Introduction
In today’s software era, APIs are everywhere—they power mobile apps, internet businesses, bank infrastructures, and IoT devices. They enable system-to-system communication effortlessly so you can integrate systems and automate processes.
In 2025, APIs are mission-critical as companies embark on microservices, cloud-first architecture, and real-time data. That’s why API testing is essential—not just to test if APIs are working but to ensure they are secure, reliable, and efficient.
That’s where this guide enters—not just for you to learn about using Postman for API testing but for getting hands-on experience with all of it—the easy way. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned QA expert, this guide is perfect for you.
What is Postman and Why Use It for API Testing?
Postman is a powerful yet intuitive platform specifically built for designing, testing, and documenting APIs. What was once a small REST client has now evolved into a full-fledged API lifecycle product, used by over 25 million developers and testers worldwide. Whether you’re debugging a single endpoint or managing hundreds in an enterprise, Postman makes it simple with minimal to no coding.
It also supports REST, SOAP, GraphQL, and WebSocket protocols, making it ideal for modern, heterogeneous API environments. Postman also shines in collaboration, allowing teams to send requests, view responses, author test scripts, and keep everything organized into collections.
In 2025, Postman is the industry standard for developers, QA engineers, DevOps engineers, and product teams. Let’s quickly touch on why API testing matters and why Postman is the standard bearer.
Understanding API Testing Fundamentals
API Testing is the process of testing how software systems communicate using APIs. Instead of testing the user interface, it validates endpoints, data formats, status codes, and response time.
In 2025, APIs drive virtually all digital systems from fintech apps to AI software — so effective API testing is key to security, performance, and user experience.
Earlier approaches relied on manually crafted scripts and minimalistic tools. Modern-day API testing, facilitated by software like Postman, provides automation, CI/CD integration, environment handling, and enhanced collaboration, thereby making testing faster, smarter, and more scalable.
Looking to build a career in coding? Check out our Web Development courses with MERN, PHP/MySQL, React, and more to master full-stack skills
Why Choose Postman for API Testing?
Postman is not just popular because it’s offered for free, but also because it’s robust, easy to understand, and scalable. It works with REST, SOAP, GraphQL, and WebSocket APIs, making it ideal for modern workflows. Both individual developers and enterprise QA teams can work with it using a visual map, built-in scripting, and live collaboration. While the free account includes all the basics, such as collections, variables, monitors, and automated testing using the Collection Runner, paid plans offer more advanced collaboration capabilities, versioning, team workspaces, API analytics, mock servers, and enterprise-level integrations. While the free version is sufficient for many, larger teams tend to find value in either the Pro or Enterprise plans.
Postman Features That Make API Testing Easy
Postman’s UI is built for speed and readability. You don’t need to remember curl syntax or code just to send a request — simply type in the method, URL, headers, and body, press “Send”, and get instant results.
With Postman’s built-in JavaScript editor, you can write efficient test cases where you send requests. Do I need to check if the status is 200 or if the response data is correct? A few lines are enough.
Collections enable you to create related API requests, keep them organised in folders, add documentation, and even automate testing on the entire group. It’s like you have a dedicated project space for a given API you’re working on.
Don’t embed URLs or tokens: Postman allows you to create variables like {{base_url}} or {{auth_token}}, which you can switch on or off depending on the environment — dev, staging, or prod — with just one click. It keeps requests clean and agile.
Getting Started with Postman: Installation and Setup
Getting started with Postman is very simple, and you can choose the method that suits you best. Here are three easy ways to install and start using Postman – on your desktop, through a browser, or on your mobile phone
Download and Install Postman (3 Methods)
- Desktop Application: Visit postman.com/downloads and install the app for Windows, macOS, or Linux.
- Web Browser Version: If you prefer not to install software, use Postman directly in your browser at web.postman.co. It syncs with your account and is great for cloud-first workflows.
- Mobile App: For on-the-go testing or reviewing, Postman’s mobile version is available for both Android and iOS. While limited in functionality, it’s handy for lightweight API work.
First-Time Setup and Account Creation
Once installed, create a free Postman account using your email or Google login. This unlocks sync, collaboration, and cloud features. Set up your workspace — think of it as your project dashboard where you’ll manage collections, requests, and environments.
Understanding Postman Interface
The interface is intuitive and modular:
- Request Builder: Where you configure and send API requests.
- Response Viewer: Displays the server’s response.
- Collections Panel: Manages grouped requests.
- Environment Selector: Switch between dev, staging, and production.
- Test Results Tab: View automated test results instantly.
