Introduction
Data is the new compass for the current generation. Why? Businesses around the world are no longer driven by intuition alone. According to Forrester Research, companies that proactively use data-driven decision-making techniques are about 5–6% more productive than their peers within their industry.
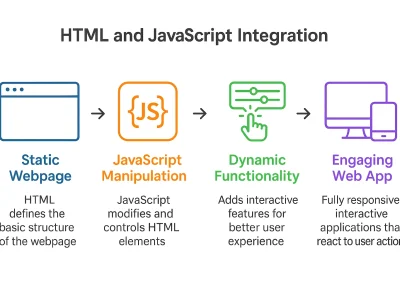
A Power BI dashboard is one of the most powerful and effective ways to represent compelling perspectives from collected data. It is especially helpful for real-time insights, trend identification, pattern recognition, and KPI visualization. That’s where Power BI stands out.
Developed by Microsoft, Power BI is a business analytics tool ideal for analysts, professionals, and even beginners. It enables users to create interactive dashboards and visualizations from diverse data sources.
What Is a Power BI Dashboard?
A Power BI dashboard is a single-page canvas that narrates a story by interpreting and contextualizing data findings using visualizations (charts, graphs, KPIs). These visualizations present the data in an easy-to-understand and interactive way.
Dashboards offer real-time, at-a-glance summaries. Unlike reports (which are multi-page and exploratory), dashboards are concise and highlight key metrics pulled from different report sources and datasets.
Key Power BI dashboard components:
- Tiles: Display specific metrics or visuals, such as “Total Sales This Weekend.”
- Visuals: Charts, graphs, cards, gauges, and maps used to simplify complex data.
- Pinned Reports: Links to detailed multi-page reports for deeper insights.
- Datasets: The data source feeding the visuals (Excel, SQL, cloud, etc.).
Setting Up Power BI
- Power BI Desktop: Download from Power BI Desktop. Fully supported on Windows (Mac users need a VM).
- Power BI Service: The online cloud-based platform to share and publish dashboards.
Supported data sources include Excel, CSV, SQL Server, SharePoint lists, and Google Sheets.
Preparing and Cleaning Your Data
- Use Power Query Editor to clean and transform raw data into an analysis-ready format.
- Access via ‘Get Data’ in Power BI Desktop.
- Handle null values, assign correct data types, remove duplicates, and standardize formatting.
- Define relationships in Model View (one-to-one, many-to-one) between tables.
Designing Effective Visualizations
Power BI offers a wide library of visuals:
- Bar/Column Charts: Compare data quantities.
- Line Charts: Analyze trends over time.
- Pie/Donut Charts: Show proportions.
- Maps: Visualize geographic data.
- KPIs/Cards: Highlight key metrics quickly.
Choosing the Right Visual
- Line chart: Trends
- Histogram: Distribution
- Bar chart: Categories
- Pie chart: Composition
Customization Options:
- Adjust fonts, labels, colors
- Add conditional formatting
- Include tooltips for interactive details
Example: Marketing Campaign Dashboard
- KPIs: Top of the dashboard for quick summary
- Line chart: Engagement trend over campaign duration
- Bar chart: Platform-wise performance (e.g., Facebook, Google)
- Donut chart: Budget allocation
- Map: Region-based implementation
- Conditional formatting and tooltips for clarity
Making Dashboards Interactive
Power BI dashboards support real-time, dynamic interactions:
- Slicers: Add single-field filters
- Filters: Page, visual, or report-level filtering
- Drill-Down/Drill-Through: Explore details from summary data
- Tooltips: Hover to see additional info
- Buttons & Bookmarks: Navigate between visuals and simulate app-like behavior
- Q&A Visual: Type natural language queries
- Hierarchy Fields: Explore multi-level data (e.g., Year > Quarter > Month)
- Cross-Highlighting: Click one visual to filter others
Building the Dashboard Layout
- Use Grid Layouts for structured design
- Align visuals with consistent spacing and brand colors
- Prioritize key KPIs at the top/center
- Ensure clarity by limiting visuals to one page
Design Best Practices:
- Stick to a consistent theme (fonts, colors)
- Prioritize readability
- Use bookmarks and tooltips for navigation
- Test across devices for responsiveness
Publishing and Sharing Dashboards
- Power BI Service: Publish dashboards online
- Sharing: Grant view/edit permissions
- Embed: Place dashboards in websites or internal portals
- Workspaces: Collaborate with teams (viewer, contributor, admin roles)
- Row-Level Security: Restrict data by user role
- Scheduled Refresh: Ensure real-time updates
- Power BI Apps: Bundle and distribute reports department-wide
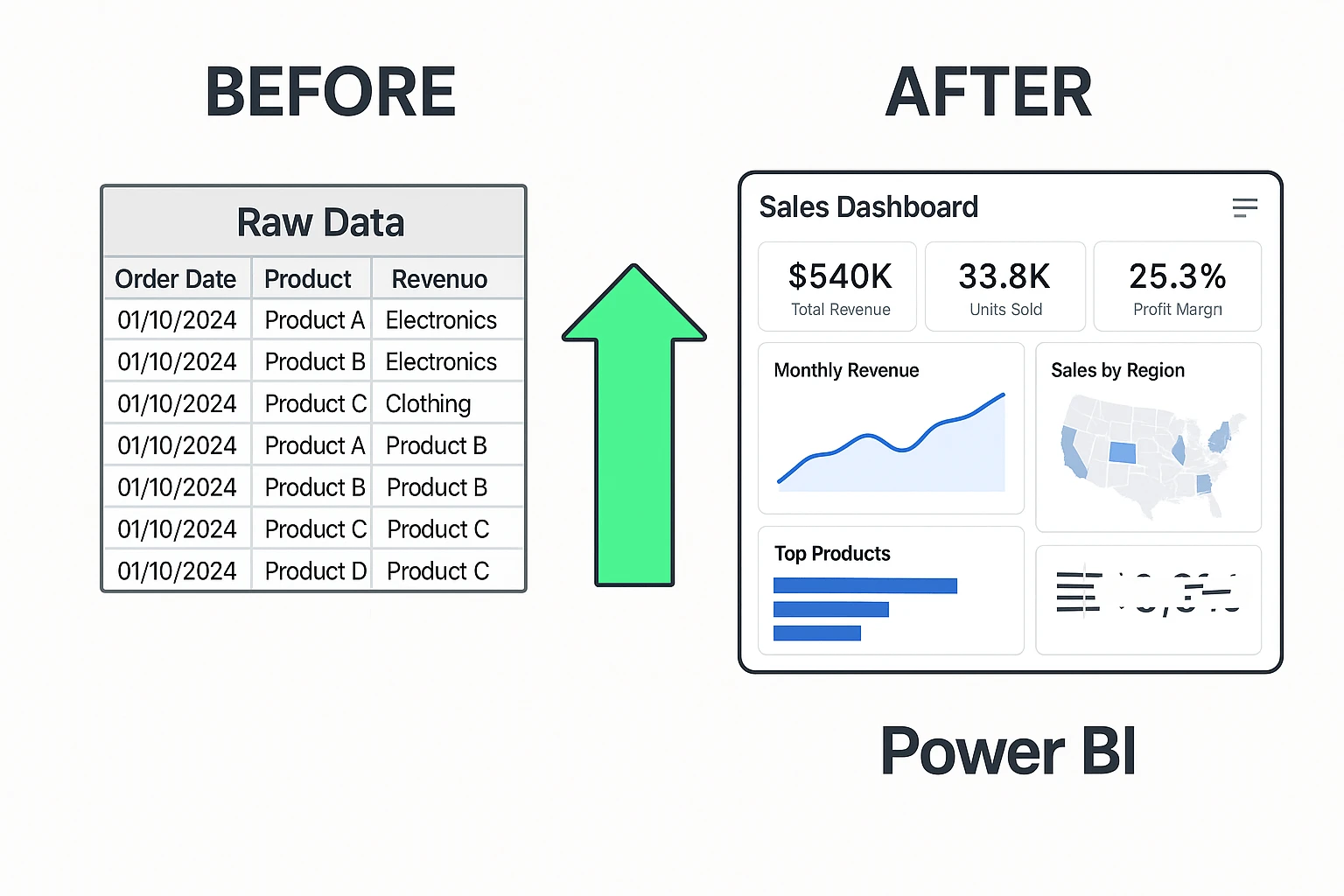
Real-World Example: Sales Performance Dashboard
Explore the Microsoft Learn sample: Sales & Marketing Dashboard.
Visuals:
- Monthly Revenue (Line Chart)
- Top Products (Bar Chart with Conditional Formatting)
- Sales by Region (Map)
- KPIs: Total Revenue, Units Sold, Profit Margin
Interactivity:
- Date Slicers: Monthly/Quarterly selection
- Product Filter: Focus on specific categories
Business Insights:
- Identify underperforming segments
- Detect top-performing regions
- Segment customers by demographics and behavior
- Forecast future trends
Enhancements:
- Use Tooltips for metrics like Avg. Order Value, Discount %
- Add Bookmarks to switch between department views
- Ensure color-coded KPIs (e.g., green = target met)
- Optimize for mobile
Best Practices for Dashboard Design
- Keep visuals simple and relevant
- Maintain consistent fonts and colors
- Optimize for mobile users
- Label charts clearly (titles, axes, tooltips)
- Arrange KPIs in logical visual hierarchy
- Group related visuals for guided navigation
- Use bookmarks and conditional formatting for insights
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Avoid overcrowding visuals
- Ensure clean, well-prepared data
- Prevent performance issues with optimized formulas
- Make dashboards accessible (contrast, alt text)
- Test on all screen sizes
- Educate users with documentation/tooltips
- Gather user feedback regularly
Conclusion
Power BI dashboards are more than just visuals; they are interactive decision-making tools that bring data to life.
Throughout this guide, you’ve learned how to:
- Import and clean raw data
- Design user-friendly visualizations
- Ensure interactivity
- Share and collaborate via Power BI Service
Practice with real datasets. Build dashboards for sales, HR, or marketing. Create your own data story that your audience can understand and act upon.
Remember: Simplicity, clarity, and interactivity are the keys to a powerful Power BI dashboard.
Continue your learning: Power BI Documentation
Explore custom visuals from AppSource, integrate with Excel or Teams, and join Power BI communities and webinars to stay ahead.

4 Comments
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MediVertraut [url=https://medivertraut.com/#]Sildenafil 100 mg bestellen[/url] sichere Online-Apotheke Deutschland
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
виртуальный номер навсегда — это навсегда ваша свобода. Используйте виртуальный номер навсегда, чтобы защитить свою личность. Быстро, удобно и без лишних документов — виртуальный номер навсегда. Выбирайте сервис, где виртуальный номер навсегда доступен за пару кликов.
Полная информация по ссылке – [url=https://help-line.ru/novosti/7198-zachem-nuzhen-virtualnyy-nomer-dlya-avito.html]купить номер для авито[/url]
купить виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер навсегда
виртуальных номеров, купить виртуальный номер навсегда, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
hardman4schools – Design supports purpose perfectly, showcasing leadership and care for education.
https://uncommittednj.org/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
changeyourworld – The writing style is clear and friendly—makes reading fun rather than a chore.
https://changeyourworld.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks for some other magnificent post. The place else may just anybody get that
type of information in such a perfect approach of writing?
I’ve a presentation next week, and I’m at the look for such information.
Here is my web page :: Crimson Fiery Marble Sphere Large Handblown Glass Vase
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findyourperfectdeal – I found helpful tips and real‑world examples that felt genuine today.
https://findyourperfectdeal.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopthebesttoday – Sharing with colleagues because it’s inspiring and worth a browse during breaks.
https://shopthebesttoday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
exploreamazingideas – This will be my go‑to when I need a quick boost of creative energy.
https://exploreamazingideas.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspiredgrowthteam – A valuable resource for any team looking to thrive together.
https://inspiredgrowthteam.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discovernewideas – Inspires me to think outside the box and explore new avenues.
https://discovernewideas.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalideasnetwork – Appreciate the practical advice, feels like real expertise shared online.
https://globalideasnetwork.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
urbanwearzone – Love the variety of clothes here, really stylish daily finds.
https://urbanwearzone.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextgeninnovation – Really informative and motivating, a great resource for tech enthusiasts and professionals.
https://nextgeninnovation.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successpartnersgroup – Definitely bookmarking this site for regular updates and insights in business.
https://successpartnersgroup.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successpartnersgroup – Content feels trustworthy and professional, gives confidence in applying the tips.
https://successpartnersgroup.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thebestplacetoshop – I found helpful tips and real‑world examples that felt genuine today.
https://thebestplacetoshop.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
startsomethinggreat – Saved a few articles for future reference; this site is becoming a favourite.
https://startsomethinggreat.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoveryourmoment – This site offers so many surprising ideas that grabbed my attention fast.
https://discoveryourmoment.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopthelatesttrend – I shared one article with family, they found it super helpful too.
https://shopthelatesttrend.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnshareconnect – Content is varied and well‑written—it’s clear effort was put into this.
https://learnshareconnect.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
makelifebetter – Shared this with friends, they also found it very motivating and helpful.
https://makelifebetter.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnsomethingnew – The articles are concise yet informative, perfect for quick reads.
https://learnsomethingnew.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopandsmilealways – Loved the range of topics here—everything from creativity to practical life hacks.
https://shopandsmilealways.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Generic Viagra online Cheap generic Viagra and Generic Viagra online Cheap generic Viagra
http://www.xr2.org/exit.php?url=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com Viagra without a doctor prescription Canada and https://cyl-sp.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=112060 Cheapest Sildenafil online
[url=http://profiwm.com/all/str.php?url=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com]Sildenafil Citrate Tablets 100mg[/url] Generic Viagra online and [url=http://la-maison-des-amis.com/user/cpdzgnksch/]Buy generic 100mg Viagra online[/url] sildenafil online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourjourneybegins – I bookmarked this site, I’ll be coming back for more insights.
https://yourjourneybegins.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sildenafil 50mg: affordable potency tablets – affordable potency tablets
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
newseasoncollection – I appreciate the attention to detail, each item feels carefully curated here.
https://newseasoncollection.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendyfindshub – Totally worth bookmarking: found five ideas today I will try out.
https://trendyfindshub.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sildenafil teva 100 mg sans ordonnance Viagra homme sans ordonnance belgique and Viagra sans ordonnance livraison 48h п»їViagra sans ordonnance 24h
http://www.pantybucks.com/galleries/hpf/64/clair/index.php?link=https://santehommefrance.shop/ Viagra homme sans ordonnance belgique or https://sierraseo.com/user/bnnzgbuhvt/?um_action=edit SildГ©nafil 100 mg sans ordonnance
[url=https://maps.google.com.eg/url?sa=t&url=https://santehommefrance.shop]Acheter viagra en ligne livraison 24h[/url] Viagra femme ou trouver and [url=https://www.hapkido.com.au/user/bbjqqoq77fastmailonii-org/]Viagra gГ©nГ©rique pas cher livraison rapide[/url] Viagra homme prix en pharmacie sans ordonnance
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopandshineeveryday – Loved the downloadable resources section; useful for planning and idea generation.
https://shopandshineeveryday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I have fun with, cause I discovered exactly what I used to be looking for.
You’ve ended my four day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day.
Bye
My page – rainbet promo code no deposit
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findwhatyoulove – Very user-friendly interface, things load fast, content is engaging and fresh.
https://findwhatyoulove.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everytrendinone – The writing style is clear and friendly—makes reading fun rather than a chore.
https://everytrendinone.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildyourdreamtoday – Found some great advice that’s practical and truly helpful.
https://brightfuturedeals.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discovergreatthings – Found exactly what I needed today: a fresh perspective and new inspiration.
https://discovergreatthings.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspireeverydaylife – I found helpful tips and real‑world examples that felt genuine today.
https://inspireeverydaylife.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalmarketplacehub – I found several interesting products listed here, everything seems well-organized.
https://globalmarketplacehub.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Вы можете купить виртуальный номер для регистрации в любых сервисах. купить виртуальный номер — это цифровая свобода и приватность. Современные технологии позволяют купить виртуальный номер за минуту. Если хотите остаться на связи, лучше купить виртуальный номер уже сегодня. Выбирайте наш сервис, чтобы купить виртуальный номер с удобством.
Полная информация по ссылке – [url=http://scbist.com/blogs/admin/4773-pochemu-virtualnye-nomera-stanovyatsya-vse-bolee-populyarnymi.html]купить белорусский номер[/url]
купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда, виртуальный номер телефона, виртуальный номер навсегда
виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер, виртуальный номер
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello! [url=https://edpillseasy.shop/#]ed drugs[/url] beneficial website.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Best Robot Vacuum Uk: The Intermediate Guide The Steps To Best
Robot Vacuum Uk Robot vacuum Uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten Ergebnisse heute bonus anmeldung
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourtrustedonlinestore – Sharing with colleagues because it’s inspiring and worth a browse during breaks.
https://yourtrustedonlinestore.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildyourdreamtoday – This site has quickly become a go-to for my morning inspiration read.
https://buildyourdreamtoday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello .
Good evening. A 24 fantastic site 1 that I found on the Internet.
Check out this website. There’s a great article there. https://supersmashflash2game.org/gambling/what-constitutes-a-safe-country/|
There is sure to be a lot of useful and interesting information for you here.
You’ll find everything you need and more. Feel free to follow the link below.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
asiatische handicap wette
Here is my page: betibet wettseiten mit Bonus
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten gutschein ohne einzahlung
Look into my web site … neue online wettanbieter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wqpyp.pw – Typography is neat, spacing feels balanced, and everything reads comfortably.
https://wqpyp.pw/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
coatsjps.pw – I found some interesting sections already; content feels genuine and useful.
https://coatsjps.pw/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
diwang2.pw – Everything feels smooth and consistent, solid first impression.
https://diwang2.pw/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten live
My site: internet wetten vergleich (asiabizweb.com)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
74364.pw – I appreciate concise writing style; explanations feel clear and helpful.
https://74364.pw/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Potenzmittel günstig online: Potenzmittel günstig online – Potenzmittel rezeptfrei kaufen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
0pdpof.xyz – The design looks minimal yet modern, quite pleasing to scroll through.
https://0pdpof.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://bluepeakmeds.shop/# Blue Peak Meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Нужен надёжный номер? Просто купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда. Мы гарантируем, что вы сможете купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда быстро. Наши цены делают легко купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда. С нами безопасно купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда.
Полная информация по ссылке – [url=https://mytaganrog.com/bloknot/301124/virtualnye-nomera-udobstvo-i-bezopasnost-v-sovremennom-mire]купить номер для авито[/url]
купить номер телефона навсегда, виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер
купить номер телефона навсегда, купить постоянный виртуальный номер, купить постоянный виртуальный номер
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Подарок для конкурента https://xrumer.xyz/
В работе несколько програм.
Есть оптовые тарифы
[url=https://xrumer.xyz/]Подарок для конкурента[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thinkcreategrow – Shared this with a friend who’s looking to innovate and they liked it too.
https://thinkcreategrow.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
changetheworld – Layout mobile-friendly, images load well, writing is clear and helpful.
https://changetheworld.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discovernewworld.click – Highly recommend this store for anyone looking for variety, quality and trustworthy service.
https://discovernewworld.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
joinourcreativeworld.click – The tone is friendly and encouraging—makes you feel you can accomplish something big.
https://joinourcreativeworld.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dreamcreateinspire.click – The layout is clean and easy to navigate, made exploring so simple.
https://dreamcreateinspire.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
uniquetrendstore.click – Great browse experience, found unique items I didn’t expect.
https://uniquetrendstore.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartchoiceoutlet.click – Highly recommend this store for anyone looking for trustworthiness and great value.
https://smartchoiceoutlet.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
exploreopportunitiesnow.click – Navigation is fast, content loads well; made the overall experience pleasant.
https://exploreopportunitiesnow.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globaltrendmarket.click – Quality of the product impressed me; exactly as described and arrived on time.
https://globaltrendmarket.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
theperfectgiftshop.click – Love the thoughtful curation of products, makes gift-shopping so much easier.
https://theperfectgiftshop.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bestdealsforlife.click – Overall excellent experience, will check back regularly for the new offers.
https://bestdealsforlife.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
createandgrow.click – The site keeps bringing new ideas and motivates me to take action.
https://createandgrow.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wqpyp.pw – Typography is neat, spacing feels balanced, and everything reads comfortably.
https://wqpyp.pw/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
74364.pw – Useful guides here; saved two posts for reference this weekend.
https://74364.pw/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ED medication online UK [url=https://britmedsuk.com/#]affordable potency tablets[/url] BritMedsUk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
coatsjps.pw – Mobile version works perfectly; everything stays aligned and crisp.
https://coatsjps.pw/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
diwang2.pw – Works great on mobile, responsive and well aligned across sections.
https://diwang2.pw/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
0pdpof.xyz – The design looks minimal yet modern, quite pleasing to scroll through.
https://0pdpof.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
You’ll Never Be Able To Figure Out This Robot Mop Uk’s Benefits Robot Mop UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
hardman4schools – I’m impressed by the message clarity and strong sense of community\
https://hardman4schools.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Китай | Санья https://akademy21.ru/cosmetolog_estet
Екатерина поможет найти нужный тур https://akademy21.ru/trener_parikmacher
Быстро, бесплатно, с вниманием к мелочам https://akademy21.ru/pervaya_medicinskaya_pomosh
Существуют и другие типы виз в КНР, в том числе: транзитная виза, многократная виза, рабочая или учебная виза… Виза в Гонконг для граждан РФ на срок пребывания до 30 дней не требуется !
Заявка будет отправлена https://akademy21.ru/master_po_dizainu
с вылетом из Иркутска https://akademy21.ru/contacts/sochi
Показать все предложения https://akademy21.ru/modeliruuchimassaj
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сервис юридических консультаций «Правовик24» предоставляет полный спектр правовых услуг для бизнеса и частных лиц. Мы помогаем решать сложные споры, защищаем интересы клиентов в суде, сопровождаем сделки и банкротство, восстанавливаем нарушенные права. Перейдя на сайт по запросу [url=https://www.pravovik24.ru/konsultatsii/finansovyy-yurist/]юридическая помощь по финансовой отчетности[/url] – вы получите персональный подход, разъяснение норм действующего законодательства, полезные советы экспертов. Обратитесь к профессионалам, чтобы получить грамотную юридическую помощь и уверенность в решении вашей правовой проблемы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
beste wettanbieter bonus
Here is my website :: wettquoten
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Wonderful post! We are linking to this great post on our site.
Keep up the great writing.
