the core pillars of Cybersecurity Best Practices, helping organizations stay resilient against human error.
Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Outdated software is a treasure trove for hackers. Staying current with patches is one of the simplest, most overlooked defenses.
Best Practices:
- Use automated patch management tools to stay current.
- Subscribe to real-time threat intelligence feeds.
- Prioritize patches for critical infrastructure and public-facing services.
Case Insight: The infamous 2017 Equifax data breach occurred due to an unpatched vulnerability in Apache Struts, affecting nearly 147 million users. This incident emphasizes the cost of delayed updates.
Conduct Frequent Security Audits and Risk Assessments
Security is not a task that you can “set and forget.” Regular reviews help you stay compliant with organizations and identify vulnerabilities that hackers may exploit.
What to Do:
- Schedule internal and third-party audits quarterly.
- Perform comprehensive risk assessments at least twice a year.
- Benchmark against frameworks like NIST, ISO/IEC 27001, or CIS Controls.
- Pro Tip: Consider implementing continuous auditing tools that operate in the background to catch issues in real-time, identifying irregularities instantly rather than postponing them until the next planned review.
Cybersecurity Best Practices: Incident Response Planning
In the event of a breach, swift and coordinated action can limit the damage.
Actions to Take:
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines clear roles and procedures to ensure a coordinated and effective response.
- Practice cyberattack scenarios with your team on a quarterly basis.
- Develop a transparent chain of command and a comprehensive communications plan for crisis management.
Tip: Maintain a “cybersecurity war room”—a designated area or platform where your team can centralize communication, updates, and logs in the event of an incident.
Secure Cloud Environments
With increasing reliance on cloud platforms, securing configurations is a non-negotiable aspect of Cybersecurity Best Practices. As cloud services become the core of operations, misconfigured settings pose a significant threat.
Security Controls:
- Implement strict cloud access policies based on the principle of least privilege.
- Implement encryption for data at rest and in transit.
- Periodically audit cloud configurations and permissions.
Cloud Tools to Utilize: AWS Config, Azure Security Center, and Google Cloud Security Command Center offer robust insights and alerts to ensure cloud hygiene.
Monitor and Manage Third-Party Risks
Your cybersecurity is as good as the weakest link within your supply chain.
Actionable Steps:
- Thoroughly screen third-party vendors for their cybersecurity protocols before onboarding.
- Include cybersecurity terms in every contract and Service Level Agreement (SLA).
- Monitor third-party access to sensitive information continuously and rescind when required.
Emerging Trend: More organizations are adopting Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) platforms, such as BitSight or SecurityScorecard, to assess vendors’ cybersecurity posture.
Invest in Advanced Threat Detection Technologies
New threats need new solutions, cyberattacks are growing smarter, and your defenses should too. Artificial intelligence and machine learning can detect patterns that are not visible to the human eye.
Leading Tools:
- Utilize Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to analyze security data in real-time and consolidate threat information in one place.
- Utilize AI-powered analytics for immediate detection of anomaly patterns or behaviours.
- Execute proactive threat detection tools to spot breaches in real-time.
New Solution: SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) systems, which operate in conjunction with SIEM tools to automate threat response workflow, bridging the gap between identification and reaction, and to reduce human error.
Back Up Data Regularly and Securely
Backups serve as your last line of defense against ransomware attacks and catastrophic loss.
Best Approaches:
- Set up consistent automated backups on a daily or weekly basis, based on the significance of the data.
- Secure all backup files with encryption and store copies of them off-site or in a secure cloud.
- Regularly test your recovery procedure to ensure business continuity.
Insider Tip: Follow the 3-2-1 backup principle by creating three total copies of your data, with two stored locally kept on various devices, with one located offsite.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity in 2025 demands vigilance, adaptability, and a mindset of constant improvement. It requires agility, flexibility, and a culture of holistic approaches. Cybercrime is estimated to cost the world more than $10.5 trillion annually by 2025; Organizations cannot afford to remain passive.
By embracing these Cybersecurity Best Practices for 2025, companies can:
- Built stronger digital trust among customers.
- Remain ahead of regulatory requirements.
- Decrease downtime and operational risk.
Cybersecurity is no longer an IT issue; it’s a business priority. All executives, employees, and vendors owe it to themselves to create a secure and more resilient digital world. By implementing these Cybersecurity Best Practices 2025, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface while contributing to a more secure digital landscape.
From Zero Trust Architecture to employee education, cloud security to threat intelligence, all the stakeholders have something to contribute. Be alert, continue learning, and treat cybersecurity as a fundamental business function, not a checkbox.
Want to read more on ethical hacking and security skills?
Head over to Tutedude’s Ethical Hacking Section to enhance your knowledge.