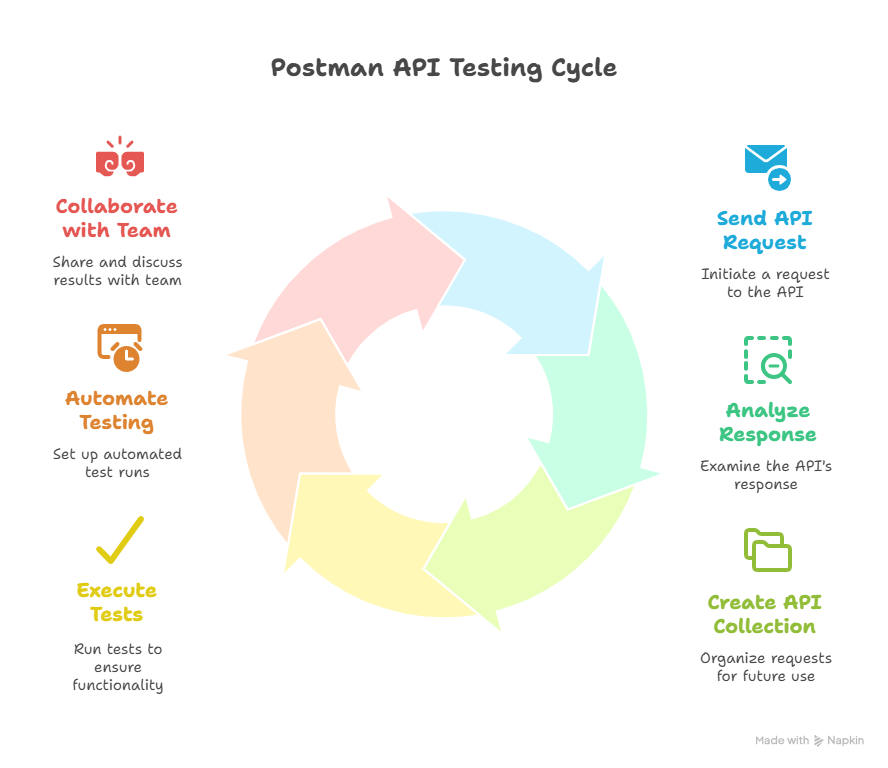
How to Use Postman for API Testing: Step-by-Step
Postman simplifies API testing with a simple, graphical workflow. You can easily test logins, form data, or payment APIs using a hands-on, code-not-required environment for creating requests, examining responses, authoring scripts, and automating testing without building a custom framework.
Let’s walk through the key steps.
Creating Requests (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
Start by selecting the request method (such as GET or POST) from the dropdown in the request builder. Enter the API endpoint URL, hit “Send”, and view the response — including status code, body, headers, and time. This lets you quickly verify if the endpoint is working as expected.
Adding Headers, Parameters, and Body Data
For more complex requests, you’ll often need to add:
- Headers (like Content-Type or Authorization)
- Query Params (e.g., ?page=2)
- Request Body (especially for POST/PUT)
- Postman provides separate tabs to organise all of these cleanly.
Writing and Running Tests in Postman
Under the Tests tab, you can write simple JavaScript-based test scripts. For example:
pm.test("Status is OK", function () { pm.response.to.have.status(200); });
This verifies that the server returns a 200 OK status. You can also test for response time, JSON schema, and specific values.
Automating API Tests with Collection Runner
The Collection Runner lets you run an entire group of requests in sequence. You can loop through them, add test scripts, and view results — ideal for regression testing or repeated validation.
Scheduling Tests Using Postman Monitors
Monitors allow you to run collections automatically at set intervals (e.g., hourly, daily) from the cloud. This helps track uptime, latency, and API health over time.
Integrating Postman with CI/CD for Automated Testing
Postman can be integrated into your CI/CD pipeline using Newman, a CLI tool. This ensures tests are triggered with every code commit or deployment, helping you catch issues early in the release process.
Postman Collections: Organizing Your API Tests
Collections in Postman are structured folders that organize all your API requests. They keep your tests well-organized, version-controlled, and easily shareable with your team.
What are Postman Collections?
Postman collections are groups of saved API requests making testing more scalable and systematic. Collections are distinct from individual requests in terms of shared scripts, variables, and configurations for all requests. They also help improve collaboration, versioning, and are easily shareable amongst teams. Collections also ensure test suites are reusable, maintainable, and more automatable.
Creating and Managing Collections
To form a collection:
- Click New > Collection or go to Collections > + > Blank Collection.
- Name it and add an optional description.
You can then:
- Add requests directly or from the Save menu.
- Use folders (e.g., Auth, Orders, Users) to group together related endpoints.