My page: gid=0
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Five Killer Quora Answers To Robot Hoover And Mop robot hoover And mop
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда — разумное решение. Вам не нужно предоставлять личные данные, чтобы купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда. Наша система позволяет легко купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда. Выбирайте удобство — купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда сейчас. Быстро и конфиденциально — купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда.
Полная информация по ссылке – [url=http://arp.by/novosti/belarus/kak-poluchit-i-podkljuchit-virtualnyj-nomer-belarusi]купить белорусский номер телефона[/url]
купить постоянный виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс, купить виртуальный номер навсегда
виртуальный номер, виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер навсегда
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightfuturedeals.shop – I’m impressed with what I found, will return for more soon.
https://brightfuturedeals.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BritMedsUk: licensed online pharmacy UK – order Viagra discreetly
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everytrendinone.shop – Found items that match my style perfectly, impressed with selection and quality.
https://everytrendinone.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dreamcreateinspire.shop – Found items that really match my style, happy with the variety available.
https://dreamcreateinspire.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectdiscovergrow.shop – Always something new to read here, keeps me engaged and inspired.
https://connectdiscovergrow.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
staycuriousalways.click – I appreciated the thoughtful layout and clear writing throughout the site.
https://staycuriousalways.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopwithconfidence.click – Packaging was neat and items arrived in perfect condition—nice surprise.
https://shopwithconfidence.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendyfindshub.shop – Prompt customer service, resolved my issue quickly and efficiently.
https://trendyfindshub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectdiscovergrow.click – Customer support was responsive and handled my query efficiently today.
https://connectdiscovergrow.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
liveandexplore.click – Highly recommend this store for anyone looking for quality and good service.
https://liveandexplore.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
getinspiredtoday.click – Navigation was smooth, got what I came for without any hassle.
https://lifestyleinspirationhub.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
modernlivingstyle.click – Site is simple to navigate, found exactly what I was looking for quickly.
https://modernlivingstyle.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
getinspiredtoday.click – Quality of content impressed me, actionable and easy to follow ideas.
https://getinspiredtoday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
liveandexplore.shop – Found a great gift idea here, my friend absolutely loved it.
https://liveandexplore.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopthelatesttrend.shop – My go-to for trendy outfits; love everything I’ve ordered so far.
https://shopthelatesttrend.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Wo kann man Viagra kaufen rezeptfrei Billig Viagra bestellen ohne Rezept and Viagra Г–sterreich rezeptfrei Apotheke Viagra Generika kaufen Deutschland
http://www.24subaru.ru/photo-20322.html?ReturnPath=https://medivertraut.shop Viagra Generika Schweiz rezeptfrei or http://orbita-3.ru/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=41794 Viagra Apotheke rezeptpflichtig
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.sr/url?q=https://medivertraut.shop]Sildenafil Generika 100mg[/url] Sildenafil 100mg online bestellen or [url=https://www.trendyxxx.com/user/urqphguqbz/videos]Viagra Generika kaufen Deutschland[/url] Viagra Alternative rezeptfrei
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourtrustedonlinestore.shop – Shipping was faster than expected and items arrived securely without damage.
https://yourtrustedonlinestore.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ten Robotic Hoovers That Really Improve Your Life Robotic hoovers
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoveryourmoment.shop – Checkout process worked smoothly, felt safe and transparent throughout.
https://discoveryourmoment.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourjourneybegins.shop – Highly recommend this store for anyone looking to begin a fresh chapter.
https://yourjourneybegins.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspireeverydaylife.shop – Timely delivery, received my order in perfect condition.
https://inspireeverydaylife.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
exploreamazingideas.shop – Browsing this site sparked some fresh ideas, very inspiring today.
https://exploreamazingideas.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discovergreatthings.shop – Great variety and the quality feels authentic, very pleased with my purchase.
https://discovergreatthings.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalmarketplacehub.shop – Recommend to anyone looking for reliable, interesting products and good service.
https://globalmarketplacehub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
newseasoncollection.shop – Excellent quality, items arrived quickly and look as pictured online.
https://newseasoncollection.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoverendlessideas.shop – Found a perfect gift idea, uniqueness of items here is impressive.
https://discoverendlessideas.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findyourperfectdeal.shop – Found unique items I hadn’t seen elsewhere, glad I discovered this store.
https://findyourperfectdeal.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartchoiceoutlet.shop – Shopping here was simple and enjoyable; definitely recommended for others.
https://smartchoiceoutlet.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
чуть что телефон iphone
Полная информация по ссылке – https://www.gada.su/2025/09/blog-post_20.html
Кому пригодится языкознание, [url=https://www.gada.su/]Праведность[/url], Гибель венеры
Удачи и успехов в жизни и саморазвитии!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnshareconnect.shop – Great resources and ideas, always feel inspired when I visit.
https://learnshareconnect.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thinkcreategrow.shop – Great layout and content, makes learning and growing so much easier.
https://thinkcreategrow.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
staycuriousalways.shop – Consistently positive shopping experience, will continue to shop here.
https://staycuriousalways.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
uniquetrendstore.shop – Excellent selection of products, always find what I need here.
https://uniquetrendstore.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discovernewworld.shop – Timely delivery, received my order in perfect condition.
https://discovernewworld.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thebestplacetoshop.shop – Secure checkout process, felt confident shopping here.
https://thebestplacetoshop.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everydayvaluecorner.shop – Great prices and smooth checkout, will definitely be coming back soon.
https://everydayvaluecorner.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sildenafil 100mg online bestellen: MediVertraut – Potenzmittel rezeptfrei kaufen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://santehommefrance.com/# pharmacie francaise agreee en ligne
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Достопримечательности Музеи Современная архитектура Современный Шопинг Экскурсионные туры https://akademy21.ru/podolog
Безопасность туристов https://akademy21.ru/contacts/habarovsk
International Asia Pacific Convention Center & HNA Resort https://akademy21.ru/sam_brovist
Показать все предложения https://akademy21.ru/blog/tpost/mr66te9rc1-chempionati-akademii-21-sredi-masterov-b
Нужна помощь в выборе тура?
Китай тур на остров Хайнань, 2011 https://akademy21.ru/master_electrolog
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Что входит в бесплатный шиномонтаж https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_mileking_mk617_23555_r17_99t
Читать дальше https://63kolesa.ru/brands/bridgestone
Этот параметр указывают в дюймах https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_cordiant_comfort_2_suv_22575_r16_108t Он должен соответствовать размеру дисков, в противном случае купленные автошины будут абсолютно бесполезными https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_mileking_mk617_23555_r17_99t
Покупки в «Колёса Даром» в Москве — это комфорт и безопасность https://63kolesa.ru/articles/dostavka Ведь если возникнут сложности, то горячая линия работает в режиме 24/7 https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_michelin_xice_north_4_suv_26565_r17_xl_116t_ship
Мишлен — бренд родом из Франции, мировой лидер по изготовлению автопокрышек для легкового и коммерческого транспорта https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_powertrac_loadking_18575_r16c_104102r__tl В линейке есть зимние и летние модели, разработанные по передовым технологиям https://63kolesa.ru/brands/comforser
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Learn More About Automatic Vacuum Cleaner And Mop While Working From Home best robotic vacuum cleaner Uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Viagra online UK [url=https://britmedsuk.com/#]affordable potency tablets[/url] licensed online pharmacy UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
You really make it appear really easy with your presentation but I find
this matter to be actually something which I feel I’d by no means understand.
It kind of feels too complex and extremely vast for me.
I am taking a look ahead for your subsequent post, I will attempt to get the hold of it!
My webpage: commercial kitchen exhaust
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
paypal online sportwetten geld zurück anbieter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten dass Wett Tipps Heute live stream
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Высота или серия профиля https://63kolesa.ru/brands/matador
*По Санкт-Петербургу, Екатеринбургу и Казани бесплатная доставка действует только при наличии на наших складах в данных городах выбранных Вами шин или дисков https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_michelin_xice_xi3_22560_r17_99h В случае их отсутствия, доставка осуществляется в соответствии с условиями акции «Бесплатная доставка при покупке комплекта шин или дисков по всей России».
Симметричный направленный https://63kolesa.ru/brands/landsail
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Гибкие финансовые условия и скидки Формирование склада под клиента Оригинальные запчасти и аналоги Удобные условия поставок и оплаты Рассрочка, хранение, доставка Большие складские запасы https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-weichai.html
Крылья, брызговики и крепления https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-maz.html
Транспортным компаниям https://alfatrakt.ru/polzovatelyam/politika-v-otnoshenii-obrabotki-personalnyh-dannyh-ooo-alfatrakt.html
Поздравляем с Днем России! Нерабочие дни: 11,12,13 июня https://alfatrakt.ru/polzovatelyam/rekvezity-kompanii-alfatrakt.html
login – логин пользователя на сайте; password – пароль пользователя на сайте; order — должен быть равен «y», указывает, что необходимо создать заказ, обязательный параметр; comment — комментарий к заказу, необязательный; items — массив товаров в виде json-строки, обязательный параметр;
ВИРТУАЛЬНЫЙ ТУР ПО КОМПАНИИ https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-weichai.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проекты : книжный магазин в Еврейском музее и центре толерантности, частный дом в Тель-Авиве, холлы театра «Современник» https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Архитектурное проектирование Дизайн интерьеров https://www.abbalk.ru/
Крупное архитектурное бюро https://www.abbalk.ru/gradostroitelstvo
Команда работает над большими проектами по всей стране: жильём, гостиницами, реновацией, мастер-планами жилых кварталов и проектированием модульного домостроения https://www.abbalk.ru/gradostroitelstvo
Также Parametrica развивает собственные IT-решения для проектирования и финансового анализа https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
LeBero- это творческая мастерская двух архитекторов: Романа и Ольги https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Главный принцип работы- проектирование и преобразование пространства https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Архитектура- это прежде всего режиссура жизни, необходимо https://www.abbalk.ru/gradostroitelstvo
Читать далее https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Телефон: 8 (499) 397-86-62 Адрес: Москва, Пресненская набережная, 6 https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
Архитектурная мастерская, которой в 2024 году исполняется 30 лет https://www.abbalk.ru/
Команда создаёт смелые экспериментальные решения — знаковые жилые комплексы и пространства для культурных организаций https://www.abbalk.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sildenafil 50 mg price: how generic Viagra works in the body – Sildenafil side effects and safe dosage
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
easyprt.xyz – Typography is neat, easy to read and well spaced across the site.
https://easyprt.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
xxau.xyz – Pages load quickly, giving a smooth and pleasant browsing experience.
https://xxau.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mm9b.xyz – Pages load fast and transitions are clean, nice optimization here.
https://mm9b.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kkgg1.xyz – Found a few interesting posts; the content feels fresh and engaging.
https://kkgg1.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rodarodaku.xyz – I just checked it out, layout looks clean and navigation is smooth.
https://rodarodaku.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Cheap generic Viagra online sildenafil 50 mg price or Cheap Viagra 100mg Cheap generic Viagra online
https://maps.google.com.kw/url?q=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com Cheap generic Viagra online and http://lostfilmhd.com/user/rcdayfuqto/ Viagra generic over the counter
[url=http://images.google.ps/url?q=https://bluepeakmeds.shop]Cheapest Sildenafil online[/url] cheapest viagra and [url=https://bebele.ru/user/iboqvjawpz/]generic sildenafil[/url] Viagra generic over the counter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Viagra pas cher inde п»їViagra sans ordonnance 24h or Viagra 100mg prix Viagra gГ©nГ©rique pas cher livraison rapide
https://www.google.com.pg/url?q=https://santehommefrance.shop Viagra 100mg prix and https://www.emlynmodels.co.uk/user/llkvitiqno/ Viagra femme sans ordonnance 24h
[url=http://dickandjanerocks.com/info.php?a[]=side+effects+of+sildenafil]Viagra sans ordonnance pharmacie France[/url] Viagra 100mg prix or [url=https://www.ixxxnxx.com/user/yrmtejllhl/videos]Prix du Viagra en pharmacie en France[/url] Sildenafil teva 100 mg sans ordonnance
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Если вы хотите стабильную связь — выбирайте постоянный виртуальный номер. Этот номер остаётся с вами навсегда. постоянный виртуальный номер подходит для личного и бизнес-использования. Удобство, простота, безопасность — всё это постоянный виртуальный номер. Получите постоянный виртуальный номер за пару кликов.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://olimpak.ru/virtualnyj-nomer-telefona-belorussii-praktichnoe-reshenie-dlya-biznesa-i-lichnogo-ispolzovaniya/
купить виртуальный номер телефона, купить номер навсегда, купить виртуальный номер навсегда
постоянный виртуальный номер для смс, купить виртуальный номер навсегда, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findsolutionsfast – I bookmarked this site because I expect to revisit for more insights.
https://findsolutionsfast.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
keepgrowingwithus – The content is motivating and gives me fresh ideas to grow each day.
https://keepgrowingwithus.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Виртуальный номер навсегда – это доступное решение для современных пользователей. Купите постоянный виртуальный номер для смс и забудьте о сложностях с регистрацией аккаунтов. Мы предоставляем номера с возможностью долгосрочного использования. Постоянный виртуальный номер – это безопасность и удобство. Выбирайте наши услуги для комфортной связи.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://novomoskov.ru/virtualnye-nomera-kak-ispolzovat-dlya-uspeshnoy-torgovli/
Виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер навсегда, купить виртуальный номер
виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер телефона навсегда, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
xxau.xyz – I’ve bookmarked it already; looks like a site worth returning to.
https://xxau.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mm9b.xyz – Navigation feels smooth, I found things easily within seconds.
https://mm9b.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
easyprt.xyz – Visuals and structure complement each other, looks very professional.
https://easyprt.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rodarodaku.xyz – Pages load super fast, definitely optimized for a good user experience.
https://rodarodaku.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kkgg1.xyz – I liked the overall design consistency; nothing feels out of place.
https://kkgg1.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
getinspiredtoday.shop – Wide variety of categories, always discover new and useful items.
https://getinspiredtoday.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Blue Peak Meds: Viagra generic price comparison – Blue Peak Meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopwithconfidence.shop – Affordable prices without compromising quality, happy with everything purchased today.
https://shopwithconfidence.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://britmedsuk.com/# NHS Viagra cost alternatives
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
КАК РАБОТАЕТ ДОСТАВКА?
Обратная связь https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/kardani.html
ЧТО МЫ ПРЕДЛАГАЕМ https://alfatrakt.ru/polzovatelyam/kak-sdelat-zakaz-alfatrakt.html
Являясь крупнейшим поставщиком запчастей для любых марок автомобилей, компания «АТИ» предлагает своим потенциальным партнерам взаимовыгодное и долгосрочное сотрудничество по следующим направлениям реализации грузовых запчастей оптом:
Аксессуары для автомобилей https://alfatrakt.ru/polzovatelyam/kak-sdelat-zakaz-alfatrakt.html
Основная задача ОптиПарт — оптовые поставки автозапчастей от ведущих европейских и российских производителей для удовлетворения быстро растущих потребностей рынка грузоперевозок https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-baaz.html
Мы уже длительное время успешно сотрудничаем с большими автопарками, транспортными компаниями, станциями техобслуживания СТО, магазинами и интернет-магазинами запчастей https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-ozaa.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
theperfectgiftshop.shop – Unique finds that you won’t see everywhere; love this shop.
https://theperfectgiftshop.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
МС Архитектс https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Полина Старцева https://www.abbalk.ru/gradostroitelstvo
Архитектурно-Строительное бюро ARXY https://www.abbalk.ru/arhitectyra
Телефон: 8 (495) 665-03-71 Адрес: Москва, Сущевская, 27/2 https://www.abbalk.ru/
Архитектурное бюро https://www.abbalk.ru/gradostroitelstvo
Проекты : дом академика Вайсберга, дом в Сестрорецке, архитектурный ансамбль в Подмосковье https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://britmedsuk.com/# order Viagra discreetly
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourdailyupdate.shop – User-friendly website, easy to navigate and find desired items.
https://yourdailyupdate.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bestdealsforlife.shop – Quality products at affordable prices, highly recommend this store.
https://bestdealsforlife.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Монтажный диаметр https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_landsail_ls_588_suv_25555_r20_110v
Что еще может потребоваться https://63kolesa.ru/brands/nokian tyres
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
keepgrowingforward.shop – Excellent resources, really helps me plan goals and track progress.
https://keepgrowingforward.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopforhappiness.shop – Great deals and fast shipping, very satisfied with my purchases.
https://shopforhappiness.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
simplybestchoice.shop – Great deals and fast shipping, very satisfied with my purchases.
https://simplybestchoice.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopthebesttoday.shop – Highly recommend for anyone looking for quality products and service.
https://shopthebesttoday.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopandsmilealways.shop – Great variety of items, found exactly what I needed quickly.
https://shopandsmilealways.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
exploreopportunitiesnow.shop – Prompt customer service, resolved my issue quickly and efficiently.
https://exploreopportunitiesnow.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findwhatyoulove.shop – Products arrived quickly, packaging was neat, totally satisfied with service.
https://findwhatyoulove.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
joinourcreativeworld.shop – Secure checkout process, felt confident shopping here.
https://joinourcreativeworld.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
startsomethinggreat.shop – Great quality products, definitely worth the investment.
https://startsomethinggreat.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildyourdreamtoday.shop – Very motivational, encourages small steps toward achieving big dreams consistently.
https://buildyourdreamtoday.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
createandgrow – If you end up using it, proceed with typical safeguards (payment method, guarantee, etc.).
https://createandgrow.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MediVertraut [url=https://medivertraut.shop/#]Potenzmittel rezeptfrei kaufen[/url] Sildenafil Wirkung und Dosierung
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopandshineeveryday.shop – Love the selection, makes finding gifts really easy and fun today.
https://shopandshineeveryday.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopforhappiness.shop – User-friendly website, easy to navigate and find desired items.
https://shopforhappiness.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Хотите купить виртуальный номер телефона навсегда? Мы предоставляем постоянные виртуальные номера с широкими возможностями. Это надежный способ оставаться на связи в любой точке мира. Постоянный виртуальный номер для смс гарантирует удобство и простоту. Закажите свой виртуальный номер уже сегодня!
Полная информация по ссылке – https://bryansk-news.net/other/2025/02/01/401408.html
купить виртуальный номер навсегда, купить номер телефона навсегда, виртуальный номер
виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
openlaunch – The design is modern; it seems aimed at startups and makers looking for exposure.
https://openlaunch.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’m curious to find out what blog platform you have been working
with? I’m experiencing some small security issues with my latest website and I’d like to find
something more safeguarded. Do you have any recommendations?
Here is my blog – SITUS SLOT4D
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacie française agréée en ligne: Viagra générique pas cher – pharmacie en ligne fiable France
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What Is The Reason Best Robotic Hoover Is The Right Choice For You?
robotic Vacuum device
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wett prognose heute
my blog post: Online sport-wetten (Drjk-iroda.hu)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findsolutionsfast – Will definitely come back here when I need to troubleshoot something fast.
https://findsolutionsfast.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoverhiddenpotential – The tone of the articles is warm and encouraging, which made me feel understood.
https://discoverhiddenpotential.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
focuslab – This website leaves a lasting impression, sleek and powerfully designed.
https://focuslab.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildyourownlegacy – The advice is thoughtful and grounded, not just ambitious fluff.
https://buildyourownlegacy.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildyourdigitalfuture – Found actionable tips I can apply to my projects this week.
https://buildyourdigitalfuture.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspirechangeandprogress – I’ll revisit here when I want to reset my mindset and move forward gently.
https://inspirechangeandprogress.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextrend – Might be worth bookmarking and revisiting once more posts or features are added.
https://nextrend.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
urbanscale – If they build more content this could become a useful resource — worth checking again.
https://urbanscale.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnandimproveeveryday – The articles are concise and full of practical ideas I could try right away.
https://learnandimproveeveryday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
goldnexus – The site looks sleek, but I couldn’t find much detailed info yet.
https://goldnexus.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findyourinnerdrive – I’m already using one idea from here in my daily routine and it’s helping.
https://findyourinnerdrive.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
keepgrowingwithus – Great resource when you need a gentle nudge to move forward.
https://keepgrowingwithus.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
becreativeeveryday – It’s refreshing to find a creative site that isn’t full of pressure or perfection.
https://becreativeeveryday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
staymotivatedandfocused – Found a great article here that got me back into my groove.
https://staymotivatedandfocused.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
esc tipps wetten heute
österreich
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
how generic Viagra works in the body: difference between Viagra and generic Sildenafil – Sildenafil online reviews
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Купите виртуальный номер для смс навсегда и будьте уверены в конфиденциальности данных. Постоянный виртуальный номер подойдет для любых цифровых задач. Мы предоставляем качественные номера, которые работают без сбоев. Виртуальный номер навсегда – это надежность, которая всегда с вами. Выбирайте наши услуги для комфортного общения.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://gorodkirov.ru/news/virtualnyj-nomer-dlya-avito-udobstvo-i-bezopasnost-v-odnom-reshenii/
купить виртуальный номер навсегда, купить виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер
купить номер телефона навсегда, виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://bluepeakmeds.com/# Viagra generic price comparison
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sildenafil 100 mg bestellen [url=https://medivertraut.com/#]MediVertraut[/url] Viagra rezeptfreie Schweiz bestellen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Brit Meds Uk: trusted British pharmacy – Viagra online UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Хотите оставаться на связи без привязки к физической SIM-карте? Постоянный виртуальный номер для смс – это ваше решение. Купите виртуальный номер навсегда и используйте его для любых целей. Наши услуги подходят для личного и делового общения. Виртуальный номер – это удобство, которое всегда с вами.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://politnews.net/356161
купить виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда, купить номер телефона навсегда
постоянный виртуальный номер, купить постоянный виртуальный номер, виртуальный номер
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourpathofsuccess – I liked how the site encourages you to define your own version of success.
https://yourpathofsuccess.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextrealm – Nice resource when you’re looking for new angles or inspiration.
https://nextrealm.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findsolutionsfast – I appreciate the no-frills layout — just the solutions I was looking for.
https://findsolutionsfast.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildyourdigitalfuture – Will keep this site in my rotation as I develop my digital skills.
https://buildyourdigitalfuture.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnandimproveeveryday – The site layout is clean, and it’s easy to find what you’re looking for.
https://learnandimproveeveryday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoverhiddenpotential – The tone of the articles is warm and encouraging, which made me feel understood.
https://discoverhiddenpotential.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
urbanmatrix – The tone felt friendly and the content didn’t overwhelm.
https://urbanmatrix.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
startcreatingimpact – Loved the simple but powerful tips that felt actionable right away.
https://startcreatingimpact.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
goldnexus – Could be a niche site in the making; keep an eye on how it develops.
https://goldnexus.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findyourinnerdrive – Great layout, easy reading, and the tone felt like a friendly coach rather than a lecturer.
https://findyourinnerdrive.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
keepgrowingwithus – I like how the site focuses on consistent growth rather than overnight success.
https://keepgrowingwithus.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
staymotivatedandfocused – I’ll come back to this site often when I need focus and a little inspiration.
https://staymotivatedandfocused.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
becreativeeveryday – Browsing here gave me more confidence to try a craft I’d avoided for weeks.
https://becreativeeveryday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Что-то пошло не так! Обратитесь в службу поддержки https://alfatrakt.ru/
6) Доставка автозапчастей для грузовиков оптом по всем регионам России собственным парком и с привлечением транспортных компаний (сроки – от 1 дня);
СОЗДАНИЕ ЗАКАЗА https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-weichai.html
к каждому покупателю с возможностью подбора запасных частей с учетом ассортимента магазина;
Для кого мы работаем?
//Ваш аккаунт на сайте (у пользователя должны быть права на использование API) “login” => “”, “password” => “”, );
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
createyourownpath – The layout is clean and the articles are easy to digest.
https://createyourownpath.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
handicap wette erklärung
Also visit my website: Sportwetten Online Paypal
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildyourownlegacy – I found some truly meaningful ideas here about creating lasting value.
https://buildyourownlegacy.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspirechangeandprogress – Great resource when you feel like you’ve hit a pause and want to move again.
https://inspirechangeandprogress.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextrend – Found some potential here; would like to see clearer purpose or content roadmap soon.
https://nextrend.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
urbanscale – This site looks clean and modern; will explore its content soon.
https://urbanscale.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildyourdreambrand – It’s one of the better branding-sites I’ve seen lately for meaningful content.
https://buildyourdreambrand.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Nowadays https://www.abbalk.ru/interier
«Архитектурное бюро А https://www.abbalk.ru/interier
С.+»
Архитектурное бюро WANT https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Офис продаж жилого комплекса «Слава» в Москве Изображение: MR Group / компания A Structura Узнать подробнее https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Архитектурное бюро https://www.abbalk.ru/
Ещё семь списков лучших студий и агентств здесь:
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourmomenttoshine – It’s a refreshing place to visit when you feel overlooked and need perspective.
https://yourmomenttoshine.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
startyourdreamproject – The posts are motivating and make me want to take action now.
https://startyourdreamproject.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
explorethepossibilitiesnow – Easy to read and full of confidence-boosting reminders that I needed.
https://explorethepossibilitiesnow.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Компания «СибЗТА» https://sibzta.su производит задвижки, клапаны и другую трубопроводную арматуру с 2014 года. Материалы: сталь, чугун, нержавейка. Прочные уплотнения, стандарты ГОСТ, индивидуальные решения под заказ, быстрая доставка и гарантия.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoveramazingstories – The tone is warm and human, unlike many sites that feel too formal or distant.
https://discoveramazingstories.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
expandyourhorizons – Happy I found this—just the kind of inspiration I needed today.
https://expandyourhorizons.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
quoten sportwetten
Feel free to surf to my web blog wettanbieter ohne limit, https://www.Webtumboon.com,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thepathofselfgrowth – Great layout and visuals, which made reading more enjoyable than usual.
https://thepathofselfgrowth.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
exploreendlesspossibilities – I’ll keep this bookmarked for the next time I need a new spark.
https://exploreendlesspossibilities.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thepowerofcreativity – Will return often — this site has lots of actionable ideas for creators.
https://thepowerofcreativity.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everythingyouneedtoday – I discovered some really practical guides that actually helped me today.
https://everythingyouneedtoday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
startsomethingamazingtoday.click – Hoping for downloadable tools or community features to be added soon.
https://startsomethingamazingtoday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findnewopportunitieshere.click – I bookmarked this site; it seems like a resource worth revisiting in future.
https://findnewopportunitieshere.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
youronlinetoolbox – The design is clean and the advice feels genuine, not over-hyped.
https://youronlinetoolbox.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspiredailyandgrow.click – The layout is clean and welcoming, made me want to explore more content.
https://inspiredailyandgrow.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
achat discret de Cialis 20mg: IntimiSanté – Cialis générique pas cher
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://pilloleverdi.shop/# dove comprare Cialis in Italia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
infinitalink.click – Visually the site is appealing; easy on the eyes and layouts flow well.
https://infinitalink.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
besten sportwetten tipps heute
my web page :: Welche Wettanbieter Haben Eine Deutsche Lizenz
(http://Www.Lambrosanalytics.Com)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shop-in.tech – Typography is readable and spacing between sections is comfortable for the eyes.
https://shop-in.tech/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
2rss5ge.xyz – Everything feels consistent and intentional, very solid presentation here.
https://2rss5ge.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
moj-kredyt.shop – I shared this post with friends, they appreciated the clarity.
https://moj-kredyt.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cloudfiles.tech – I’m bookmarking it — seems like a resource I’ll return to for more insight later.
https://cloudfiles.tech/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
comprar Cialis online España [url=https://tadalafiloexpress.com/#]Tadalafilo Express[/url] Cialis genérico económico
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The 10 Most Scariest Things About Best Robot Vacuum And Mop best robot vacuum and mop
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis precio: cialis generico – farmacia online fiable en España
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke rezept eu apotheke ohne rezept and online apotheke online apotheke
https://www.google.mg/url?q=https://potenzvital.com online apotheke and https://brueckrachdorf.de/user/whoiqgbykp/ beste online-apotheke ohne rezept
[url=https://tenzidetailer.com/redirect.php?url=http://bluepharmafrance.com]beste online-apotheke ohne rezept[/url] internet apotheke and [url=https://brueckrachdorf.de/user/uhiimzjdyc/]online apotheke gГјnstig[/url] online apotheke deutschland
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
How Robot Cleaners Uk Influenced My Life For The Better Automatic cleaning robot
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find
this topic to be really something that I think I would never understand.
It seems too complex and extremely broad for me. I’m looking forward for your next post,
I will try to get the hang of it! https://nativeheaven.com/index.php/User:VetaStrom730
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Farmacia online più conveniente: pillole verdi – dove comprare Cialis in Italia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
markettrendalerts.bond – Visuals and layout give a good first impression — clean and tidy.
https://markettrendalerts.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://potenzvital.shop/# tadalafil 20 mg preis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
experttradingguide.cfd – The design is professional but I’d like to see more real case-studies.
https://experttradingguide.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
modernlifestylezone.shop – Could benefit from more filters/categories to refine search further.
https://modernlifestylezone.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
businessconnectworld.bond – I found some insights here that caught my attention, planning to explore further.
https://businessconnectworld.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnforexstrategy.cfd – The writing style is friendly and accessible for beginners, liked that.
https://learnforexstrategy.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightmarketplace.cfd – Just discovered this site, looks like a fresh marketplace with interesting potential.
https://brightmarketplace.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
businessleadersclub.bond – Hope the content deepens soon, more actionable tools would be great.
https://businessleadersclub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildstrongrelationship.bond – Just found this site, looks like it might offer some relationship-growth tools.
https://buildstrongrelationship.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildsuccessnetwork.cfd – I found some interesting content here but would like to see more depth.
https://buildsuccessnetwork.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
professionalgrowthhub.bond – The visuals and layout gave a good first impression — clean and engaging.
https://professionalgrowthhub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
advancedtradingtools.bond – I found some interesting sections here, will return later to dig deeper.
https://advancedtradingtools.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Tadalafilo Express [url=https://tadalafiloexpress.shop/#]farmacia barata[/url] tadalafilo
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustedleaderscircle.cfd – Still, I’d keep an eye on how established the organisation is before relying on it fully.
https://trustedleaderscircle.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalnetworkvision.bond – I found some content that piqued my interest — will explore more tonight.
https://globalnetworkvision.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildtogethernow.bond – Good first impression, but I’d like to see more case studies or examples.
https://buildtogethernow.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I have been surfing online more than 4 hours today,
yet I never found any interesting article like yours.
It’s pretty worth enough for me. Personally, if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the web will be a lot more useful than ever
before.
Visit my website казино старда отзывы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dailyprofitupdate.cfd – I saw a few recent posts; will explore more to gauge the depth.
https://dailyprofitupdate.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
unitedvisionnetwork.bond – Overall, a positive start — excited to track updates and see how it evolves.
https://unitedvisionnetwork.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
futuregrowthteam.cfd – Navigation is smooth, site works well on mobile which is a plus.
https://futuregrowthteam.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smarttradingmentor.bond – I wish there were more video tutorials but content feels solid so far.
https://smarttradingmentor.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
classyhomegoods.bond – Navigation works nicely, felt comfortable exploring multiple collections quickly.
https://classyhomegoods.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://purebeautyoutlet.bond/
https://purebeautyoutlet.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustbridgealliance.bond – Overall good impression; I’ll keep this bookmarked for future visits.
https://trustbridgealliance.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
forexlearninghub.cfd – Good mix of strategy and mindset content, appreciated the balance.
https://forexlearninghub.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
2rss5ge.xyz – The overall design feels polished, gives a credible and fresh vibe.
https://2rss5ge.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
moj-kredyt.shop – Nice read today, tips feel practical and easy for beginners.
https://moj-kredyt.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cloudfiles.tech – Overall the site feels professional, trustworthy and well maintained.
https://cloudfiles.tech/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
modernvaluecorner.bond – The tone is professional yet approachable, nice balance.
https://modernvaluecorner.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
profitabletraderpath.cfd – Navigation is smooth, I found what I needed quickly and easily.
https://profitabletraderpath.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustbridgealliance.cfd – Wish there were more testimonials or case-studies to validate their claims.
https://trustbridgealliance.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Cialis genérico económico: farmacias online seguras – cialis precio
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacie en ligne fiable Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe and Pharmacie Internationale en ligne pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es
https://maps.google.ki/url?q=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance and http://lostfilmhd.com/user/tddlwdqcmw/ Pharmacie Internationale en ligne
[url=http://www.drachenzaehmenleichtgemacht.at/notice.php?url=https://intimisante.com]pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique[/url] pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance and [url=http://jonnywalker.net/user/ldkxfpbfkd/]acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance[/url] trouver un mГ©dicament en pharmacie
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
happytrendzone.cfd – I bookmarked this shop — I’ll revisit when new arrivals drop.
https://happytrendzone.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smarttechmukesh.xyz – Found a few useful articles here, seems like valuable information overall.
https://smarttechmukesh.xyz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
emeryflowers – Beautiful aesthetic, every section blooms with creativity and emotion.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacia online barata y fiable farmacia online madrid and farmacia barata farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a
http://www.constructionnews.co.nz/Redirect.aspx?destination=http://pharmalibrefrance.com/ farmacia online barata and https://www.hapkido.com.au/user/bnbnbbb20fastmailonii-org/ farmacia online espaГ±a envГo internacional
[url=https://images.google.co.zm/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalafiloexpress.com]farmacias direct[/url] farmacia en casa online descuento and [url=https://www.trendyxxx.com/user/ihkjkwpmam/videos]п»їfarmacia online espaГ±a[/url] farmacias online seguras
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
financialgrowthplan.cfd – Would like to see more transparency around the offerings and results.
https://financialgrowthplan.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
experttradingzone.cfd – The blog area is promising, might become a go-to resource.
https://experttradingzone.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
purebeautyoutlet.cfd – Found some nice items, the product preview gave good details and clarity.
https://purebeautyoutlet.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
forexstrategyguide.bond – The visuals look good and navigation is smooth, nice experience so far.
https://forexstrategyguide.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
forexlearninghub.bond – Good mix of strategy and mindset content, appreciated the balance.
https://forexlearninghub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
regina4congress – The campaign feels genuine, site design clean and trustworthy.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
over under wetten erklärung
Feel free to visit my web page sportwetten strategie surebets
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Cialis Preisvergleich Deutschland: PotenzVital – cialis kaufen ohne rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://pilloleverdi.shop/# PilloleVerdi
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wettbüro leipzig
Also visit my web site – Deutschland spiel wetten
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartfashionboutique.cfd – Would love to see more size-options and international shipping details though.
https://smartfashionboutique.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis kaufen ohne rezept [url=https://potenzvital.com/#]Cialis Preisvergleich Deutschland[/url] tadalafil 20 mg preis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
experttradingzone.bond – I like how they explain concepts simply, friendly for newcomers.
https://experttradingzone.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
forexlearninghub.cfd – The design is clean, though I’d like to see more interactive tools added.
https://forexlearninghub.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartforexacademy.bond – The site loads fast and navigation is straightforward which is nice.
https://smartforexacademy.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Квартира с отделкой https://новостройкивспб.рф экономия времени и предсказуемый бюджет. Фильтруем по планировкам, материалам, классу дома и акустике. Проверяем стандарт отделки, толщину стяжки, ровность стен, работу дверей/окон, скрытые коммуникации. Приёмка по дефект-листу, штрафы за просрочку.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectforprogress.bond – Bookmarking this site for future visits, seems promising for sure.
https://connectforprogress.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
classyhomegoods.bond – Mobile view was responsive and easy to use on my phone earlier today.
https://classyhomegoods.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://purebeautyoutlet.bond/
https://purebeautyoutlet.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
visionpartnersclub.cfd – The articles read well, exploring more of what’s here now.
https://visionpartnersclub.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bestdealcorner.bond – I visit weekly, always discovering new and useful deals here.
https://bestdealcorner.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
geld Wetten spiele online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
profitgoalsystem.cfd – Hoping they include more case studies soon, but good start.
https://profitgoalsystem.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustandstrength.bond – Found some good ideas here, will revisit to explore further.
https://trustandstrength.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartfashionboutique.cfd – The modern vibe works for me, feels trendy yet approachable.
https://smartfashionboutique.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
PilloleVerdi: miglior prezzo Cialis originale – PilloleVerdi
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
futuregrowthteam.bond – The writing style is friendly and approachable, nice change of pace.
https://futuregrowthteam.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successmindsetnetwork.bond – The tone is real and human, not overhyped which is nice.
https://successmindsetnetwork.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wette gratis
my web blog buchmachern
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
protraderacademy.cfd – The trading strategies taught here are practical and effective.
https://protraderacademy.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalchoicehub.cfd – Appreciate the variety of categories, from tech to home essentials.
https://globalchoicehub.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextleveltrading.bond – Just signed up for updates, excited to learn more.
https://nextleveltrading.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
beste sportwetten anbieter deutschland
Feel free to surf to my website Buchmacher Ohne Wettsteuer
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
protradinginsights.cfd – The educational resources here are top-notch for continuous learning.
https://protradinginsights.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал о строительстве домов https://doma-land.ru проекты и сметы, сравнение технологий (каркас, газобетон, кирпич, брус), фундамент и кровля, инженерия и утепление. Калькуляторы, чек-листы, тендер подрядчиков, рейтинги бригад, карта цен по регионам, готовые ведомости материалов и практика без ошибок.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopandshine.shop – Overall positive experience; looking forward to exploring more products soon.
https://shopandshine.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
advancedtradingtools.shop – Good value tools and the design makes shopping enjoyable.
https://advancedtradingtools.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globaltradingnetwork.cfd – Provides multi-asset trading across 90+ markets, enhancing global reach.
https://globaltradingnetwork.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
forexlearninghub.shop – Clean layout and easy navigation make exploring forex concepts enjoyable today.
https://forexlearninghub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
uniquedecorstore.shop – Site loads quickly and the mobile version is nicely responsive.
https://uniquedecorstore.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brandlift.click – Pages load smoothly and visuals look crisp and professional.
https://brandlift.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
webrevive.click – On mobile it’s quite smooth; no weird layout quirks or misalignment.
https://webrevive.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boostengine.click – I like how clean the design is and how well-organized the menus appear.
https://boostengine.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sitefoundry.click – The site has a polished clean design and navigation feels intuitive.
https://sitefoundry.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pixelpush.click – The visual style complements the text nicely—very polished feeling.
https://pixelpush.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
richtig tippen sportwetten prognose Heute
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wett prognosen
my web site … wette tipps heute (Lettie)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Best Robot Vacuum Uk: The Intermediate Guide Towards Best Robot Vacuum Uk Best robot vacuum Uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
niederlande deutschland wetten
Check out my homepage – kombiwetten tipps heute
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke rezept online apotheke preisvergleich and eu apotheke ohne rezept ohne rezept apotheke
https://horizoninteractiveawards.com/index.php?URL=http://bluepharmafrance.com/ online apotheke preisvergleich and https://act2day.eu/profile/esywfxxyqg/ beste online-apotheke ohne rezept
[url=https://www.google.co.ke/url?q=https://potenzvital.com]online apotheke versandkostenfrei[/url] beste online-apotheke ohne rezept or [url=https://raygunmvp.com/user/robnqoeseq-robnqoeseq/?um_action=edit]п»їshop apotheke gutschein[/url] online apotheke gГјnstig
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
You’ll Never Be Able To Figure Out This Robotic Vacuum Cleaners Uk’s Tricks robotic Vacuum cleaners uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://potenzvital.com/# Cialis generika gunstig kaufen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
acquistare Cialis online Italia: cialis – miglior prezzo Cialis originale
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Best Robot Vacuum Uk: The Intermediate Guide To
Best Robot Vacuum Uk best robot vacuum uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Vacuum Robot: The Intermediate Guide In Vacuum Robot Vacuum robot
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacia online barcelona [url=http://tadalafiloexpress.com/#]comprar cialis[/url] cialis generico
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis kaufen ohne rezept: europa apotheke – PotenzVital
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacie en ligne pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale and pharmacie en ligne france fiable pharmacie en ligne france fiable
https://cse.google.je/url?q=https://intimisante.com Pharmacie sans ordonnance or https://cv.devat.net/user/ngtbqrtsjp/?um_action=edit Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable
[url=http://cse.google.pl/url?q=https://intimisante.com]pharmacie en ligne[/url] pharmacie en ligne fiable or [url=https://cv.devat.net/user/pkshsuadxu/?um_action=edit]pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale[/url] Pharmacie sans ordonnance
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
purebeautytrend.shop – The collection seems fresh and well-curated for current beauty trends.
https://purebeautytrend.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
creativefashionworld.shop – I appreciate the clear photos and detailed descriptions for items.
https://creativefashionworld.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
budgetfriendlyfinds.shop – Will bookmark this shop for future finds of everyday essentials.
https://budgetfriendlyfinds.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Five Killer Quora Answers To Robot Vacuum Uk robot Vacuum uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
powerofcollaboration.bond – The content tone is welcoming, professional, and easy to engage with.
https://powerofcollaboration.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://tadalafiloexpress.com/# farmacias online baratas
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dailyessentialstore.shop – Customer service section appears straightforward, offers helpful contact information and support.
https://dailyessentialstore.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectforgrowth.bond – Just discovered this site, seems like a strong growth hub.
https://connectforgrowth.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
modernlifestylezone.shop – I appreciate the clear photos and product descriptions featured here.
https://modernlifestylezone.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dreambuyworld.shop – The product descriptions are clear and helped my selection process.
https://dreambuyworld.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smarttraderacademy.bond – Just found this site, looks like a solid trading mentorship platform.
https://protraderacademy.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
simplelivingstore.shop – Found charming items today, perfect for calm living and minimal décor.
https://simplelivingstore.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalalliancenetwork.bond – I appreciate the idea of global alliances focused on mutual success.
https://globalalliancenetwork.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
visionaryfutureteam.bond – The tone is professional yet inclusive, welcoming all levels of involvement.
https://visionaryfutureteam.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everydayvaluehub.shop – The website layout is neat and navigation feels smooth today.
https://everydayvaluehub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
innovationdriventeam.bond – I appreciate the collaborative mindset and creativity underlying their approach.
https://innovationdriventeam.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successfultradersclub.shop – Feel confident this could become a valuable hub for traders.
https://successfultradersclub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartfashionboutique.bond – Overall positive experience, excited to return and explore more styles.
https://smartfashionboutique.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learntradingtoday.cfd – Visuals and examples really helped me understand chart patterns clearly.
https://learntradingtoday.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
partnershipgrowthhub.bond – Resources are well-organized and the content gives clear practical value.
https://partnershipgrowthhub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
investprofitgrow.cfd – Good first impression; looking forward to exploring deeper content here.
https://investprofitgrow.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smarttradingmentor.cfd – Overall positive first impression, excited to dive deeper into content.
https://smarttradingmentor.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
compresse per disfunzione erettile: Farmacia online miglior prezzo – PilloleVerdi
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafil sans ordonnance [url=https://intimisante.shop/#]pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique[/url] cialis prix
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten test vergleich
Also visit my blog wetten die man nicht Gewinnen kann (Overalladvisor.Com)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello !
Hello. A 24 very cool website 1 that I found on the Internet.
Check out this site. There’s a great article there. https://wsfworldjuniors.org/progressive-slots/5-products-that-will-transform-your-skin-in-a-matter-of-days/|
There is sure to be a lot of useful and interesting information for you here.
You’ll find everything you need and more. Feel free to follow the link below.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bester willkommensbonus beste sportwetten seite (Ciara)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительство и ремонт https://repair-house.kiev.ua дома без ошибок: пошаговые инструкции, выбор материалов и подрядчиков, смета и экономия, фундамент, кровля, инженерия, утепление, отделка. Чек-листы, калькуляторы, типовые узлы, лайфхаки по срокам и качеству. Экономим бюджет — повышаем комфорт.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
compresse per disfunzione erettile: cialis generico – dove comprare Cialis in Italia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wettbüro erfurt
My webpage: pferderennen Düsseldorf wetten
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Excellent blog right here! Additionally your website so much up very fast!
What host are you using? Can I am getting your affiliate link
on your host? I wish my web site loaded up as fast as yours lol
Also visit my site: professional companions Mumbai
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все о коттеджных посёлках https://cottagecommunity.ru как выбрать локацию, проверить инфраструктуру и коммуникации, понять цены и налоги. Сравнение ИЖС/ДНП, надёжность застройщиков, ипотека и субсидии, отзывы жителей, карта проектов и чек-листы для осмотра. Поможем принять взвешенное решение о покупке.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://potenzvital.shop/# tadalafil 20 mg preis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
strongpartnershipnetwork.cfd – Excellent site layout and simple navigation make partnering easy and effective.
https://strongpartnershipnetwork.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужен сайт? создание сайтов под ключ с акцентом на конверсию: UX-исследование, дизайн-система, чистая вёрстка, CMS на выбор, подключение метрик и событий. Интернет-магазины, B2B-порталы, лендинги. SEO-структура, микроразметка, скорость 90+. Поддержка и развитие без скрытых расходов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужна вывеска? сделать вывеску для магазина логотипы, надписи, декор для кафе, офисов и дома. Индивидуальный дизайн, энергосберегающие материалы и эффектный свет в любом стиле.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Cialis genérico económico: tadalafilo 5 mg precio – Cialis genérico económico
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmaci senza ricetta elenco [url=http://pilloleverdi.com/#]tadalafil italiano approvato AIFA[/url] PilloleVerdi
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dailyessentialfinds.bond – Great selection of essentials, made my shopping experience smooth.
https://dailyessentialfinds.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopandshine.cfd – The product range feels fresh and well-organized for easy selection.
https://shopandshine.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I savour, cause I discovered just what I used to be taking a look for.