- Add documentation using markdown to describe the purpose for each request, parameters, and expected responses.
- That helps maintain large API suites clutter-free.
Running Collection Tests
Run tests in batches with the Collection Runner. It facilitates:
- Batching together numerous requests on a single pass.
- Data-driven testing using CSV or JSON to inject the variables’ values.
- Test result analysis using detailed reports showing pass/fail outcome, response time, and errors.
Postman Environment Variables and Data Management
It is inefficient to work between development, staging, and production if you are updating values like base URLs or authentication tokens per request. Postman remedies this using environment variables.
Understanding Environment Variables
Environment variables are run-time placeholders (e.g., {{base_url}}) to store values such as URLs, tokens, or user IDs. They help to avoid hardcoding and simplify testing inside different setups.
Postman supports global variables, which are shared by all workspaces , whereas env variables are for chosen environments.
Scope and Precedence for Variables follow this order:
- Local
- Data (Collection Runner)
- Environment
- Global
- Collection
The highest-priority variable is employed in case of overlapping names.
Setting Up Development Environments
To handle various stages of testing:
- Go to → Manage Environments → Add Environment
- Create key-value pairs for the Dev, Staging, and Production environments (e.g., base_url)
- Switch between environments using the dropdown in the main interface.
- For best practice, use descriptive naming, eliminate duplicates, and encrypt sensitive values.
Dynamic Data and Variables
Postman supports pre-request scripts in JavaScript, allowing variables to be changed on the fly. You can generate random data, such as names or email addresses.
Pull data out of one request (like a user ID or token), save it as a variable, then use it within other requests. Chaining requests facilitates automating workflows and recreating realistic scenarios.
Access tokens are stored as variables, allowing you to adjust and reuse them throughout requests without requiring human intervention.
Advanced Postman API Testing Techniques
Postman allows you to write test scripts, automate runs, and handle authentications all in one platform.
Writing Test Scripts in Postman
Postman allows you to execute custom JavaScript code in the Tests tab after receiving a response. This enables the automation of validation, data extraction, and even request chaining.
Here is basic JavaScript for testing:
You write statements with the pm API using standard JavaScript syntax (variables, conditionals, functions). For example:
pm.test("Response status is 200", function () { pm.response.to.have.status(200); });
Assertions while testing generally confirm status codes, response time, headers, or data:
- Status: pm.response.to.have.status(200)
- JSON body fields: pm.expect(jsonData.id).to.eql(1001)
You may create and reuse custom test functions in scripts for complex validation or data processing, enhancing code reusability.
Automated API Testing with Postman
Test automation permits you to repeatedly test APIs with minimal human intervention. You can automate test cases with Postman’s Collection Runner by executing all the requests included in a collection with test scripts.
For CI/CD integration, Postman offers Newman as a CLI utility, which allows you to run collections via the command line. That way, you can run tests automatically on commit of code, during deployment, or scheduled build, and get bugs identified early in your delivery pipeline.
To perform scheduled test runs, Postman’s built-in Monitors feature allows you to run collections on a specific schedule (hourly, daily, etc.), perfect for testing uptime or API stability over time.
API Authentication Testing
Postman offers different methods for authentication testing.
- Basic Auth: Using a password and a username in the actual request.
- Bearer Token: You send an access token in the authorization header.
- OAuth 2.0: Supports multi-step auth flows, typical for enterprise apps and social networks.
- API Key: A simple key transmitted in headers or query parameters.
They can be saved as variables or dynamically assigned using the assistance of pre-request scripts for safe and reusable testing.
Postman API Testing Best Practices
Postman helps keep your tests clean, maintainable, and scalable as your projects grow.
Test structure and organization
- Provides informative, descriptive names for collections, requests, and variables (e.g., POST_CreateUser_Valid). Makes it more readable.
- Organise tests by endpoint, feature, or scenario using folders and tags for convenience as well as batch execution.
- Provide detailed explanations for all requests, tests, collections, and variables. Use Postman’s built-in documentation feature to ensure consistency between teams.
- Export collections and keep them in source control (such as Git), allowing for collaborative updates and rollback.
Conducting Tests using Postman
- Use built-in scripts to track and assert response times (e.g., pm.expect(responseTime).to.be.below(500)).
Postman is not designed for load testing, but you can test small loads by using the Collection Runner with data files. - Minimise storage of data in global/env variables and avoid using extremely large response payloads. Track slow requests and observe trends to identify and notify about performance bottlenecks early.
Error Handling and Debugging
- Prevent CORS errors, wrong responses, and timeouts in advance. Use Postman Console for logging, see raw requests, and iteratively rule out problems.