You have ended my four day lengthy hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day.
Bye
Also visit my web-site – Lorirexon
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartinvestorhub.cfd – Found some actionable takeaways today that I’ll apply this week.
https://smartinvestorhub.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s up, I log on to your blog regularly.
Your story-telling style is awesome, keep it up!
My blog … digi 995
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ultimateprofitplan.bond – Well-structured content, made complex concepts easy to understand.
https://ultimateprofitplan.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
teamworkinnovation.cfd – Will bookmark this site to revisit for fresh teamwork strategies.
https://teamworkinnovation.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dailytrendstore.cfd – Site loads fast and product descriptions are clear and helpful.
https://dailytrendstore.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dailyessentialfinds.cfd – Overall positive experience, I’ll definitely return here for future essentials.
https://dailyessentialfinds.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis sans ordonnance: pharmacie qui vend du cialis sans ordonnance – IntimiSanté
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dailytradingupdate.cfd – The clean layout and quick updates make it easy to read.
https://dailytradingupdate.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
maskchallengeusa – Clear purpose and bold message, layout supports awareness beautifully.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Pretty nice post. I simply stumbled upon your blog and wanted
to mention that I have really loved surfing around your weblog posts.
In any case I’ll be subscribing on your feed and I am hoping you write again very
soon!
Here is my web page – OK9 com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
unityandprogress.bond – Great platform, I’m inspired by the unity and shared vision.
https://unityandprogress.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustedpartnergroup.bond – Just discovered this group, seems promising for building strong partnerships.
https://trustedpartnergroup.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildsuccessnetwork.bond – Love the design and easy navigation, very user-friendly experience.
https://buildsuccessnetwork.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fastgrowthsignal.cfd – Content loads quickly and the experience is really user-friendly.
https://fastgrowthsignal.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smarttradingmentor.bond – Practical tips and real examples make learning trading much easier.
https://smarttradingmentor.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
strategicgrowthplan.bond – Helps me visualise next steps clearly and with confidence.
https://strategicgrowthplan.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustedleaderscircle.bond – Overall great impression, looking forward to exploring further materials here.
https://trustedleaderscircle.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fastgrowthsignal.bond – Love the clear insights and fast-moving strategy advice offered here.
https://fastgrowthsignal.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnandtrade.cfd – Content is up-to-date and covers many useful trading topics.
https://learnandtrade.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bestdealcorner.cfd – Nice promotional offers today, definitely worth checking out bargains.
https://bestdealcorner.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
freshfashionfinds.cfd – Clean layout and smooth browsing, makes finding info simple.
https://freshfashionfinds.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
forexsuccessguide.cfd – Really useful content, helps me stay updated with trends fast.
https://forexsuccessguide.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://tadalafiloexpress.com/# cialis precio
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
creativegiftworld.bond – Site loads quickly and content feels relevant and fresh.
https://creativegiftworld.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
teamworkinnovation.bond – This platform has some of the best tips I’ve seen.
https://teamworkinnovation.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
advancedtradingtools.cfd – Smooth navigation and quick loading, makes information access very convenient.
https://advancedtradingtools.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
visionpartnersclub.bond – This platform has some of the best tips I’ve seen.
https://visionpartnersclub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
urbanstylehub.cfd – Just discovered this site, really enjoying the fresh content daily.
https://urbanstylehub.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
z9hl4.info – The color scheme is subtle and soothing, doesn’t strain the eyes at all.
https://z9hl4.info/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nathanjones.shop – Typography and spacing are well-balanced—comfortable for reading longer content.
https://nathanjones.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brittanydominguez.shop – Already bookmarked the site—looks like a valuable resource to return to.
https://brittanydominguez.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://pilloleverdi.com/# farmacia online italiana Cialis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kuvalis.com – I bookmarked this because it seems worth revisiting later for more insight.
https://kuvalis.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brandmetric.click – Pages load quickly and smoothly, no lag or weird behavior when switching tabs.
https://brandmetric.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fitproawardsuk – Easy to understand entry process and benefits, quite user-friendly.
https://fitproawardsuk.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перейти к полному поиску https://akademy21.ru/parikmaher
Дополнительная информация https://akademy21.ru/master_po_dizainu
Mangrove Tree Resort World Sanya Bay – Kapok https://akademy21.ru/trener_nogtevogo_servisa
Чем заняться?
В ближайшее время наш менеджер свяжется с Вами!
Самые популярные места Китая https://akademy21.ru/prepodavatel_podologii
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Yes! Finally someone writes about Lorirexon.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tradeandwin – Easy to navigate site and clear explanations for strategies I like.
https://tradeandwin.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rasecurities – Secure feel and clean presentation make the browsing experience comfortable.
https://rasecurities.net/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
markettrendalerts – The layout is simple and the alerts are easy to digest quickly.
https://markettrendalerts.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tradingmasterclass – The examples used felt realistic and relevant to real trading situations.
https://tradingmasterclass.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Cialis générique pas cher [url=https://intimisante.com/#]IntimiSanté[/url] cialis sans ordonnance
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successfultradersclub – Some of the methods seem advanced, great resource if you’ve got experience trading.
https://successfultradersclub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
modernwoodcases – Secure payment process and clear return policy made me feel comfortable buying.
https://modernwoodcases.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
imprintregistry – The site feels credible, with clear explanation of blockchain-backed registry methods. :contentReference[oaicite:1]index=1
https://imprintregistry.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
masterthemarket – Navigation was smooth and I found useful content without too much fluff.
https://masterthemarket.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pillole verdi: cialis prezzo – acquistare Cialis online Italia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
businesssuccesshub – The professional tone and depth of content are impressive.
https://businesssuccesshub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Link exchange is nothing else but it is just placing the other person’s blog link on your page at proper place and other person will also do similar in support of you.
Visit my site; FreundGentak TEST
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
netmatrix.click – Overall, the experience is solid and gives a trustworthy first impression.
https://netmatrix.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rankflow.click – The pages load quickly, and the visuals are sharp—nice user experience.
https://rankflow.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightmarketplace – Enjoyed exploring different categories, nice mix of everyday and special-find pieces.
https://brightmarketplace.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
justvotenoon2 – The resources here are practical and useful for everyday needs.
https://justvotenoon2.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
z9hl4.info – I found several useful links already—definitely worth revisiting later.
https://z9hl4.info/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brittanydominguez.shop – I just visited and the site feels sleek with a very modern clean layout.
https://brittanydominguez.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nathanjones.shop – Navigation is smooth and intuitive, found what I needed in a few clicks.
https://nathanjones.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
financialgrowthplan – This has become a go-to resource in my plan to ramp up savings and investments.
https://financialgrowthplan.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Таможня https://akademy21.ru/courses/nailservice
В 2018 году услугами компании Библио-Глобус воспользовались 2 934 056 человек https://akademy21.ru/master_nogtevogo_servisa
Цены на горящие туры в Китай из Иркутска могут быть ниже обычных цен на 20-40% https://akademy21.ru/master_epiliacii
по данным открытого голосования на сайте с 25 июля по 10 ноября 2014 https://akademy21.ru/prepodavatel_podologii
Подобрать тур в агентстве https://akademy21.ru/blog/tpost/mr66te9rc1-chempionati-akademii-21-sredi-masterov-b
С высоты Великой стены для всех открывается невероятная природа Китая https://akademy21.ru/contacts/vladivostok
Тут не только рисовые поля-террасы, пагоды и … заводы до горизонта https://akademy21.ru/kurs_cosmetolog_estet
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendandstyle – Stylish fashion finds, loved the unique designs and quality.
https://trendandstyle.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
miglior prezzo Cialis originale: cialis generico – Farmacia online miglior prezzo
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growthnetworkgroup.cfd – Found valuable resources and insights that are helping my business.
https://growthnetworkgroup.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
winwithus.bond – Site loads quickly and content feels relevant and fresh.
https://winwithus.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
urbanstylehub – Clean layout and smooth shopping experience made things easy.
https://urbanstylehub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dailytrendstore – Fashion and lifestyle trends galore, found a bunch of items I liked.
https://dailytrendstore.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it.
Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! However, how
could we communicate?
My web page Spot Codrix 300
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
musionet – The site loads fast and the sections are well-structured for users.
https://musionet.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendandstyle.bond – Great selection of ideas, keeps me coming back often here.
https://trendandstyle.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I was suggested this blog by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post
is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my problem.
You’re incredible! Thanks!
Feel free to surf to my blog – 홍대셔츠룸
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
investprofitgrow – Secure feel and clear information which builds confidence in the platform.
https://investprofitgrow.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
simplelivinghub – Great ideas for practical minimalist living, really helpful for my space.
https://simplelivinghub.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learntradingtoday – Secure payment process and transparent information made me confident to explore.
https://learntradingtoday.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://intimisante.com/# acheter Cialis en ligne France
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
judiforcongress – Strong campaign site, message feels inspiring and presentation confident.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
investsmarttoday.bond – Love the design and easy navigation, very user-friendly experience.
https://investsmarttoday.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectforprogress.cfd – Clean layout and smooth browsing, makes finding info simple.
https://connectforprogress.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopwithsmile.cfd – Really enjoyed reading here, all information is clear and practical.
https://shopwithsmile.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everydaytrendshop.bond – Content is useful, helps me stay up-to-date with trends fast.
https://everydaytrendshop.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis precio [url=https://tadalafiloexpress.com/#]tadalafilo 5 mg precio[/url] tadalafilo
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cuttingthered – Sharp branding, message delivers confidence and determination effectively.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis 20 mg achat en ligne: Intimi Santé – IntimiSanté
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
modernvaluecorner – This store has become one of my go-to spots for smart online shopping.
https://modernvaluecorner.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
15 Best Robot Vacuum And Mop Bloggers You
Must Follow Best Robot Vacuum And Mop
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cuttingthered – Sharp branding, message delivers confidence and determination effectively.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
seoignite.click – Visuals complement the text nicely; the design feels polished and thought-out.
https://seoignite.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://pilloleverdi.shop/# cialis generico
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все о коттеджных посёлках https://cottagecommunity.ru/lesmoi/ фото, описание, стоимость участков и домов. Всё о покупке, строительстве и жизни за городом в одном месте. Полезная информация для покупателей и инвесторов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnandtrade – Valuable strategies for improving team performance and business efficiency.
https://learnandtrade.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rankseed.click – On mobile it’s flawless—everything adapts and looks good on the phone.
https://rankseed.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendandstyle – Stylish fashion finds, loved the unique designs and quality.
https://trendandstyle.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartbuytoday – Secure payment options and fast site loading, felt trustworthy.
https://smartbuytoday.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
classyhomegoods – This site has become my favorite for online fashion shopping.
https://classyhomegoods.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Te annyira klassz vagy! Nem hiszem, hogy olvastam ehhez hasonlót korábban. Jó érzés, hogy van valakit, akinek egyedi gondolatai vannak erről a tárgyról.
Nagyon köszönöm, hogy elindítottad ezt.
Ez az site tényleg fontos az interneten, valaki, aki hoz egy kis eredetiséget. https://casinovilag.net/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wettanbieter in deutschland
my web-site wetten erfahrungen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
freshfashionfinds – Found unique pieces not available elsewhere, great shopping experience.
https://freshfashionfinds.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’ve been using [url=https://www.nothingbuthemp.net/products/brez-5mg-thc-2200mg-lions-mane ]thc and lion’s mane drink[/url] constantly on account of during the course of a month at the moment, and I’m indeed impressed before the absolute effects. They’ve helped me feel calmer, more balanced, and less solicitous in every nook the day. My snore is deeper, I wake up refreshed, and uniform my focus has improved. The trait is distinguished, and I appreciate the natural ingredients. I’ll categorically keep buying and recommending them to everybody I be aware!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalmarketinsight – Helpful mix of visuals and explanations, made complex data easier.
https://globalmarketinsight.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
simplelivinghub – Quality content with heart, feels like advice from a friend.
https://simplelivinghub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
uniquedecorstore – Found some rare décor items not seen on other stores, very pleased.
https://uniquedecorstore.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
strongfoundation – The team behind this appears professional and attentive to details.
https://strongfoundation.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
strongpartnershipnetwork – Helpful guides and resources, learned a lot about building strong networks.
https://strongpartnershipnetwork.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shoplocaltrend – Smooth browsing and secure payment options, very trustworthy site.
https://shoplocaltrend.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten schweiz online heute tipps
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The 10 Most Terrifying Things About Laser Cut Key Repair Laser Cut Key Repair (Greta)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
futuregrowthteam – Found unique items not available elsewhere, great shopping experience.
https://futuregrowthteam.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Experience the best Nuru massage in Bangkok at HisoMassage.com
your ultimate destination for authentic erotic massage, soapy massage, and happy ending massage
on Sukhumvit. Our expert Nuru therapists provide a luxurious,
sensual experience that defines true relaxation in the heart of Bangkok.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’ll immediately take hold of your rss as I can’t in finding your email subscription link or e-newsletter service.
Do you’ve any? Please allow me know so that I could subscribe.
Thanks.
My web page :: 6bpro
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Тысячи клиентов постоянно ищут единственно верный способ для входа на торговую площадку Kraken, сталкиваясь с обилием фейковых ресурсов и неактуальной информацией. Дабы минимизировать подобные проблемы и сохранить ваше время, мы предлагаем простое и эффективное решение. [url=https://kradark.net]кракен даркнет ссылка[/url] Данный сайт служит в роли постоянно обновляемого агрегатора актуальных ссылок, позволяя любому пользователю в любой момент найти рабочий вход на площадку Кракен. Запомнив этот адрес, вы навсегда решите проблему от необходимости выискивать рабочие ссылки на посторонних ресурсах, подвергая риску собственными данными.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextleveltrading – Excellent trading platform, helping sharpen skills and boost confidence.
https://nextleveltrading.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bestforexstrategies – Good mix of visuals and explanations, helped me understand one strategy better.
https://bestforexstrategies.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successfultradersclub – Found a tip I hadn’t seen on other sites, that was a nice bonus today.
https://successfultradersclub.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hey there! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could find a captcha
plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having trouble finding
one? Thanks a lot!
Also visit my blog post :: prn huh
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourtradingmentor – Clear, easy to follow advice that’s great for both new and seasoned traders.
https://yourtradingmentor.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I am curious to find out what blog platform you happen to be utilizing?
I’m experiencing some small security issues with my latest blog and
I’d like to find something more safeguarded. Do you have any solutions?
My homepage … sex miễn phí miễn phí
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Potenz Vital [url=https://potenzvital.shop/#]Potenz Vital[/url] Tadalafil 20mg Bestellung online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ultimateprofitplan – This plan is a game-changer for anyone serious about business growth.
https://ultimateprofitplan.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
visionpartnersclub – Helpful product descriptions and reviews, made decision-making easier today.
https://visionpartnersclub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
seoignite.click – Navigation is smooth and intuitive, found what I needed in a few clicks.
https://seoignite.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
constantly i used to read smaller articles which as well clear
their motive, and that is also happening with this article which I am reading at this time.
Feel free to surf to my web site toto togel
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://tadalafiloexpress.com/# Tadalafilo Express
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafilo: Cialis genérico económico – farmacia online fiable en España
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopandshine – Awesome variety of items, loved how easy the site is to use.
https://shopandshine.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rankseed.click – Found some useful articles here, will be saving them to read later.
https://rankseed.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
seowhale.click – Found some helpful links already; seems like there’s good content inside.
https://seowhale.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
metaboost.click – Found some interesting sections already; I’ll explore more later.
https://metaboost.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Truly no matter if someone doesn’t know then its up to other viewers that they will help, so here
it takes place.
Also visit my site: kusuri no fukutaro pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalchoicehub – Quality items arrived well packaged and in good condition.
https://globalchoicehub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopwithsmile – Very user-friendly site, easy navigation and clear product pages.
https://shopwithsmile.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
forexstrategyguide – Clear and concise, perfect for entrepreneurs looking to grow efficiently.
https://forexstrategyguide.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
наиболее востребованных покупателями наименований в постоянном наличии на нашем центральном распределительном складе;
Филиал СПБ ул https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-weichai.html
Рощинская 36 График работы филиала День недели Время работы Понедельник-Пятница 8:00 – 20:00 Суббота-Воскресенье 9:00 – 19:00 График доставки заказов День недели Размещение заказа Доставка заказа в филиал Понедельник-Пятница до 10:00 в тот же день, в 15:00 Понедельник-Пятница с 10:00 до 18:00 на следующий день в 10:00 Понедельник-Пятница после 18:00 на следующий день в 15:00 Суббота до 18:00 Воскресенье в 10:00 Суббота после 18:00 Понедельник в 10:00 Воскресенье до 18:00 Понедельник в 10:00 Воскресенье после 18:00 Понедельник в 17:00 https://alfatrakt.ru/polzovatelyam/polzovatelskoe-soglashenie.html
Запчасти по алфавиту https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs
Ассортимент запчастей для грузовиков MAN https://alfatrakt.ru/forms/pomosch-v-podbore-zapasnyh-chastei
Запчасти:
Цепи противоскольжения https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/kardani.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successnetworkgroup – Found useful tools for collaboration and success, will revisit for more.
https://successnetworkgroup.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
classyhomegoods – Great value décor finds, perfect for refreshing my home space.
https://classyhomegoods.cfd/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
teamworksuccesspath – Excellent insights into team dynamics, helped me work better with my group.
https://teamworksuccesspath.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если вы предпочитаете спортивный стиль езды и очень часто перемещаетесь по скоростным трассам, тогда для вас лучшей альтернативой станут покрышки с направленным симметричным протекторным рисунком https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_mileking_mk687_21555_r17_xl_98t Они показывают впечатляющую управляемость, помогают точно держать траекторию и уверенно маневрировать https://63kolesa.ru/articles/indeksi-skorosti-shin
«Белшина» — белорусский производитель, специализирующийся на изготовлении резины для легковых авто и коммерческого транспорта разной грузоподъёмности https://63kolesa.ru/articles?page=1
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnandtrade – The mix of theory and practical examples really made a difference.
https://learnandtrade.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
20 Interesting Quotes About Robot Vacuum Cleaner Robot vacuum cleaners uk (http://Www.metooo.io)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Москва > Битез, 13 https://akademy21.ru/contacts/ixelles
03 https://akademy21.ru/contacts/habarovsk
19 / 7 ночей / 2 взр https://akademy21.ru/trener_estetika_tela
Турфирмы подбирают туры https://akademy21.ru/apparatniy_pedecur
Расстояние до пляжа https://akademy21.ru/sam_vizajist
Показать все предложения https://akademy21.ru/obucheniye-lazernoye-udaleniye-sosudov-kuperoza-varikoza
Расстояние до пляжа https://akademy21.ru/combinirivaniy_manicur
Конечно, китайская еда – это то, о чем говорят все, кто вернулся из Китая здоровым и невредимым (что бы это ни значило)! Все рассказывают, как пробовали китайскую еду на родине https://akademy21.ru/cosmetolog_estet_sale
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Поскольку конфиденциальность и защита данных являются ключевыми приоритетами при взаимодействии с даркнет-маркетплейсами, выбор правильного канала доступа имеет решающую роль. Применение непроверенных источников чревато к краже персональных данных и финансовых средств, поэтому следует соблюдать максимальную бдительность. [url=https://worldclasslearning.com/]рабочая ссылка на кракен[/url] Перейдя по этому адресу, вы получаете стопроцентный вход к широчайшему ассортименту платформы, в том числе рейтинги продавцов и круглосуточную службу поддержки. Этот способ позволяет целиком исключить риск попадания на поддельный сайт и гарантирует высочайшую уровень конфиденциальности при совершении всех сделок.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
seowhale.click – On mobile it adapts nicely, nothing seems broken or misaligned.
https://seowhale.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
metaboost.click – Overall experience is positive; the site seems thoughtfully designed.
https://metaboost.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacie en ligne france pas cher [url=https://intimisante.com/#]IntimiSanté[/url] cialis generique
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
2D/3D планировки https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
GAFA https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
Архитектурное бюро https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
Блог https://www.abbalk.ru/
В портфолио бюро входят дома и коттеджи, усадьбы, дворцы и виллы, общественные здания и проекты целых коттеджных поселков https://www.abbalk.ru/gradostroitelstvo
Контакты https://www.abbalk.ru/arhitectyra
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
PilloleVerdi: tadalafil senza ricetta – dove comprare Cialis in Italia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ultimateprofitplan – Loved the actionable insights, really helped streamline my operations.
https://ultimateprofitplan.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стать оптовым клиентом Стать поставщиком Аттестация магазинов ГАЗ https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-baaz.html
Санкт-Петербург, пр https://alfatrakt.ru/polzovatelyam/polzovatelskoe-soglashenie.html
Полюстровский д https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-stal.html
54 https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-weichai.html
5) Наличие 12 складов в 8 городах ЦФО позволяет осуществлять доставку грузовых запчасти оптом в кратчайшие сроки;
Преимущества OptiPart https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-baaz.html
Компания «АТИ» приглашает к взаимовыгодному сотрудничеству поставщиков и производителей автозапчастей и аксессуаров для иностранных и отечественных автомобилей https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-wabco.html
Для подключения Вас в качестве Поставщика к интернет-магазину ati-auto https://alfatrakt.ru/remont-i-servis/remont-i-servis.html
ru нужно соответствовать минимальным требованиям https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-ozaa.html
Компания «СТАТ» предлагает широкий ассортимент запчастей и комплектующих https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-maz.html
Мы предоставляем помощь в выборе — если вы не уверены, какие детали вам подойдут, обратитесь в нашу компанию, и опытные специалисты помогут найти нужное решение https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-weichai.html
Наша компания предоставляет возможность купить оригинальные запчасти и качественные аналоги дешевле, чем в фирменных магазинах https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-baaz.html
Это позволяет экономить деньги, сохраняя по-прежнему высокий уровень качества и надежности https://alfatrakt.ru/polzovatelyam/politika-v-otnoshenii-obrabotki-personalnyh-dannyh-ooo-alfatrakt.html
Обращайтесь к нам!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если вы любитель небольшой скорости, тогда смело приобретайте комплект резины с симметричным направленным протектором https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_triangle_tr646_18575_r16c_104102q__tl Он прослужит несколько сезонов без потери ключевых свойств, обеспечит безопасность передвижения в дождь и слякоть, поможет сэкономить на расходе топлива https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_bridgestone_dueler_hp_sport_23555_r19_101w___ao Шины с направленным протекторным рисунком устойчивы к абразивному износу, быстро реагируют на команды руля, гарантируют полный акустический комфорт в салоне https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_cordiant_business_cw2_18575_r16c_104102q_ship_tl
Артикул: 79538 7×17 5×110 ET35 DIA65,1 https://63kolesa.ru/brands
А еще в «Колёса Даром» представлены АКБ, колеса в сборе и другие автотовары https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_matador_mp_30_sibir_ice_2_suvfr_23565_r17_xl_108t_ship
2 https://63kolesa.ru/catalog/restored Возврат и обмен, доставленного товара, надлежащего качества, производится за счет клиента https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_matador_mp_30_sibir_ice_2_20565_r15_xl_99t_ship
Если вам потребуется погрузить колеса в машину, наши специалисты помогут https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_mileking_mk687_20555_r17_xl_95h
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
strongpartnershipnetwork – Helpful content and easy navigation, keeps me coming back regularly for tips.
https://strongpartnershipnetwork.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://tadalafiloexpress.com/# cialis generico
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tradingmasterclass – Excellent content with actionable tips, highly recommend this site to traders.
https://tradingmasterclass.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://potenzvital.shop/# cialis 20mg preis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
melbet – paris sportif 1xbet afrique apk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
protraderacademy – Easy to navigate and very informative, helped me improve trading skills.
https://protraderacademy.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[url=https://vk.com/nakrutkapfonline]накрутка пф![/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
quote berechnen wetten
Review my website … wette tipps heute (Motor.Wejustdesign.com)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Универсальное архитектурное бюро https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Компания занимается проектированием жилых зданий, культурных учреждений, образовательных и торговых центров, офисов, гостиниц и частных домов https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
География проектов не ограничивается только Москвой https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Бюро работало с заказчиками из Калининграда, Якутска, Тбилиси и Алматы https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Endless House https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
Сергей Скуратов Архитектс https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Дом в Комарово Изображение: архитектурная мастерская «Головин & Шретер»
Какую цель мы ставили, создавая этот рейтинг архитектурных бюро Москвы? В первую очередь мы заботились о вашем удобстве https://www.abbalk.ru/arhitectyra
Вместо того, чтобы исследовать десятки различных сайтов, изучать отзывы о компаниях, теряя драгоценное время, вы можете найти всю нужную информацию в одном месте https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
Это текущий каталог https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Здесь вы можете найти интересующее вас бюро, сравнить его с конкурирующими организациями, моментально получить более детальную информацию о компании и даже ознакомиться с ее портфолио https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
И все это – на одном ресурсе https://www.abbalk.ru/gradostroitelstvo
Не нужно искать, терять время, держать открытыми одновременно несколько вкладок, чтобы выбрать лучшего исполнителя https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
Buromoscow https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
musionet – Very helpful guides, made my tasks much simpler and faster.
https://musionet.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
purebeautyoutlet – The images are appealing, and checkout process was smooth overall.
https://purebeautyoutlet.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafilo 5 mg precio: farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a – tadalafilo sin receta
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
modernwoodcases – The minimalist designs are sleek and stylish; love them.
https://modernwoodcases.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smarttradingmentor – Excellent mentorship tips, really helped me improve trading strategies today.
https://smarttradingmentor.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourtradingmentor – Clean design and easy navigation, makes following lessons really simple today.
https://yourtradingmentor.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendinggiftcorner – Excellent selection and useful recommendations, I’ll definitely come back.
https://trendinggiftcorner.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trafficpulse.click – Navigation is smooth and intuitive, found what I needed in a few clicks.
https://trafficpulse.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В условиях частых блокировок со стороны государственных регуляторов, стабильный доступ к таким востребованным ресурсам, как Кракен может быть серьезно осложнен. Именно поэтому первостепенное значение имеет умение находить актуальные и безопасные способы обхода ограничений, чтобы не потерять возможность пользоваться услугами. [url=https://ai-translation-services.com/]как зайти на кракен[/url] Именно данный проверенный канал гарантирует вам прямое попадание на настоящий сервер Kraken, в обход любые посредников и скрытые опасности. Такой подход является единственно верным решением для всех, кто дорожит свою безопасность и желает иметь полную уверенность в защите своего профиля и баланса на счету.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
seoloom.click – Pages load quickly and visually everything feels sleek and professional.
https://seoloom.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rankforge.click – The visual style complements the content nicely — very polished.
https://rankforge.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
keywordorbit.click – Already bookmarked this — I think I’ll keep checking back here.
https://keywordorbit.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendhunterplace – This site is practical and enjoyable, keeps me coming back.
https://trendhunterplace.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
webtide.click – I found a couple of interesting links already—will explore more later.
https://webtide.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildlastingtrust.shop – Photos are good quality; copy feels honest and thoughtful.
https://buildlastingtrust.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextgenproject.shop – Layout is promising, assuming content matches the vision.
https://nextgenproject.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findyourlook.shop – Already bookmarked several pieces, thinking about ordering soon.
https://findyourlook.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
technologydreamhub.shop – Definitely sharing this with my friends who love new gadgets.
https://technologydreamhub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
gute wettanbieter
Visit my homepage … online sportwetten neu
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten heute tipps
my webpage :: doppelte chance wetten erklärung
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
modernvaluecorner – The site loads fast; navigation is intuitive and user-friendly.
https://modernvaluecorner.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everydayvaluefinds.shop – Clean design and easy browsing make shopping here fun.
https://everydayvaluefinds.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
stylemebetter – Will definitely shop here again; satisfied with my purchase.
https://stylemebetter.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
modernvisionlab.shop – Layout is intuitive; even new visitors won’t feel lost.
https://modernvisionlab.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Регионы РФ Самовывоз https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-weichai.html
Запчасти на спецтехнику https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-proizvoditeli-maz.html
Мы — команда, которая работает в ваших интересах https://alfatrakt.ru/polzovatelyam/kontaktnaya-informatsiya-alfatrakt.html
Менеджеры знают рынок, ориентируются в новинках и решают задачи любой сложности https://alfatrakt.ru/polzovatelyam/dostavka-i-oplata-alfatrakt.html
Ежедневно с 9:00 до 21:00 https://alfatrakt.ru/postavschikam/priglashenie-k-sotrudnichestvu.html
Удобный онлайн-склад https://alfatrakt.ru/polzovatelyam/kak-sdelat-zakaz-alfatrakt.html
Амортизаторы https://alfatrakt.ru/catalogs/zapasnye-chasti-tovarnye-gruppy-amortizatory.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dailyprofitupdate – Smooth checkout process; received my order on time.
https://dailyprofitupdate.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На сайте «Колёса Даром» просто совершать покупки: безналичная или наличная оплата, покупка в кредит, рассрочка, оплата от юрлица, возможна доставка до шинного центра, где шины поставят на автомобиль, а также доставка до подъезда или отдела транспортной компании https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_powertrac_ice_xpro_17570_r13_82s
Типоразмер https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_triangle_te301_22565_r17_102h
технологическая мойка колеса чистка и смазка ступицы герметизация борта колеса датчики давления и их установка крепежные болты, вентили, пакеты и другие расходные материалы https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_formula_energy_21565_r16_98h
Бесплатная доставка при покупке комплекта шин или дисков по всей России*
Не менее востребованный бренд на территории РФ — Maxxis https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_formula_energy_18565_r15_88t Азиатский производитель покорил российских водителей оптимальным соотношением качества и цены https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_hankook_kinergy_eco_2_k435_18560_r14_82h Покрышки спокойно ходят несколько сезонов без потери своих эксплуатационных и ездовых характеристик https://63kolesa.ru/products/legkovye_shiny_powertrac_ice_xpro_17570_r13_82s
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
livraison rapide et confidentielle [url=http://intimisante.com/#]п»їpharmacie en ligne france[/url] achat discret de Cialis 20mg
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Heya i am for the primary time here. I found this board and I to find
It really useful & it helped me out a lot. I am hoping to present one thing again and help others like you aided
me.
Here is my homepage: đọc truyện sex mới nhất
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
justvotenoon2 – Really enjoyed reading this, very helpful info for beginners here.
https://justvotenoon2.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
ПокерОК сайт
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successjourneyclub.shop – Definitely bookmarking; want to revisit when I have more time.
https://successjourneyclub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bestdealcorner – Helpful product descriptions and reviews, made decision-making easier today.
https://bestdealcorner.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
classytrendstore – This site has become my favorite for online fashion shopping.
https://classytrendstore.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartbuytoday – Helpful product descriptions and reviews, made decision-making easier today.
https://smartbuytoday.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
официальный сайт ПокерОК
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trafficpulse.click – I found several useful links already—definitely worth revisiting later.
https://trafficpulse.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
keywordorbit.click – Colour palette is subtle and pleasant, nice choice for long reading.
https://keywordorbit.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightmarketplace – Impressed with the packaging and timely delivery, will shop again.
https://brightmarketplace.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rankforge.click – The visual style complements the content nicely — very polished.
https://rankforge.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
webtide.click – Already bookmarked this site—it looks like a resource worth revisiting.
https://webtide.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
seoloom.click – I found a few useful links already; the navigation really helps you find things fast.
https://seoloom.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
ПокерОК сайт
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
livraison rapide et confidentielle: cialis generique – tadalafil sans ordonnance
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://pilloleverdi.shop/# farmacia online italiana Cialis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Не доверяйте монтаж «знакомому мастеру» — выбирайте из Топ 10 компаний по установке кондиционеров. Профессиональные компании по установке кондиционеров имеют страхование ответственности и работают по договору. Рейтинг компаний по установке кондиционеров учитывает скорость реагирования на поломки и качество ТО. Компании по продаже и установке кондиционеров с собственным call-центром — всегда на связи!
Полная информация по ссылке – https://vrf-montazh.ru/top-10-kompaniy-po-ustanovke-konditsionerov-2025/
тендеры монтаж систем вентиляции, монтаж vrv и vrf систем, монтаж кондиционера температура
монтаж вентиляции, [url=https://vrf-montazh.ru/montazh-ventilyatsii/]монтаж вентиляции в доме[/url], оренбург монтаж вентиляции
Удачи и хорошего климата!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafil tablets without prescription: affordable Cialis with fast delivery – discreet ED pills delivery in the US
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Так как конфиденциальность и защита данных являются ключевыми аспектами при взаимодействии с даркнет-маркетплейсами, выбор правильного канала доступа играет определяющую роль. Использование сомнительных источников чревато к краже аккаунта и финансовых средств, ввиду чего следует соблюдать максимальную бдительность. [url=https://101hrm.com/]даркнет кракен[/url] Используя данный линк, вы получаете стопроцентный доступ к полному функционалу платформы, в том числе рейтинги продавцов и круглосуточную техническую помощь. Этот способ позволяет полностью нивелировать риск перехода на поддельный ресурс и обеспечивает максимальную степень анонимности во время проведения любых операций.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[url=https://vk.com/nakrutkapfonline]накрутка пф яндекс![/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Монтаж кондиционеров дома — с минимальным шумом и пылью. Стоимость монтажа кондиционера фиксируется в договоре. Гарантия — 3 года. Бесплатный выезд.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://vrf-montazh.ru/top-10-kompaniy-po-ustanovke-vrf-2025/
монтаж кондиционеров пример сметы, компании по установке вентиляции, монтаж соединение вентиляции
компании по продаже и установки VRV и VRF, [url=https://vrf-montazh.ru/top-10-kompaniy-po-ustanovke-ventilyatsii-2025/]компании по установке вентиляции и ремонту[/url], инструкция монтажа вентиляции
Удачи и хорошего климата!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
walgreens online pharmacy <a href=" http://km10805.keymachine.de/php.php?a%5B%5D=can+you+buy+viagra+online “>legit online pharmacy and mail order pharmacy precription drugs from canada
https://www.google.cf/url?sa=t&url=https://zencaremeds.shop online pharmacy price checker or http://mbuild.store/user/adyhzsgeeg/?um_action=edit pharmacies in canada that ship to the us
[url=https://www.pfizer.es/redirect.aspx?uri=http://pharmalibrefrance.com/]canadian pharmacy generic cialis[/url] ordering drugs from canada and [url=http://www.1gmoli.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=213019]pharmacy coupons[/url] online otc pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildlastingties.bond – The site gives me a vibe of real community bonding.
https://buildlastingties.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustedbusinesslink.shop – Looks like a decent place to connect with reliable business services.
https://trustedbusinesslink.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
modernchoice.store – I like how clean the design is, space makes browsing relaxing.
https://modernchoice.store/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightfuturegroup.bond – Already sharing with friends — this has serious potential.
https://brightfuturegroup.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalpartnershipteam.bond – Definitely recommending this to people interested in meaningful collaborations.
https://globalpartnershipteam.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
clicksignal.click – I found useful links quickly, categories are well organized indeed.
https://clicksignal.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pagevector.click – Just visited, the layout feels clean and content is welcoming to read.
https://pagevector.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rankmotion.click – Already bookmarked this — seems like a site I’ll revisit.
https://rankmotion.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartstylehub.shop – I bookmarked several items, will come back for them.
https://smartstylehub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis [url=https://tadalifepharmacy.shop/#]tadalafil tablets without prescription[/url] safe online pharmacy for Cialis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
seoanchor.click – Typography is comfortable and spacing feels well thought out.
https://seoanchor.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
netfusion.click – The visuals support the content nicely, not distracting at all.
https://netfusion.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Продувают окна? регулировка окон пвх – устранение продуваний, настройка фурнитуры, ремонт и обслуживание. Опытные мастера, выезд в день обращения, гарантия на все виды работ.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustandunity.shop – Images are quality, site feels polished — positive first impression.
https://trustandunity.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findnewtrend.shop – Love the vibe here—very up-to-date and stylish items.
https://findnewtrend.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildlastingtrust.bond – Design is clean, message is clear — feels very sincere.
https://buildlastingtrust.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dailyvaluehub.shop – It’s refreshing to see so many useful items in one place.
https://dailyvaluehub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
startsomethingnew.shop – The site’s vibe motivates me to try something different.
https://startsomethingnew.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мастер на час в Москве https://masternadom24.ru быстрое решение бытовых проблем. Мелкий ремонт, установка, сборка и подключение техники. Пунктуальность, качество и удобный вызов мастера.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspiredgrowthteam.shop – Found something that really resonated with me, good find!
https://inspiredgrowthteam.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendfinder.bond – My go-to place whenever I want to spot new trends fast.
https://trendfinder.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Robot Vacuum Cleaner With Mop: The Intermediate Guide
Towards Robot Vacuum Cleaner With Mop robot vacuum cleaner With mop
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildbrand.online – Nice visuals and good layout — makes learning branding fun.
https://buildbrand.online/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnonline.bond – Smooth checkout, no hiccups while signing up for a class.
https://learnonline.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
All purchasers need to comprehend that communication viagra effects on heart port fifty three is blocked,
except it is addressed to our DNS server. You don’t want one
other Buzzfeed quiz.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
creativegiftzone.shop – Nice themes and seasonal items — exactly what I was hoping to see.
https://creativegiftzone.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Слив курсов подготовки ЕГЭ профильная математика https://courses-ege.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartdesigncorner.space – Great job balancing visuals and content—doesn’t feel overwhelming.
https://smartdesigncorner.space/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online sport wetten
Feel free to surf to my web-site: Wettseiten Vergleich
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspiredmind.shop – Products look thoughtful and original, just what I was hoping for.
dt13.internetmarketingforum.biz:777
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rankmotion.click – Just browsed it, layout’s smooth and everything’s easy to follow.
https://rankmotion.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pagevector.click – Overall experience is positive, feels like a solid, trustworthy site.
https://pagevector.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
netfusion.click – The color scheme feels subtle and comfortable for long reading.
https://netfusion.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
clicksignal.click – I just browsed this site, the layout feels very modern and friendly.
https://clicksignal.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
seoanchor.click – Overall the experience is pleasant and the site feels trustworthy.
https://seoanchor.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustinyou.bond – The message here feels very empowering and personal, I like that.
https://trustinyou.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopwithpurpose.shop – Really love how the value-driven mission shines through every product.
https://shopwithpurpose.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalunity.bond – Found several parts inspiring; feels like a community I’d like to join.
https://globalunity.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
partnershippowerhouse.shop – I like how they showcase joint value and mutual growth.
https://partnershippowerhouse.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительство складов https://velestent.ru и ангаров в Москве под ключ. Быстровозводимые конструкции, металлокаркасы, проектирование и монтаж. Качество, надёжность и соблюдение сроков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexico pharmacy: farmacia pharmacy mexico – mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
order medicine discreetly USA: ZenCareMeds – online pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://tadalifepharmacy.com/# trusted online pharmacy for ED meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten online
Also visit my web page Wettseite Eröffnen (https://Holidaydeal.ae)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartpartnership.bond – Good synergy, feels like collaboration is central to their mission always.
https://smartpartnership.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Бюро переводов юридических данных выполняет переводы договоров и контрактов. Бюро переводов экономических документов помогает с бухгалтерской и финансовой отчетностью. Бюро переводов для компаний обеспечивает комплексный подход к бизнес-заказам. Бюро переводов для иностранных организаций выполняет легализацию документов. Бюро переводов для студентов переводит учебные материалы и справки.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://byuro-perevodov1.ru/
бюро переводов, бюро переводов для студентов, бюро переводов для частных клиентов
бюро переводов для студентов, [url=https://byuro-perevodov1.ru/]где заказать перевод для бизнеса[/url], переводчик для научных статей
Удачи и хорошего перевода!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Переводы документов срочно выполняются в день обращения. Купить перевод диплома онлайн можно с нотариальным заверением. Заказать перевод книги легко через бюро переводов с профессионалами. Перевод медицинских документов срочно выполняется опытными специалистами. Где заказать перевод для бизнеса — в нашем бюро переводов.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://byuro-perevodov1.ru/
перевод документов для наследства, бюро переводов для обучения, нотариус бюро переводов
бюро переводов с нотариальным заверением, [url=https://byuro-perevodov1.ru/]бюро переводов заказать перевод по нотариусу[/url], бюро переводов юридических данных
Удачи и хорошего перевода!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Заказать перевод в бюро переводов быстро и удобно для всех клиентов. Бюро переводов с выездом приезжает к клиенту для оформления документов. Перевод документов дешево предлагает бюро переводов недорого и качественно. Бюро переводов с недвижимостью выполняет переводы договоров купли-продажи. Бюро переводов с иностранными языками работает с более чем 50 направлениями.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://byuro-perevodov1.ru/
ближайший бюро переводов, бюро переводов недорого, бюро переводов с гибкими тарифами
переводчик для обучения, [url=https://byuro-perevodov1.ru/]бюро переводов для бизнеса[/url], бюро переводов срочно и недорого
Удачи и хорошего перевода!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
порно онлайн
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
websummit.click – Already bookmarked this — I think I’ll return often here.
https://asfjkbsdvb.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
searchnest.click – Already bookmarked this—seems like a site worth revisiting.
https://adsfjbsivfcvos.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ranktrail.click – I like the way content is structured—sections flow naturally.
https://asfkksvbdskmnsd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ranktrail.click – Typography and spacing are well balanced, easy on the eyes.
https://asklhsgdvsd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boostcraft.click – The layout feels balanced, nothing feels out of place.
https://asfdjkbsvdsk.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Mikigaming merupakan salah satu situs taruhan online
yang sangat terkenal, yang menyediakan berbagai macam
pilihan permainan Slot Gacor Online.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
e sport wetten
Also visit my homepage … sportwetten Vorhersage
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
affordable online pharmacy for Americans [url=http://zencaremeds.com/#]buy Doxycycline[/url] affordable online pharmacy for Americans
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Squad variety became achievable once I discovered how to buy fifa coins efficiently for multiple formations. Active sellers with real account protection provide fast delivery and non drop guarantees across different league requirements.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacy mexico mexico pet pharmacy or can i order online from a mexican pharmacy mexico city pharmacy
http://wiki.wlug.org.nz/~matt/m.php?a%5B%5D=%3Ca%20href%3Dhttp%3A%2F%2Fbluepharmafrance.com%2F%3E%C3%91%C5%8D%C3%90%C2%BB%C3%90%C2%B5%C3%90%C2%BA%C3%91%E2%80%9A%C3%91%E2%82%AC%C3%90%C2%BE%C3%91%81%C3%90%C2%BD%C3%90%C2%B0%C3%90%C2%B1%C3%90%C2%B6%C3%90%C2%B5%C3%90%C2%BD%C3%90%C2%B8%C3%90%C2%B5%20%C3%91%83%C3%91%E2%80%A1%C3%90%C2%B0%C3%91%81%C3%91%E2%80%9A%C3%90%C2%BA%C3%90%C2%B0%20%C3%91%E2%80%A0%C3%90%C2%B5%C3%91%E2%80%A6%C3%90%C2%B0%20%C3%90%C2%B4%C3%90%C2%B8%C3%90%C2%BF%C3%90%C2%BB%C3%90%C2%BE%C3%90%C2%BC%3C%2Fa%3E mexico farmacia or http://asresin.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=168057 pharmacy in mexico that ships to us
[url=http://images.google.sr/url?q=https://medicosur.com]purple pharmacy online ordering[/url] online mexican pharmacy and [url=https://virtualchemicalsales.ca/user/ecfcwztzmy/?um_action=edit]mexico pharmacy price list[/url] farmacia online usa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hi colleagues, how is all, and what you want to say about this piece of writing, in my view its really remarkable
in support of me.