- Use assert and log failed responses to distinguish between server-side and client-side errors. Maintain a list for common issues and solutions to speed up resolution and onboarding for the team.
Real-World Postman API Testing Examples
Postman fits into real-life scenarios in different fields, like –
E-commerce API Testing Scenario
API testing for an online store may include:
- User Registration: Testing registration endpoints using valid/invalid data.
- Product Catalogue: Ensuring GET requests return proper, filterable lists of products.
- Processing Orders: Checking order creation, stock updates, and pricing logic.
- Integration with Payment Gateway: A simulation for payment requests and secure transaction verification.
Social Media API Testing Project
This test includes –
- User Auth Flow: Testing login, logout, and validation of the token.
- Post Retrieval and Construction: Ensuring content posts are accurately stored and retrieved.
- File Upload: Check media upload APIs for images, videos, or docs.
- Real-Time Features: Notification or message delivery testing using polling or WebSockets.
Banking API Security Testing
Banking requires high-security APIs. It may include –
- Financial Transaction Testing: Validation of transfer amount limits, account verification, and accuracy.
- Data Encryption: Ensuring sensitive fields are encrypted in transit.
- Compliance Checks: Validation against standards like PCI-DSS or GDPR.
- Detection of Fraud: Triggering rare patterns to validate mechanisms for fraud alerts.
Postman vs Other API Testing Tools
Postman has many features. However, it is also beneficial to compare it with other software so you know where it excels.
| Feature / Tool | Postman | Insomnia | Thunder Client | cURL | Swagger UI |
| User Interface | Graphical, intuitive | Clean, minimal | Simple (VS Code extension) | CLI only | Web-based |
| Ease of Use | Very easy, beginner-friendly | Easy | Very easy | Hard (CLI knowledge is needed) | Easy |
| Automation Support | Built-in test scripts, monitors | Limited scripting | Minimal scripting | Full scripting via bash/scripts | None |
| Collaboration | Team workspaces, sharing, comments | Basic | Does not include integrated team capabilities | Manual (shared scripts) | Not built for collaboration |
| CI/CD Integration | Using Newman CLI | Manual | Not natively supported | Easy via scripts | Not applicable |
| Mock Server Support | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes
|
When to Use Postman
Use Postman when you need a visual, collaborative, automated solution for end-to-end API workflows — from design to testing to monitoring and documentation.
Common Postman API Testing Challenges and Solutions
Although Postman has impressive abilities, there are some troubles people may encounter:
Frequent Issues and Quick Fixes
- Browser security policies induce CORS Errors. To avoid them, use the Postman desktop app instead of the browser app.
- SSL Certificate Problems: Disable “SSL certificate verification” in Settings > General during self-signed or expired cert testing.
- Timeout Issues: Increase the request timeout in Settings or enhance the server’s response time.
- Authentication Failures: Verify the correct token formats, header placement, and refresh expired tokens using pre-request scripts.
Performance Optimization Tips
- For collections optimisation, remove duplicate requests and bundle large collections with folders.
- For request optimisation, minimise payload size and remove unnecessary headers.
- For Memory Management, eliminate unused variables and environments to reduce resource usage.
- For Speed Optimizations, use variables and scripts efficiently for reducing manual steps and execution time.
Postman API Testing Certification and Learning Path
Official Postman Training Resources
Postman Academy offers free, structured learning from beginner to expert on API testing, automation, and scripting. There are certifications available to prove proficiency, ideal for resumes and LinkedIn. There are practice exercises and quizzes to ensure learning.
Building Your API Testing Career
Develop your career by learning a skill path for test scripts, CI/CD tools like Jenkins, and performance testing. Stay up to date on industry best practices like versioning, documentation, and automation. Since digital products are API-powered, all QA roles, DevOps, and backend roles in startups, enterprises, and multinational technology firms require talented testers.
Conclusion: Mastering Postman for API Testing
Postman mastery is more than just making API requests. It is understanding environments, authoring well-crafted test scripts, automating with Newman, and working with well-formed collections. These are essential skills for efficient, predictable, and scalable testing.
Follow best practices, such as using variables, keeping collections organized, documenting thoroughly, and automating tasks where possible.
Lastly, make continuous learning a habit. Engage with real-world scenarios and stay current with new feature releases and API trends. In an API-driven world, becoming a Postman testing expert puts you at the centre of modern software development.
Reference Links: –
- https://learning.postman.com/docs/introduction/overview/
- https://academy.postman.com/
- https://blog.postman.com/
- https://www.postman.com/api-platform/api-testing/
- https://learning.postman.com/docs/tests/writing-tests/
- https://learning.postman.com/docs/publishing-your-api/documenting-your-api/