Here is my blog :: deutsche online casinos
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить справку о болезни
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ranktrail.click – Just browsed this, layout’s clean and the UI feels quite intuitive.
https://asfkksvbdskmnsd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
websummit.click – The visuals are crisp, and pages load fast without hesitation.
https://asfjkbsdvb.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ranktrail.click – Visually the site feels polished and thoughtfully designed.
https://asklhsgdvsd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
searchnest.click – The typography is clean and comfortable for reading long posts.
https://adsfjbsivfcvos.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boostcraft.click – Overall experience positive and inviting — I’ll be visiting again.
https://asfdjkbsvdsk.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
порно анал
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growthnetwork – Good balance of inspiration and practical advice, very well done.
https://growthnetwork.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
best canadian pharmacy for viagra: discount pharmacy mexico – buy propecia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
innovateandbuild – Looking forward to what’s next, potential is very strong.
https://innovateandbuild.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildtogether – Content is helpful and practical, not just buzzwords — very appreciated.
https://buildtogether.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://tadalifepharmacy.com/# affordable Cialis with fast delivery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growtogetheralliance – Always learning something new here, variety keeps it interesting.
https://growtogetheralliance.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
affordable Cialis with fast delivery: safe online pharmacy for Cialis – buy cialis online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightdeal – The images support the message nicely, clean aesthetic.
https://brightdeal.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Перевод документов для наследства осуществляется с нотариусом и гарантией. Перевод документов для учебы готовится быстро и официально. Бюро переводов для обучения выполняет переводы учебных материалов и дипломов. Бюро переводов для карьеры помогает с переводом резюме и рекомендаций. Бюро переводов для иммиграции готовит документы для ПМЖ и виз.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://byuro-perevodov1.ru/
услуги по нотариальному заверению, переводы документов срочно, бюро переводо онлайн заказ
бюро переводов, [url=https://byuro-perevodov1.ru/]бюро переводов для иностранцев[/url], переводчик с нотариальным заверением
Удачи и хорошего перевода!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectinnovationhub – Everything loads smoothly, zero clutter — great user experience.
https://connectinnovationhub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s up colleagues, nice post and pleasant urging commented here, I am in fact enjoying by
these.
Stop by my website Pink Salt Trick
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Монтаж VRF систем — это когда вы забываете о климате, потому что он идеален. Мы используем только проверенные технологии и материалы. Монтаж кондиционирования VRF включает настройку по зонам и графикам. Стоимость монтажа VRF систем включает вакуумирование, заправку и пусконаладку. Гарантия — до 5 лет. Работаем с юрлицами и физлицами. Бесплатный выезд инженера.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://vrf-montazh.ru/top-10-kompaniy-po-ustanovke-vrf-2025/
монтаж системы противопожарной вентиляции, монтаж вентиляции в частном доме своими руками, монтажа кондиционера самому
монтаж вентиляции и кондиционирования, [url=https://vrf-montazh.ru/top-10-kompaniy-po-ustanovke-vrf-2025/]рейтинг компаний по установке VRV и VRF[/url], кондиционер монтаж щелково
Удачи и хорошего климата!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
exploreideasworld – The content feels imaginative, full of possibility and creativity.
https://exploreideasworld.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
leadersunitedgroup – I’ve bookmarked several pages, looks like a resource worth revisiting.
https://leadersunitedgroup.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
best online pharmacy no prescription tops pharmacy or pharmacy discount card humana online pharmacy
http://air-hose-reel-fitting.com/info.php?a%5B%5D=cialis+online international pharmacy no prescription and https://armandohart.com/user/jocszofptv/?um_action=edit pharmacy website
[url=http://www.infoanda.com/viewcomments.php?li=pharmaexpressfrance.com]script pharmacy[/url] promo code for canadian pharmacy meds or [url=http://umsr.fgpzq.online/home.php?mod=space&uid=142151]safe canadian pharmacy[/url] cheapest pharmacy for prescriptions
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findtrendystuff – Images and product layout are clean and well thought.
https://findtrendystuff.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoverdaily – I’ve bookmarked several posts, they keep surprising me.
https://discoverdaily.online/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalpartnershipteam – I found helpful content quickly, no fluff, straight to the point.
https://globalpartnershipteam.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discovervalue</a – I’m bookmarking this site, feels like long-term resource territory.
https://discovervalue.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successjourneyclub – Great balance between inspiration and actionable steps, love that.
https://successjourneyclub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
futuregoalsnetwork – I feel motivated every time I visit — powerful ideas.
198.23.198.125
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findsomethingnew – Content here is fresh and vibrant, keeps me coming back.
https://findsomethingnew.online/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
winmore – Already bookmarking several sections, there’s depth here.
https://winmore.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectinnovationhub – The ideas here feel fresh, this is a creative space indeed.
https://connectinnovationhub.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
leadersunitedgroup – Really like the leadership-focus here, feels inspiring every time.
https://leadersunitedgroup.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://moveiscardeal.com.br/o-que-voce-precisa-saber-antes-de-fazer-o-orcamento-dos-bancos-para-sua-igreja/
https://successpathway.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sitepilot.click – On mobile it’s flawless, everything adapts beautifully to smaller screens.
https://asfjkbsdvb.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
netvortex.click – Already saved in my bookmarks, this seems like a useful resource.
https://asklhsgdvsd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
keywordfuel.click – Already bookmarked — this looks like a solid resource to revisit.
https://asfdjkbsvdsk.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trafficcraft.click – This site has a really smooth feel, I enjoyed browsing around.
https://adsfjbsivfcvos.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pagepilot.click – Content layout is well structured, helps guide the eyes smoothly.
https://asfkksvbdskmnsd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacy express best online pharmacy reddit and online pharmacy pain drugs from canada
https://www.google.com.ai/url?q=https://zencaremeds.shop canadian pharmacies compare or http://umsr.fgpzq.online/home.php?mod=space&uid=142203 reliable canadian pharmacy reviews
[url=https://www.google.mn/url?q=https://zencaremeds.shop]mexican pharmacies online drugs[/url] canada pharmacy 24h and [url=https://www.bsnconnect.co.uk/profile/gprtofgxoi/]canadianpharmacymeds com[/url] discount pharmacy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
getthedeal – Prices are super low, I shared this with friends.
https://getthedeal.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successbridge – Great structure, easy to follow what to do next.
https://successbridge.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Бюро переводов экономических документов выполняет переводы бухгалтерской и финансовой отчетности. Бюро переводов для компаний предлагает комплексные решения для бизнеса. Бюро переводов для иностранных организаций обеспечивает легализацию документов. Бюро переводов для студентов помогает с переводами учебных материалов. Бюро переводов с консультацией помогает выбрать правильный формат перевода.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://byuro-perevodov1.ru/
перевод договоров, бюро переводов купить документы срочно, бюро переводов документов для нотариального заверения купить
бюро переводов с рейтингом, [url=https://byuro-perevodov1.ru/]переводчик и переводчик для туристов цена[/url], бюро переводов недорого
Удачи и хорошего перевода!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
futuregoalsnetwork – I’ve bookmarked this, it seems like a long-term resource.
https://futuregoalsnetwork.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
digitalinnovationzone – Nice job balancing creativity and usefulness, this is solid.
https://digitalinnovationzone.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustandunity – Already feel connected, even though it’s just my first few visits.
https://trustandunity.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
businessgrowthhub – I find fresh business ideas each time I explore this.
https://businessgrowthhub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online pharmacy [url=https://zencaremeds.com/#]ZenCare Meds com[/url] affordable online pharmacy for Americans
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Монтаж VRF — это доверие. Мы работаем с 2010 года и реализовали более 1200 проектов. Монтаж VRF систем кондиционирования включает настройку по паспорту производителя и тестирование в экстремальных режимах. Стоимость монтажа VRF систем остаётся неизменной в течение всего срока работ. Гарантия — до 5 лет. Бесплатный выезд инженера в пределах города.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://vrf-montazh.ru/montazh-konditsionerov/
калькулятор стоимости монтажа кондиционеров, рейтинг компаний по установке VRV и VRF, монтаж кондиционера челны
Топ 10 компаний по установке вентиляции, [url=https://vrf-montazh.ru/montazh-ventilyatsii/]монтаж вентиляции в частном доме своими руками[/url], фото монтажа кондиционеров
Удачи и хорошего климата!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wagocjapmeom – The site feels mysterious, layout hints at deeper content waiting.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy amoxil: online pharmacy – trusted online pharmacy USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wagocjapmeom – The site feels mysterious, layout hints at deeper content waiting.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
futureopportunitynetwork – The layout is crisp and clear, makes exploring effortless.
https://futureopportunitynetwork.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лестницы в Москве https://лестницы-в-москве.рф продажа и изготовление под заказ. Прямые, винтовые, модульные и чердачные конструкции. Качество, гарантия и монтаж по всем стандартам.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Деревянные лестницы https://rosslestnica.ru под заказ в любом стиле. Прямые, винтовые, маршевые конструкции из массива. Замеры, 3D-проект, доставка и установка. Гарантия качества и точности исполнения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growthpoint – The site has a sharp professional look, very trustworthy impression.
https://growthpoint.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://medicosur.shop/# mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
affordable Cialis with fast delivery: TadaLife Pharmacy – trusted online pharmacy for ED meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten kombiwetten tipps
Feel free to surf to my website Wir Wetten Bonus Code
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rankshift.click – The content feels well organized, nicely divided into readable parts.
https://asklhsgdvsd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
happylifestylehub – The vibe is so positive, feels like a calm retreat.
https://happylifestylehub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
linkhorizon.click – The color scheme is pleasing, doesn’t overwhelm the page at all.
https://asfjkbsdvb.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
netlaunch.click – This site gives a trustworthy impression; glad I checked it out.
https://asfdjkbsvdsk.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growmetric.click – The content seems solid and the visuals support it nicely.
https://adsfjbsivfcvos.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnsharegrow – They deliver value without overcomplicating things, I appreciate that.
https://learnsharegrow.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
futurevisiongroup – Good balance between visuals and content, nothing overwhelming.
https://futurevisiongroup.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://online-spr2.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growstrongteam – Everything loads fast, layout is smooth and easy to use.
https://growstrongteam.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Рейтинг компаний по установке кондиционеров помогает избежать ошибок при выборе подрядчика. В Топ 10 компаний по установке кондиционеров входят фирмы с минимальным количеством рекламаций и максимальной скоростью реагирования. Надёжные компании по установке кондиционеров используют медь высшего сорта, изоляцию Armaflex и вакуумные насосы. Компании по продаже и установке кондиционеров с онлайн-калькулятором и фиксированными ценами — залог прозрачного сотрудничества.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://vrf-montazh.ru/
монтаж дренажа кондиционера кассетного, компании по продаже и установки VRV и VRF, монтаж кондиционера севастополе
монтаж кондиционеров прайс, [url=https://vrf-montazh.ru/top-10-kompaniy-po-ustanovke-konditsionerov-2025/]рейтинг компаний по установке кондиционеров[/url], монтаж оцинкованной вентиляции
Удачи и хорошего климата!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
seoignite.click – The content is clear and the layout keeps everything organized nicely.
https://asfkksvbdskmnsd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
futureopportunitynetwork – The content is engaging and relevant, keeping me informed.
https://futureopportunitynetwork.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
strategicgrowthalliance – The content is well-organized, enhancing the user experience.
https://strategicgrowthalliance.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustedbusinesslink – Easy-to-use interface, makes me feel confident about using their services.
https://trustedbusinesslink.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trustconnectionnetwork – Easy navigation and detailed product descriptions aid in informed decisions.
https://trustconnectionnetwork.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
uniquefashionstyle – Love how the clean layout lets the products shine.
https://uniquefashionstyle.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextvision – Always best to verify such sites carefully before engaging or sharing data.
https://nextvision.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Турецкие сериалы https://prokazan.ru/adverting/view/tureckie-serialy-v-rossii-kak-vostocnaa-drama-pokorila-serdca-zritelej смотреть онлайн бесплатно — все сезоны и серии в HD. Любимые актёры, захватывающие сюжеты и новые премьеры с переводом. Без регистрации и рекламы!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findyourfuture – The homepage caught my eye, looks promising and well structured.
https://findyourfuture.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Монтаж кондиционеров дома — с возможностью скрытой прокладки. Стоимость монтажа кондиционера рассчитывается бесплатно. Гарантия — 3 года.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://vrf-montazh.ru/
монтаж кондиционеров сервис, компании по установке кондиционеров, напольный кондиционер монтаж
рейтинг компаний по установке кондиционеров, [url=https://vrf-montazh.ru/montazh-konditsionerov/]монтаж кондиционеров ключ[/url], отзывы о монтаже кондиционеров
Удачи и хорошего климата!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Любишь складчины? складчик официальный сайт вход в личный. Управляйте своими покупками, подписками и профилем. Доступ ко всем материалам и обновлениям в один клик.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Изготовление флагов https://flagman-com.ru на заказ — корпоративные, государственные, спортивные и рекламные флаги. Печать любой сложности, качественные материалы, быстрая доставка.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ohne oasis sportwetten
my web page: esc wettquoten deutschland
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
alle wettseiten
Also visit my homepage … Asiatische Wettanbieter (http://Www.Jurgenvandervelde.Com)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discovernewpath – Checkout seems hassle-free, appreciated that straightforward process.
https://discovernewpath.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trusted online pharmacy USA [url=http://zencaremeds.com/#]order medicine discreetly USA[/url] trusted online pharmacy USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В условиях частых блокировок со стороны государственных регуляторов, стабильный доступ к таким востребованным ресурсам, как Кракен может быть серьезно осложнен. В связи с этим первостепенное значение приобретает умение находить проверенные и рабочие альтернативные методы доступа, чтобы сохранить связь с площадкой. [url=https://botanicadelamor.com/]тор кракен[/url] Перейдя по этому адресу, вы получаете стопроцентный вход к полному функционалу платформы, в том числе рейтинги продавцов и оперативную службу поддержки. Данный метод дает возможность полностью нивелировать вероятность перехода на мошеннический сайт и обеспечивает высочайшую степень анонимности при совершении всех сделок.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
gratiswette ohne einzahlung sportwetten
My blog; wetten com erfahrung
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tijuana pharmacy online worldwide pharmacy and mexico farmacia purple pharmacy online
https://images.google.gp/url?sa=t&url=https://medicosur.com purple pharmacy or http://www.88moli.top/home.php?mod=space&uid=1656 mexican pharmacies that ship to the united states
[url=https://www.google.bj/url?q=https://medicosur.com]mexican pharmacies that ship to us[/url] mexico rx or [url=http://156.226.17.6/home.php?mod=space&uid=1331751]phentermine in mexico pharmacy[/url] mexican pharmacy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy amoxil: affordable online pharmacy for Americans – buy propecia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
onlinecanadianpharmacy 24: best online foreign pharmacies – buy propecia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://medicosur.shop/# pharmacy mexico online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wettseite eröffnen
my web site … wettquote erklärt (http://Www.Tickethuddle.Com)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
partnershippowerhouse – The branding feels strong and authentic, very trustworthy presence online.
https://partnershippowerhouse.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
visionaryleadersclub – Definitely keeping this in mind when I think leadership or vision related.
https://visionaryleadersclub.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
formative-coffee.com – Bookmarking this for when I want to explore premium coffee options.
https://formative-coffee.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextgeninnovation – I like how minimal yet powerful this site looks and works.
https://nextgeninnovation.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Администрация платформы Kraken официально советует клиентам системы использовать исключительно официальные каналы для поиска рабочих ссылок для входа. Данная мера служит основной гарантией безопасности вашего аккаунта и совершаемых операций внутри платформы Кракен. [url=https://www.dravidianuniversity.ac.in/]кракен сайт что это[/url] Именно представленный здесь линк является официально рекомендованный шлюз, который не только гарантирует стабильное соединение с серверами маркетплейса, но и полностью оберегает ваши персональные данные от многочисленных попыток кражи аккаунта. Рекомендуется сохранить этот адрес, чтобы в будущем избежать потенциально опасных поисков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rockyrose.org – The articles here are thoughtful, I read with interest.
https://rockyrose.org/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ukrainianvictoryisthebestaward.com – If you were expecting content about awards, this isn’t delivering that now.
https://ukrainianvictoryisthebestaward.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pinellasehe.org – Visiting felt like discovering a calm, thoughtful space online.
https://pinellasehe.org/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Great delivery. Great arguments. Keep up the amazing spirit.
Feel free to surf to my blog post Web Site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growyourdigitalpresence – Even small changes suggested here bring noticeable impact over time.
https://growyourdigitalpresence.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
summerstageinharlem.org – Free music events like this make city life feel so richer.
https://summerstageinharlem.org/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
luxurytrendstore – Checkout process was quick and hassle-free, very user-friendly.
https://luxurytrendstore.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspiredgrowthteam – I appreciate sites that respect simplicity but deliver impact.
https://inspiredgrowthteam.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
foreign online pharmacy cyprus online pharmacy or pharmacy near me best canadian pharmacy for viagra
https://islamcenter.ru/go.php?url=https://zencaremeds.com pharmacy website india or https://www.ipixels.com/profile/172046/vtlndgjoev mexican pharmacies online drugs
[url=https://maps.google.com.gi/url?q=https://zencaremeds.com]canadian pharmacy ratings[/url] no prescription required pharmacy or [url=http://orbita-3.ru/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=37368]reputable indian pharmacies[/url] legit non prescription pharmacies
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
createimpact – Definitely a site I’ll revisit when I need motivation or ideas.
https://createimpact.online/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
doppelte chance kombiwette
My blog post; wettanbieter Bonus vergleich
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discovernewideas – So many cool ideas packed in, I’m excited to explore more.
https://discovernewideas.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Рейтинг лучших подоконников https://luchshie-podokonniki-iz-kamnya.ru из искусственного камня в Москве. Сравнение брендов, цены, фото и отзывы. Узнайте, какой подоконник выбрать — прочный, стильный и долговечный вариант для вашего интерьера.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-спортивный http://sportsat.ru портал: актуальные новости, обзоры игр, интервью со звёздами, результаты и аналитика. Следите за событиями в мире спорта каждый день!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cryptotephra-clagr.com – I saw their Twitter “Cryptotephra Lab-CLAGR” account. :contentReference[oaicite:0]index=0
https://cryptotephra-clagr.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
medical mall pharmacy pharmaceutical online ordering and canadian pharmacy online reviews online pharmacy indonesia
https://image.google.dz/url?q=https://zencaremeds.shop mail order prescription drugs from canada and https://virtualchemicalsales.ca/user/sesghyyvhh/?um_action=edit austria pharmacy online
[url=http://images.google.gm/url?q=https://zencaremeds.shop]save on pharmacy[/url] best mail order pharmacy canada or [url=http://www.donggoudi.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3736292]canadian pharmacy without prescription[/url] reliable canadian online pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalideasnetwork – Browsing here feels smooth, no lag and clear navigation.
https://globalideasnetwork.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
norigamihq – Interesting domain name, curious what this site offers.
https://norigamihq.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
laetly.com – The branding is bold, makes me want to see the catalog.
https://laetly.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thespeakeasybuffalo – I noticed “Nothing found” currently; hope content fills soon.
https://thespeakeasybuffalo.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
electlarryarata – Bookmarking this; I’ll revisit when content is live.
https://electlarryarata.org/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
myvetcoach.org – The layout is neat, navigation is intuitive and smooth.
https://myvetcoach.org/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
stacoa.org – I browsed a bit and found useful information already.
https://stacoa.org/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
filamericansforracialaction.com – Good to see WordPress used, content seems accessible and organized.
https://filamericansforracialaction.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кракен маркетплейс в телеграмме
Фраза кракен телеграм маркетплейс отражает интерес к торговой части ресурса. Настоящий кракен телеграм маркетплейс помогает быстро находить рабочие магазины, обсуждать их качество и делиться отзывами. Люди доверяют этому инструменту, потому что кракен телеграм маркетплейс исключает риск подделки.
Основные ссылки:
кракен даркнет тор — k-market.ccофициальная рабочая ссылка kraken — kmarket.cc
KRAKEN™ 2025 — кракен маркет тор
Кракен современный маркетплейс для покупок Магазин в Тор сети Рабочая ссылка на маркет Kraken в Тор
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendyfashioncorner – Checkout process was quick and hassle-free, very user-friendly.
https://trendyfashioncorner.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successpartnersgroup – Their team clearly knows how to deliver top-notch experiences online.
https://successpartnersgroup.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
clickoptim.click – This site loads fast for me, no annoying delays so far.
https://asklhsgdvsd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brandlift.click – Found something useful here already; glad I stopped by today.
https://asfjkbsdvb.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
creativevision – Truly inspiring work that challenges traditional artistic perspectives.
https://creativevision.bond/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafil tablets without prescription: tadalafil tablets without prescription – generic Cialis online pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
webrevive.click – I like the balance of whitespace and content, feels neither crowded nor sparse.
https://asfdjkbsvdsk.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boostengine.click – I like how the images and text balance without being overwhelming.
https://adsfjbsivfcvos.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online pharmacy [url=https://zencaremeds.com/#]safe online medication store[/url] ZenCareMeds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mystylecorner – The collection is solid, wide styles and great variety.
https://mystylecorner.shop/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Поскольку безопасность и анонимность выступают ключевыми приоритетами при работе с даркнет-маркетплейсами, поиск надежного канала доступа играет определяющую роль. Применение непроверенных источников может привести к краже аккаунта и финансовых средств, ввиду чего необходимо проявлять максимальную осторожность. [url=https://diproansa.com/]kraken tor[/url] Данный сайт служит в роли постоянно обновляемого агрегатора актуальных зеркал, позволяя любому пользователю в любой момент найти рабочий адрес на маркетплейс Кракен. Сохранив эту страницу, вы навсегда избавите себя от необходимости искать зеркала на сомнительных форумах, рискуя своей безопасностью.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить справку
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
canadian pharmacy review: affordable online pharmacy for Americans – ZenCare Meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://zencaremeds.com/# affordable online pharmacy for Americans
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Информационный блог https://gidroekoproekt.ru для инженеров и проектировщиков. Всё об инженерных изысканиях, водохозяйственных объектах, гидротехническом строительстве и современных технологиях в отрасли.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ваша Недвижимость https://rbn-khv.ru сайт о покупке, продаже и аренде жилья. Разбираем сделки, налоги, ипотеку и инвестиции. Полезная информация для владельцев и покупателей недвижимости.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sportwetten In Der NäHe live ergebnisse
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Купольные дома https://kupol-doma.ru под ключ — энергоэффективные, надёжные и современные. Проектирование, строительство и отделка. Уникальная архитектура, комфорт и долговечность в каждом доме.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Риэлторская контора https://daber27.ru покупка, продажа и аренда недвижимости. Помогаем оформить сделки безопасно и выгодно. Опытные риэлторы, консультации, сопровождение и проверка документов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Тысячи клиентов постоянно ищут надежный и проверенный способ для доступа на торговую площадку Kraken, встречаясь с множеством фейковых ресурсов и устаревшей информацией. Чтобы минимизировать эти риски и сохранить ваше время, существует простое и эффективное место для поиска. [url=https://worldclasslearning.com/]kraken onion[/url] Только данный официальный источник обеспечивает вам прямое попадание на оригинальный сервер Kraken, в обход любые промежуточные звенья и потенциальные угрозы. Это считается единственно верным способом для тех, кто ценит собственную анонимность и желает иметь полную уверенность в защите личного аккаунта и средств на нем.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
createimpactfulstories – Beautifully written, this site encourages me to keep creating.
https://createimpactfulstories.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
staycuriousandcreative – Such a fresh perspective on blending curiosity with creativity.
https://staycuriousandcreative.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
die buchmacher
Feel free to visit my blog Sportwette Ohne oasis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В условиях регулярных блокировок со стороны государственных регуляторов, стабильный доступ к таким востребованным ресурсам, как Кракен может быть серьезно осложнен. Именно поэтому первостепенное значение приобретает умение находить актуальные и безопасные способы обхода ограничений, чтобы сохранить связь с площадкой. [url=https://ai-translation-services.com/]рабочая ссылка на кракен[/url] Именно этот проверенный канал гарантирует пользователю прямое попадание на настоящий сайт Kraken, в обход любые посредников и скрытые опасности. Такой подход является единственно верным решением для всех, кто дорожит свою безопасность и желает быть уверенным в сохранности личного аккаунта и баланса на нем.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
TadaLife Pharmacy: cialis – discreet ED pills delivery in the US
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourjourneytowin – Simple but powerful content, it hit me where it matters.
https://yourjourneytowin.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Площадка Кракен
Фраза кракен зеркало сегодня интересует тех, кто хочет войти прямо сейчас. Настоящее кракен зеркало сегодня всегда заканчивается на .onion и дублируется в Telegram. Пользователи проверяют его подлинность и делятся отзывами.
Основные ссылки:
официальный кракен маркетплейс тор — krakenc.ccрабочая ссылка kraken в телеграмме — kmarket.cc
KRAKEN™ 2025 — кракен зайти зеркало
Сайт интернет магазина в Тор браузере Сайты магазинов в сети Тор Официальная ссылка на маркет Кракен в Тор браузере
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discreet ED pills delivery in the US [url=https://tadalifepharmacy.shop/#]Cialis online USA[/url] trusted online pharmacy for ED meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
startyourdigitaljourney – I love how user-friendly the interface is for beginners.
https://startyourdigitaljourney.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
theartofsuccess – This site is a gem for anyone chasing their purpose.
https://theartofsuccess.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspireeverymoment – Every post feels like a little boost to my day.
https://inspireeverymoment.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thefuturestartsnow – Love the vision here, really makes me look forward to tomorrow.
https://thefuturestartsnow.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnnewthingsdaily – Every post leaves me thinking and experimenting with new ideas.
https://learnnewthingsdaily.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discovergreatideas – The articles here are a catalyst for creative breakthroughs.
https://discovergreatideas.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis: affordable Cialis with fast delivery – generic Cialis online pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growtogetherwithus – Very uplifting content, makes me want to improve myself daily.
https://growtogetherwithus.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shareyourvisiontoday – Great mix of inspiration and practical advice for visionaries.
https://shareyourvisiontoday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://zencaremeds.shop/# online pharmacy bc
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wettanbieter mit sitz in deutschland
Also visit my website … live wetten Online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspireeverymoment – Feeling energized and hopeful after spending time here.
https://startsomethingamazingtoday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный портал https://v-stroit.ru всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Полезные советы, технологии, материалы, новости отрасли и практические инструкции для мастеров и новичков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
deutsche online wettanbieter
Here is my web-site – wett Tipps-Heute
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал о строительстве https://pamel-stroy.ru и ремонте. Пошаговые инструкции, идеи, технологии, новости и советы экспертов. Всё, что нужно, чтобы строить и ремонтировать грамотно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Хочешь пиццу? https://tula.pizzeriacuba.ru быстро, вкусно и горячо! Заказывайте пиццу с доставкой на дом или в офис. Большой выбор начинок, свежие ингредиенты, акции и бесплатная доставка по городу.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://tadalifepharmacy.com/# Cialis online USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexican pharmacy [url=http://medicosur.com/#]MedicoSur[/url] MedicoSur
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online pharmacy: buy Doxycycline – order medicine discreetly USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
eurovision buchmacher
Also visit my blog post: öSterreichische Wettanbieter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://medicosur.com/# mexican online pharmacy wegovy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Аутстаффинг персонала https://skillstaff2.ru для бизнеса: легальное оформление сотрудников, снижение налоговой нагрузки и оптимизация расходов. Работаем с компаниями любого масштаба и отрасли.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужна недвижимость? Черногория купить недвижимость лучшие объекты для жизни и инвестиций. Виллы, квартиры и дома у моря. Помощь в подборе, оформлении и сопровождении сделки на всех этапах.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить мед справку
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourgatewaytosuccess – The homepage gives a vibe of encouragement and positivity, nice
https://yourgatewaytosuccess.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findyourinspirationhere – Love coming here when I need a boost, content is uplifting
https://findyourinspirationhere.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sitefoundry.click – Found useful articles quickly, the categories are well labelled.
https://asklhsgdvsd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pixelpush.click – Already bookmarked, looks like a go-to resource for me.
https://asfjkbsdvb.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
togetherwecreateimpact – Lots of practical advice, not just ideas floating without action
https://togetherwecreateimpact.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
netmatrix.click – This site has good flow, sections are clearly defined and helpful.
https://asfdjkbsvdsk.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rankflow.click – The images and text balance well, gives a polished impression.
https://adsfjbsivfcvos.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
webpulse.click – Mobile version works flawlessly, that’s a huge plus today.
https://taktycnisd.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить справку
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnexploreandshine – Browsing feels fluid, I didn’t feel lost anywhere
https://learnexploreandshine.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnandearndaily – It feels like someone wants to see readers succeed
Kala
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discovertrendingideas – The latest posts are really on point, I’m impressed
https://discovertrendingideas.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
jointhenextbigthing – Loved the recent article, it gave me fresh ideas instantly.
https://jointhenextbigthing.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectandgrowonline – I appreciate the comprehensive resources available for online marketing.
https://connectandgrowonline.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кракен отзывы пользователей > открыть зеркало Сегодня я протестировал несколько вход на кракен маркет без проблем, и вот что стабильно работает: Фраза официальная ссылка на кракен в тор стала необходимой для тех, кто хочет быть уверен в подлинности ресурса. Настоящая официальная ссылка на кракен в тор всегда дублируется администрацией и сообществом. Она никогда не попадает в поисковые системы и исключает риск мошенничества.
Проверил лично несколько зеркал — стабильно открываются: кракен тор — kraktor.ccпроверенное зеркало — krakenphone.cc Если нужна помощь — пишите.Проверено лично (Пермь). Kraken Marketplace площадка для покупок мессенджер Telegram
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectwithbrilliantminds – This feels like space for collaboration and intelligent conversation
https://connectwithbrilliantminds.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
licsupport – Helped me clear doubts about policy options, thank you
https://licsupport.org/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoveryourpassion – A must-visit for anyone looking to ignite their inner fire.
https://discoveryourpassion.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everythingaboutmarketing – Highly recommend this site for anyone in the marketing field.
https://everythingaboutmarketing.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growyourpresenceonline – Seems trustworthy, with resources that are actually actionable
https://growyourpresenceonline.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoverlearnandshare – Very educational content, feels like learning in fun way
https://discoverlearnandshare.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
inspireandgrowtogether – I shared this with a friend, they’ll love it too.
https://inspireandgrowtogether.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
HOME CLIMAT https://homeclimat36.ru кондиционеры и сплит системы в Воронеже. Скидка на монтаж от 3000 рублей! При покупке сплит-системы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лазерные станки https://raymark.ru для резки металла в Москве. 20 лет на рынке, выгодная цена, скидка 5% при заявке с сайта + обучение
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy penicillin alternative online [url=http://amoxicareonline.com/#]buy amoxicillin[/url] generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
makethemostoflife – I’m already excited to read more posts tomorrow
https://makethemostoflife.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кракен маркетплейс ссылка на сайт
Фраза как найти кракен в торе подсказывает, что люди ищут безопасный способ войти. Настоящий вариант как найти кракен в торе — это использовать официальные каналы, где ссылки проверены пользователями и администрацией.
Основные ссылки:
ссылка кракен даркнет — krakencc.ccрабочая ссылка кракен телеграмм — krakenc.cc
KRAKEN™ 2025 — переходник кракен
Используйте актуальное зеркало для входа на Кракен Зеркало Кракен в телеграмме Как войти на Kraken через браузер
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
viagra uk: British online pharmacy Viagra – British online pharmacy Viagra
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://britmedsdirect.com/# order medication online legally in the UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BuildYourDreamFuture – The examples are relatable, helps me envision my own path.
https://buildyourdreamfuture.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
DiscoverNewOpportunities – Their approach to education is both innovative and impactful.
https://discovernewopportunities.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
DiscoverUsefulTipsDaily – The daily tips keep me motivated to improve small habits.
https://discoverusefultipsdaily.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
StartChangingYourLife – The community feedback makes the journey feel shared, not lonely.
https://startchangingyourlife.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
YourGuideForSuccess – Content is well paced, I don’t feel overwhelmed reading through lessons.
https://yourguideforsuccess.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
FindInspirationEverywhere – It’s a go-to when I feel stuck and need a spark.
https://findinspirationeverywhere.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
InspireChangeAndProgress – The inspiration here feels genuine, not forced or cliché at all.
https://inspirechangeandprogress.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
markmackenzieforcongress – I can tell the message here comes from a genuine place.
https://ukrainianvictoryisthebestaward.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
madeleinemtbc – I often share these updates with friends and neighbors
https://madeleinemtbc.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
DiscoverWorldOfIdeas – I appreciate the topics, not generic, actually feel relevant and interesting.
https://discoverworldofideas.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sport wett
Also visit my blog post: buchmacher wetten [Tobias]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
amoxicillin uk generic amoxicillin and buy penicillin alternative online cheap amoxicillin
https://maps.google.ro/url?sa=t&url=https://amoxicareonline.com amoxicillin uk and http://la-maison-des-amis.com/user/jvejzxdbhd/ buy amoxicillin
[url=http://www.yabuno.net/w3a/redirect.php?redirect=http://bluepharmafrance.com]generic amoxicillin[/url] amoxicillin uk or [url=https://act2day.eu/profile/uesnulzzvc/]Amoxicillin online UK[/url] amoxicillin uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
FindSolutionsForLife – This site really helped me see problems through a fresh lens today.
https://findsolutionsforlife.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ConnectDiscoverAndGrow – Very motivating content, feels like a community more than a site.
https://connectdiscoverandgrow.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
UnlockYourPotentialToday – I enjoy reading the stories—they remind me change is possible.
https://unlockyourpotentialtoday.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кракен маркет — в продаже телефон > кракен телеграм маркетплейс Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен безопасный вход, и вот что стабильно работает: Фраза кракен переходник ссылка обсуждается в каждом сообществе, потому что она играет роль безопасного мостика. Настоящая кракен переходник ссылка помогает попасть в систему и исключает мошенничество. Она всегда ведёт к onion-домену.
Проверил лично несколько адресов — стабильно открываются: как найти кракен в торе — kraktor.ccкракен тг — kratg.cc Если нужна помощь — оставляйте комменты.Проверено лично (Тюмень). Кркн теневой маркет Телекрам
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cheap prednisolone in UK [url=http://medreliefuk.com/#]buy corticosteroids without prescription UK[/url] buy corticosteroids without prescription UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
GetConnectedWithPeople – I’ve already met interesting people through this site, very cool.
https://getconnectedwithpeople.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
все самое лучшее тут: https://midialmed.ru/effektivnye-metody-lecheniya-bolej-bez-medikamentov-vosstanovim-zdorove-estestvennym-putem/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy corticosteroids without prescription UK: UK chemist Prednisolone delivery – Prednisolone tablets UK online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
YourDigitalDestination – Helpful insights, nice to see such thoughtful explanations.
https://yourdigitaldestination.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
FindAnswersAndIdeas – This site gives practical answers, not just vague philosophy, which is rare.
https://findanswersandideas.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
FindNewWaysToGrow – I’m using tips from here to set new goals for myself.
https://findnewwaystogrow.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
LearnShareAndGrow – This platform offers great resources for community development projects.
https://learnshareandgrow.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
FindTheBestIdeas – Found several ideas I want to explore in my upcoming projects.
https://findthebestideas.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://bachinese.com/66/2007/02/18/E58FAFE6809CE79A84E88FB2/
https://thepowerofcreativity.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten online
Also visit my web-site – Der Beste wettanbieter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
LearnSomethingAwesome – Wow, this site really sparks curiosity and fun learning every visit.
https://learnsomethingawesome.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
schüsse aufs tor wetten
Also visit my blog post: beste sportwetten anbieter deutschland; Imogen,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
best UK online chemist for Prednisolone: MedRelief UK – order steroid medication safely online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wettbüro in der nähe
My webpage … deutsche wettanbieter online [Joan]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
TurnIdeasIntoAction – Great site to get unstuck and actually move forward daily.
https://turnideasintoaction.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
order ED pills online UK BritPharm Online and British online pharmacy Viagra buy sildenafil tablets UK
https://www.woolstoncp.co.uk/warrington/primary/woolston/CookiePolicy.action?backto=https://britpharmonline.com Viagra online UK or https://voicebyjosh.com/user/bodcmjrkso/ viagra
[url=https://maps.google.co.mz/url?q=https://britpharmonline.com]buy viagra online[/url] BritPharm Online and [url=http://www.psicologiasaludable.es/user/aczztlikli/]buy sildenafil tablets UK[/url] viagra
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://medreliefuk.shop/# best UK online chemist for Prednisolone
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
was bedeutet kombiwette
Here is my web blog: alle buchmacher; arashplast.com,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
адрес фитнес клуба фитнес клуб с бассейном в москве
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
CreateInspireAndGrow – The content here is top-notch, really helps me stay motivated.
https://createinspireandgrow.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
UK chemist Prednisolone delivery MedRelief UK and UK chemist Prednisolone delivery MedRelief UK
http://906090.4-germany.de/tools/klick.php?curl=https://medreliefuk.com buy corticosteroids without prescription UK and http://orbita-3.ru/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=36431 MedRelief UK
[url=https://www.google.com.eg/url?q=https://medreliefuk.com]cheap prednisolone in UK[/url] buy prednisolone and [url=https://alphafocusir.com/user/npaphlbshp/?um_action=edit]MedRelief UK[/url] order steroid medication safely online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BuildABetterTomorrow – I appreciate how they focus on sustainable solutions for all.
https://buildabettertomorrow.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
TogetherWeCreateChange – Really inspiring platform, makes collaboration feel easy and productive today.
https://togetherwecreatechange.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
papst wettquoten
Also visit my web blog Buchmacher Deutschland (https://Audio.Offre.It)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
YourTrustedSourceOnline – This platform is a valuable tool for community leaders.
https://yourtrustedsourceonline.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy penicillin alternative online [url=http://amoxicareonline.com/#]buy amoxicillin[/url] buy amoxicillin
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
GrowWithConfidenceHere – Great initiative, the guides and tips feel practical and usable.
https://growwithconfidencehere.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BuildSomethingMeaningful – I love how they integrate technology into their initiatives.
https://buildsomethingmeaningful.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wettanbieter mit freiwette
my website; sportwette deutscher meister
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
SimpleWaysToBeHappy – This platform offers valuable insights for boosting happiness.
https://simplewaystobehappy.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cheap amoxicillin: UK online antibiotic service – cheap amoxicillin
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://sada-news.com/?p=1039
https://inspiredailyandgrow.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
makeimpactwithideas – Helpful tools and sections make it worthwhile to stay and explore.
https://makeimpactwithideas.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growyourbusinessfast – Navigation is intuitive, got to what I needed quickly.
https://growyourbusinessfast.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoverendlessinspiration – Tone is uplifting yet grounded, doesn’t feel overly idealistic.
https://discoverendlessinspiration.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Amoxicillin online UK: cheap amoxicillin – amoxicillin uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten prognosen heute
Visit my blog post :: sportwetten guthaben ohne einzahlung (Angelo)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnsomethingneweveryday – Visual elements are engaging but don’t distract from the content.
https://learnsomethingneweveryday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findwhatyouarelookingfor – Overall very polished, gives confidence that I’ll find what I need.
https://findwhatyouarelookingfor.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everythingaboutsuccess – Found useful advice, not fluffy, straight to things I can use.
https://everythingaboutsuccess.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
alphaimpact – Fonts and spacing are pleasant, reading is effortless throughout.
https://alphaimpact.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
getreadytoexplore – Pages load fast even when images are heavy, which is great.
https://getreadytoexplore.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
makelifebettereveryday – Could be great for daily reminders or habits to improve life gradually.
https://makelifebettereveryday.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thebestplacetostarttoday – Overall experience uplifting, this feels like the right place to begin.
https://thebestplacetostarttoday.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnshareandsucceed – Navigation is clear, I easily found a section I liked.
https://learnshareandsucceed.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
You’ll Never Guess This Robot Cleaner’s Benefits robot Cleaner
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
LearnWithConfidence – I keep returning, each module adds valuable insights every time.
https://learnwithconfidence.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
ПокерОК сайт
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
играть на сайте ПокерОК
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В 2024 году туры в Китай на двоих выбрали туристов https://akademy21.ru/narachivabie_browei
Пик популярности пришелся на август, а самым популярным курортом оказался https://akademy21.ru/konturnaya-plastika-gub
Самые дешевые путевки можно купить на январь, а наиболее дорогие туры приходятся на октябрь https://akademy21.ru/osnovinutriciolog
Всем, кто задумался купить тур в Китай, всегда следует помнить: вы готовитесь к межпланетному путешествию https://akademy21.ru/pereatestacia
Туры в Китай популярны сегодня, как никогда https://akademy21.ru/dolgovremenaia_ukladka
Пекин https://akademy21.ru/jenskie_strijki
Цена на двоих с вылетом из Иркутска ?
Не забывайте, что вседозволенность в Китае под запретом https://akademy21.ru/podolog
Так просто не получится посидеть и ВК или Инсте https://akademy21.ru/trener_nutriciolog
Самыми крупными городами Китая являются Пекин и Шанхай, именно в этих городах можно ощутить и увидеть массу интересных достопримечательностей, таких как Храм Неба, Императорский дворец Гугун, Храм Нефритового Будды и Храм Конфуция https://akademy21.ru/courses/massage/intimnoye-otbelivaniye-iapparatnoye-omolozheniye
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
ПокерОК
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
YourPathOfGrowth – This platform offers great resources for community development projects.
https://yourpathofgrowth.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
joinourcreativecommunity – Typography is friendly and readable, spacing makes it easygoing.
https://joinourcreativecommunity.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кракен даркнет — как войти? > кракен бот телеграм Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен маркет, и вот что стабильно работает: Сегодня кракен тор воспринимается как символ стабильного входа, и именно поэтому сообщество так активно обсуждает его. Настоящий кракен тор работает только в анонимной сети, и все остальные варианты — подделки.
Проверил лично несколько адресов — стабильно открываются: кракен тор тг — kraktor.ccтелеграм бот кракен — krakenbot.cc Если нужна помощь — оставляйте комменты.Проверено лично (Махачкала). KRAKEN платформа тэлеграм
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK: amoxicillin uk – UK online antibiotic service
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy corticosteroids without prescription UK: order steroid medication safely online – best UK online chemist for Prednisolone
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK or buy penicillin alternative online generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK
https://rufox.ru/go.php?url=https://amoxicareonline.com cheap amoxicillin or http://umsr.fgpzq.online/home.php?mod=space&uid=138602 buy penicillin alternative online
[url=http://sc.devb.gov.hk/TuniS/bluepharmafrance.com]cheap amoxicillin[/url] amoxicillin uk and [url=http://mbuild.store/user/jeiqvswuaf/?um_action=edit]buy amoxicillin[/url] generic amoxicillin
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://medreliefuk.com/# buy corticosteroids without prescription UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kchqi – Quality content here, images load fast and look crisp too.
https://taktycnisd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boldspark – Looks professional, gives confidence that the offerings are high quality.
https://boldspark.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
zenithmedia – The visuals are sharp, design elements well balanced throughout.
https://zenithmedia.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourbrandzone – Love the branding, feels vibrant and full of personality.
https://yourbrandzone.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pixelplanet – Navigation is smooth, no confusion, found sections effortlessly.
https://pixelplanet.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Suchen Sie Immobilien? montenegro-immobilien-kaufen wohnungen, Villen und Grundstucke mit Meerblick. Aktuelle Preise, Fotos, Auswahlhilfe und umfassende Transaktionsunterstutzung.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ultrawave – Pages load fast, great performance on mobile too.
https://ultrawave.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доставка пиццы Воронеже https://pizzeriacuba.ru самая вкусная сочная пицца в городе Воронеж. Доставим пиццу горячей круглочуточно в Воронеже скидки от 3500 рублей. Скидка на самовывоз на каждую пиццу. Доставка бесплатно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
explorecreativeideasdaily – Navigation is smooth, discovering content was effortless today.
https://explorecreativeideasdaily.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
digitalstorm – The visuals here are powerful, gives strong tech energy.
https://digitalstorm.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoveramazingthingsonline – Navigation is smooth, helped me stumble on cool things fast.
https://discoveramazingthingsonline.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everythingyouneedtoknow – Useful sections are easily accessible, menus do their job well.
https://everythingyouneedtoknow.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextbrand – Overall feels polished, would return for more content here.
https://nextbrand.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bestchoiceonline – Overall experience positive, likely to recommend to friends.
https://bestchoiceonline.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cloudmark – Visuals are crisp and layout looks modern and polished.
https://cloudmark.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Brit Meds Direct: online pharmacy – pharmacy online UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
innovatewithus – Pages load quickly, no clutter, really smooth user experience.
https://innovatewithus.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightchain – The tone feels authentic, not too formal or too casual.
https://brightchain.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sharpwave – The site loads without glitches, smooth experience on mobile too.
https://sharpwave.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
order steroid medication safely online cheap prednisolone in UK or best UK online chemist for Prednisolone buy corticosteroids without prescription UK
http://domzy.com/pharmalibrefrance.com UK chemist Prednisolone delivery or https://rightcoachforme.com/author/fhznpdmhda/ cheap prednisolone in UK
[url=https://images.google.ro/url?sa=t&url=https://medreliefuk.com]cheap prednisolone in UK[/url] order steroid medication safely online or [url=https://istinastroitelstva.xyz/user/dvvoanrnvu/]buy corticosteroids without prescription UK[/url] buy corticosteroids without prescription UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
metarise – Content is high quality, I feel like I learned something solid.
https://metarise.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cyberlaunch – Love the futuristic feel, this site gives such good vibes.
https://cyberlaunch.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightideaweb – Pages load quickly, even images render nicely.
https://brightideaweb.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wavefusion – Overall impression positive, this site feels very professional.
https://wavefusion.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все спортивные новости http://sportsat.ru в реальном времени. Итоги матчей, трансферы, рейтинги и обзоры. Следите за событиями мирового спорта и оставайтесь в курсе побед и рекордов!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
viagra: buy sildenafil tablets UK – British online pharmacy Viagra
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
strongrod – The layout gives good structure, brings focus where needed.
https://strongrod.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Частный заем денег домашние деньги россия альтернатива банковскому кредиту. Быстро, безопасно и без бюрократии. Получите нужную сумму наличными или на карту за считанные минуты.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
die besten Wettanbieter Mit Bonus Ohne Einzahlung
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Узнавайте события первыми: http://ds1spb.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Надёжный источник информации: https://lookdecor.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Только проверенные факты: http://nirvanaplus.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
alihidaer2313 – The site feels minimal, design is simple yet somewhat intriguing.
https://bit.ly/m/clickshopboost
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectwiththeworldnow – Pages load fast, layout is clean and not overwhelming.
https://connectwiththeworldnow.click/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ynaix – Design elements are balanced, not too cluttered or overwhelming.
https://ynaix.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
18 https://akademy21.ru/jenskie_strijki
01 https://akademy21.ru/master_electrolog
2024 На Хайнань теперь 4 раза в неделю 11 https://akademy21.ru/master_manikura
12 https://akademy21.ru/mmedsestra
2023 Отдых на острове Хайнань стал ближе с прямыми рейсами из Москвы 11 https://akademy21.ru/courses/cosmetology
09 https://akademy21.ru/osnovi_koloristiki
2023 Китай https://akademy21.ru/master_brovist
Старт продаж! Турпакеты из Москвы https://akademy21.ru/courses/leshmaker
Чем заняться?
Пекин https://akademy21.ru/courses/trener
К сожалению, у нас нет подходящих туров для отображения https://akademy21.ru/
групповая виза (или въезд по безвизовому списку согласно соглашению между РФ и КНР об упрощении визового режима) – используется для разового посещения, пересечение границы только с группой; индивидуальная виза оформляется заблаговременно в Генеральном консульстве КНР в Иркутске (существуют ограничения по месту постоянного проживания); виза по прилету/въезду – разновидность индивидуальной визы, оформляемой на границе КНР по приглашению китайской стороны https://akademy21.ru/contacts/ussuriysk
USD EUR 19 https://akademy21.ru/lazernoe-udalenie-permanentnogo-makiyazha
01 https://akademy21.ru/ruchnaiaplastika
2024 91 https://akademy21.ru/kurs_cosmetolog_estet
30 RUR 99 https://akademy21.ru/konturnaya-plastika-gub
50 RUR 20 https://akademy21.ru/trener_elektro-epilyatsiya
01 https://akademy21.ru/konturnaya-plastika-gub
2024 – –
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
amoxicillin uk: generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK – Amoxicillin online UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://amoxicareonline.com/# cheap amoxicillin
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wettstrategien einzelwetten
Also visit my web blog :: Online wetten bonus Vergleich
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten vorhersagen halbzeit endstand
Also visit my page: Sportwetten bonus Test
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wette gegen euro
Also visit my website :: sportwetten strategie forum
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Источник, которому доверяют: https://waterlux.ua
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё самое новое тут: https://carina-e.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё актуальное в одном месте: https://opengroup.net
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Только проверенные новости: https://olimpia-nv.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё самое свежее здесь: http://volgazdrav.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pferderennen meran wetten (avmartinmalharro.edu.ar) bonus ohne einzahlung
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boldnetwork – Clean aesthetic, I’ll check back later for updates.
https://boldnetwork.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextrend – The tone is friendly yet professional — feels trustworthy.
https://nextrend.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextlayer – Navigation is seamless, and the visuals are appealing.
https://nextlayer.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
UK online antibiotic service: UK online antibiotic service – cheap amoxicillin
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thinkbeyondtech – Navigation is seamless, and the visuals are appealing.
https://thinkbeyondtech.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
greenmotion – The content is engaging, and the site is responsive.
https://greenmotion.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
zenithlabs – Found exactly what I was looking for, very intuitive.
https://zenithlabs.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Amoxicillin online UK amoxicillin uk or UK online antibiotic service UK online antibiotic service
https://cse.google.com.nf/url?q=https://amoxicareonline.com amoxicillin uk and https://blog.techshopbd.com/user-profile/vnlxreunjr/?um_action=edit buy penicillin alternative online
[url=http://clink.nifty.com/r/search/srch_other_f0/?https://amoxicareonline.com]buy amoxicillin[/url] cheap amoxicillin or [url=https://boyerstore.com/user/sfizbribjl/?um_action=edit]amoxicillin uk[/url] amoxicillin uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
maxvision – The content is engaging, and the site is responsive.
https://maxvision.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
goldbridge – The layout is nice, good color palette and visuals.
https://goldbridge.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Brit Meds Direct: Brit Meds Direct – private online pharmacy UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fastgrowth – Love the clean design, really easy to navigate today.
https://fastgrowth.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cloudmatrix – A pleasure to browse, everything is well-organized and clear.
https://cloudmatrix.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
elitegrowth – Consistently impressed with the site’s performance and design.
https://elitegrowth.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
No fakes or speculation: https://www.cricketweb.net
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все самое актуальное тут: https://consolit.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все лучшее у нас: https://kanctanta.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We value honesty: https://badgerboats.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
solidvision – Hoping they launch soon; curious what they’ll offer.
https://solidvision.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bluetrail – Smooth navigation, I didn’t feel lost exploring the pages.
https://bluetrail.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sharpbridge – The color scheme is nice, very calming on the eyes.
https://sharpbridge.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
alphaunity – Very promising site, I’ll be back to explore more.
https://alphaunity.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Only real events: https://hyundaimobil.co.id
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Source of truthful news: https://sportzpoint.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Events without embellishment: https://sportsfanbetting.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
No exaggerations: https://www.cricketweb.net
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
A source for current events: https://kariyanichigeki.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
quantumreach – Friendly tone, feels like there’s a real person writing here.
https://quantumreach.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boldimpact – The domain looks strong, hoping content is up soon.
https://boldimpact.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy corticosteroids without prescription UK Prednisolone tablets UK online and cheap prednisolone in UK Prednisolone tablets UK online
http://www.glasscontrol.co.uk/gallery/main.php?g2_view=core.UserAdmin&g2_subView=core.UserRecoverPassword&g2_return=https://medreliefuk.com cheap prednisolone in UK and http://jonnywalker.net/user/vycjitgrfc/ MedRelief UK
[url=http://forum.schwarzes-bw.de/wbb231/redir.php?url=http://pharmalibrefrance.com]buy corticosteroids without prescription UK[/url] UK chemist Prednisolone delivery or [url=https://fionadobson.com/user/tbgmffhwtf/?um_action=edit]order steroid medication safely online[/url] MedRelief UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendforge – Domain sounds strong; curious what kind of content they’ll share.
https://trendforge.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartgrid – If content matches the name, this could become useful resource.
https://smartgrid.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Trustworthy news: https://amt-games.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We write as is: https://petitedanse.com.br
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Only real facts: https://ween.tn
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Only verified facts: https://verspk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Only verified information: https://g-r-s.fr
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
skyportal – Love the colors used here, makes reading very pleasant.
https://skyportal.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Велосипед Горы Заповедники Природа Трекинг Эко-туризм https://akademy21.ru/contacts/ixelles
Климат https://akademy21.ru/courses/massage/elektromagnitnaya-stimulyatsiya-hifem
Достопримечательности Музеи Современная архитектура Современный Шопинг Экскурсионные туры https://akademy21.ru/contacts/ekaterinburg
Китай | Санья https://akademy21.ru/courses/meditsinskie-kursy
Пляжная линия https://akademy21.ru/courses/trener
Viasun https://akademy21.ru/medsestra_cosmetolog
ru – лучший интернет-сервис подбора туров по версии National Geographic https://akademy21.ru/apparatniy_pedecur
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growthverse – The content is engaging, and the site is responsive.
https://growthverse.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK: cheap amoxicillin – generic amoxicillin
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
valuevision – Seems like a solid brand idea; content just needs fleshing out.
https://valuevision.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy viagra online: buy viagra online – buy viagra
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Information you can trust: https://www.pondexperts.ca
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Time-tested and proven: https://www.amakmeble.pl
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Only important details: https://astra-hotel.ch
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We select the best: https://angersnautique.org
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мир архитектуры https://vineyardartdecor.com и дизайна в одном месте! Лучшие идеи, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и города. Узнай, как создаются красивые и функциональные пространства.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://britpharmonline.com/# order ED pills online UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
News as it is: https://aquietrabalho.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Only the latest updates: https://hello-jobs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Find out the truth here: https://www.trimartolod.fr
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We tell it like it is: https://cfsl.in
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BritPharm Online [url=http://britpharmonline.com/#]BritPharm Online[/url] buy viagra online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
futurelink – Navigation is smooth, didn’t feel lost anywhere.
https://futurelink.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
blueorbit – Overall experience is strong, I’m impressed with this site.
https://blueorbit.click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Find out the truth here: https://fish-pet.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Only the latest updates: https://telrad.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Information you can trust: https://theshaderoom.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
News as it is: https://astra-hotel.ch
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We tell it like it is: https://nature-et-avenir.org
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We check every word: https://davisa.es
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
No lies – just facts: https://www.maxwaugh.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Stay up to date: https://manorhousedentalpractice.co.uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We only tell the facts: https://deogiricollege.org
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
A trusted source: https://www.feldbahn-ffm.de
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
9 Things Your Parents Taught You About Car Flip Key Repair Car Flip Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Only verified sources: https://www.sportsoddshistory.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
9 Things Your Parents Taught You About Emergency Car Key Repair Emergency Car Key Repair (Walker)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Only verified data: https://playplayfun.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Information you can trust: https://www.radio-rfe.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Only reliable facts: https://www.zdravnitza.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We have reliable sources: https://redclara.net
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
order steroid medication safely online: Prednisolone tablets UK online – order steroid medication safely online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Viagra online UK: order ED pills online UK – viagra uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кракен магазин зайти легко > маркетплейс кракен актуальный Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен в телеграмме ссылка, и вот что стабильно работает: Фраза кракен телеграм маркетплейс остаётся одним из самых популярных способов поиска рабочих ссылок. Настоящий кракен телеграм маркетплейс подтверждается официальными источниками и открывается только через Tor.
Проверил лично несколько ссылок — стабильно открываются: кракен магазин тор — krakenmagazin.ccнайти актуальный сайт кракен — krakenactual.cc Если нужна помощь — оставляйте комменты.Проверено лично (Москва). Кракен сайт онлайн-магазин Телеграм
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
order ED pills online UK viagra and BritPharm Online BritPharm Online
https://www.google.co.ug/url?sa=t&url=https://britpharmonline.com viagra and https://bbs.hy2001.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=668138 viagra uk
[url=https://www.google.dk/url?q=https://britpharmonline.com]buy sildenafil tablets UK[/url] viagra or [url=http://la-maison-des-amis.com/user/eepmkftseu/]buy sildenafil tablets UK[/url] viagra uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
9 Things Your Parents Taught You About Car Flip Key Repair car flip
key repair; https://posteezy.com/why-car-Key-circuit-repair-fast-becoming-hottest-trend-2025,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
telecharger 1xbet pour android pronostic foot gratuit
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
telecharger 1xbet apk https://parifoot-afrique1.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
melbet – paris sportif pariez sur le foot
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная студия дизайна https://bconline.com.ua архитектура, интерьер, декор. Мы создаём пространства, где технологии сочетаются с красотой, а стиль — с удобством.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Keyless Push Button Start Repair: The Intermediate Guide In Keyless Push Button Start Repair Keyless Push Button Start Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
amoxicillin uk generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK or buy penicillin alternative online cheap amoxicillin
http://alovio.com/bluepharmafrance.com.html amoxicillin uk and http://orbita-3.ru/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=35783 buy amoxicillin
[url=https://images.google.li/url?q=https://amoxicareonline.com]generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK[/url] Amoxicillin online UK or [url=http://www.donggoudi.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3722682]buy penicillin alternative online[/url] buy penicillin alternative online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tour de france wettquoten
My page; Handicap wette Unentschieden
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
goldnexus – The design feels polished, very professional presentation overall.
https://u6ks8s6ge51.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://faktualtimes.com/2025/nasional/perayaan-hut-ri-ke-80-di-beranda-ganesha-1-telaga-kahuripan-berlangsung-meriah-dan-penuh-kebersamaan/
https://vydtu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your Family Will Thank You For Having This Car Key Guard Repair Key Fob Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
urbannexus – Found several new ideas I hadn’t thought of before.
https://8iaoi63.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
primeimpact – Found several tips I plan to apply immediately.
https://agoqkmd3i.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
powercore – Love the energy this site gives off, feels bold and strong.
https://vydtu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
urbanshift – Bookmarking this — I’ll return often for updates.
https://wh76a3dijrxn.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Prednisolone tablets UK online [url=https://medreliefuk.com/#]UK chemist Prednisolone delivery[/url] Prednisolone tablets UK online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://britpharmonline.com/# buy viagra
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
urbanscale – Bold visuals, well-designed site, easy to skim through.
https://gcmv1k49sf8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
novaorbit – Found several ideas I can use right away.
https://dolrq1o3nsu8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ascendmark – The posts are clear, useful, and well-written.
https://sgw6u7mv.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boldvista – The tone is friendly and accessible, nice balance.
https://qhkjwb.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ultraconnect – The content is both inspiring and practically applicable, nice.
https://pinah8hg58o.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growthverse – These tools and guides feel like they were tailored to real needs.
https://iip36t4foszf.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ascendgrid – The name alone suggests growth, excited to explore.
https://j5fnbpanu9x.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
vividpath – Found some creative frameworks I hadn’t seen before.
https://hf6on6.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
9 Lessons Your Parents Taught You About Vehicle Key Fob Repair Vehicle Key Fob Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brandvision – The tone is friendly but professional, good balance.
https://rlvyz47zo.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
truelaunch – Found a few tips I’m going to try out immediately.
https://3xfq6z.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
elitegrowth – Clear writing, solid examples, exactly what I was searching for.
https://e5mekv.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
innovatek – Love how they explain complex tech simply.
https://wekaxgwcixfg.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
purehorizon – Just browsed your sections, found some really helpful insights.
https://0ujn69ntt3lh.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brandcrest – The tone is friendly and content feels human, nice job.
https://o67rp.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
summitmedia – Good visuals, solid writing, and useful links throughout.
https://2vshqicrvxd.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
skyvertex – Nice clean design, makes exploring content feel effortless.
https://64u19k.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обзор площадки Кракен: как начать > перейти по ссылке Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен зеркало сегодня, и вот что стабильно работает: Ключ рабочая кракен ссылка без регистрации стал популярным среди тех, кто хочет проверить доступность ресурса. Настоящая рабочая кракен ссылка без регистрации используется для быстрого теста, но не заменяет полноценный аккаунт.
Проверил лично несколько ссылок — стабильно открываются: кракен тор — kraktor.ccзабытый пароль кракен — krakenlogin.cc Если нужна помощь — пишите.Проверено лично (Ульяновск). Кракен дарк маркет торговая площадка мессенджер Telegram
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
visionlane – Found several useful resources I hadn’t seen elsewhere.
https://g9x8n5z1cx.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
linkcraft – Great content quality, I’ll be returning often to this.
https://oom8jnr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartvibe – Found several helpful tips I can apply right away.
https://7y61u4.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
elitepulse – Impressed by how current the articles are.
https://n60t5vd0.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
techmatrix – Frequent updates keep the content fresh and relevant.
https://2vshqicrvxd.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
grandlink – Very helpful guides, easy to follow step by step.
https://ofl47cq0s.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten sport Sportwetten Online Deutschland
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
vectorrise – Their motion graphics look polished and professionally produced.
https://ypwlo21.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Proximity Key Repair Tools To Ease Your Daily Life Proximity
Key Repair Trick That Everyone Should Be Able To Proximity Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
neue online Beste tour de france wettanbieter – chenle.vn –
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten bonus aktionen
Feel free to surf to my web site … Wettseiten Ohne lugas
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
best UK online chemist for Prednisolone UK chemist Prednisolone delivery or best UK online chemist for Prednisolone buy prednisolone
https://www.google.com.na/url?q=https://medreliefuk.com UK chemist Prednisolone delivery or http://dnp-malinovka.ru/user/rrpzeeovfo/?um_action=edit Prednisolone tablets UK online
[url=https://maps.google.com.gi/url?sa=t&url=https://medreliefuk.com]cheap prednisolone in UK[/url] best UK online chemist for Prednisolone or [url=https://myrsporta.ru/forums/users/bbgsdd4-2/]buy prednisolone[/url] MedRelief UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MedRelief UK: order steroid medication safely online – MedRelief UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ремонт и строительство https://fmsu.org.ua без лишних сложностей! Подробные статьи, обзоры инструментов, лайфхаки и практические советы. Мы поможем построить, отремонтировать и обустроить ваш дом.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Студия дизайна https://bathen.rv.ua интерьеров и архитектурных решений. Создаём стильные, функциональные и гармоничные пространства. Индивидуальный подход, авторские проекты и внимание к деталям.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
UK chemist Prednisolone delivery: best UK online chemist for Prednisolone – MedRelief UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Car Ignition Repair Tools To Streamline Your Everyday Lifethe
Only Car Ignition Repair Trick That Everybody Should Learn Car Ignition Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic amoxicillin [url=https://amoxicareonline.com/#]generic amoxicillin[/url] buy amoxicillin
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buchmacher bedeutung
My page paypal sportwetten Anbieter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://medreliefuk.com/# UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ссылка на бота кракена тг актуальная > где купить смартфон кракен Сегодня я протестировал несколько список актуальных ссылок на кракен, и вот что стабильно работает: Словосочетание официальная ссылка площадки кракен помогает не заблудиться в фейках. Настоящая официальная ссылка площадки кракен проверяется пользователями и модераторами, что исключает риск мошенничества.
Проверил лично несколько адресов — стабильно открываются: кракен тор — kraktor.ccновый телефон кракен — kphone.cc Если нужна помощь — задавайте вопросы.Проверено лично (Хабаровск). kraken url даркнет магазин Телеграмм
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
maxvision – Impressed with the customer support, they resolved my issue promptly.
https://ur58v225s30j.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
quotenvergleich sportwetten wettanbieter
Also visit my web site … zuverlässige wett Tipps
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ZenithLabs – Informative posts, explained things clearly without being overly complicated at all.
https://ddt0f.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
metarise.click – Just landed here, everything feels polished and really easy to use.
https://woqea9.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online wetten
Look into my site best wettanbieter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
order medication online legally in the UK: pharmacy online UK – pharmacy online UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tipwin wettbüro
Feel free to surf to my site: betibet beste bonus sportwetten, Multivisioncable.com,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sharpwave.click – Loads fast even on mobile, design feels clean and modern.
https://pi6za0.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://medreliefuk.shop/# UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
progrid – Fantastic insights, broadened my understanding of the subject.
https://uxevxaa3zyh.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
visionmark – Just received our order; the quality is top-notch.
https://sf464q0kbs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boldmatrix – Enhanced customer satisfaction through personalized fit recommendations.
https://cd0eafp7qb66.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
prolaunch – This is exactly what I was looking for, amazing!
https://29mml8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
truegrowth – They provided actionable insights that improved our conversion rates.
https://n7k061fm.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
alphaimpact.click – Loving the content layout, feels both polished and professional throughout.
https://jzi31n.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ultrafocus.click – Useful content sprinkled throughout, feels like a serious site.
https://8xpzfxj1uii.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nexasphere – Can’t believe how much this helped me today, thanks!
https://9xhls4v5.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ultrawave.click – The navigation here is so intuitive, makes everything super simple honestly.
https://wh76a3dijrxn.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
newgenius.click – Everything loads smoothly, fonts look good, navigation is very intuitive.
https://cb86t5zj.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightchain.click – Strong first impression; looks trustworthy and professional.
https://e1z5huzf.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
elitefusion.click – Loving every section here, truly feels polished and professional.
https://o57hsj9e4cw.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
maxbridge.click – Found new features here I didn’t expect, pleasantly surprised by variety.
https://gxbs5.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
elitezone.click – Smooth interface, no glitches so far, feeling very professional.
https://evgerr77.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brandmatrix.click – Impressed by how polished this feels, definitely professional quality site.
https://u3fbhw.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
alphaorbit.click – Just found this site; visuals look crisp and navigation is smooth.
https://rwu0a.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
coreimpact.click – I appreciate the balance between visuals and simple readability.
https://0rvwwsgxbzlr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightvault.click – Clear headings, easy calls-to-action, user flows are well thought out.
https://gi9eo7j8x.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
zenithmedia.click – I like how clean and sharp the imagery is.
https://nb3jn87ai.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
507193.com – Pages load quickly, which is always a plus.
https://dzli92u87g.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Туристический портал https://feokurort.com.ua для любителей путешествий! Страны, маршруты, достопримечательности, советы и лайфхаки. Планируйте отдых, находите вдохновение и открывайте мир вместе с нами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectwiththeworldnow – Strong presence, design complements message and intent clearly.
https://asdqasdsad.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Студия ремонта https://anti-orange.com.ua квартир и домов. Выполняем ремонт под ключ, дизайн-проекты, отделочные и инженерные работы. Качество, сроки и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
UK online antibiotic service [url=https://amoxicareonline.shop/#]cheap amoxicillin[/url] generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Рабочий вход: кракен зайти на площадку > магазин кракен шоп Сегодня я протестировал несколько форум кракен россия, и вот что стабильно работает: Многие ищут кракен шоп сайт в поисковиках, но это ошибка. Настоящий кракен шоп сайт никогда не появляется в Google или Яндекс. Он публикуется только в официальных каналах и открывается через Tor.
Проверил лично несколько ссылок — стабильно открываются: кракен магазин зеркало — krakenmagazin.ccподдержка кракен шоп — krakeshop.cc Если нужна помощь — задавайте вопросы.Проверено лично (Белгород). КРАКЕН онлайн-рынок tg
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
order steroid medication safely online: UK chemist Prednisolone delivery – order steroid medication safely online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://rosetti.com.ua о стиле, здоровье и семье. Новости моды, советы экспертов, тренды красоты и секреты счастья. Всё, что важно и интересно женщинам любого возраста.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Главный автопортал страны https://nmiu.org.ua всё об автомобилях в одном месте! Новости, обзоры, советы, автообъявления, страхование, ТО и сервис. Для водителей, механиков и просто любителей машин.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт о металлах https://metalprotection.com.ua и металлообработке: виды металлов, сплавы, технологии обработки, оборудование и новости отрасли. Всё для специалистов и профессионалов металлургии.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный сайт https://okna-k.com.ua для профессионалов и новичков. Новости отрасли, обзоры материалов, технологии строительства и ремонта, советы мастеров и пошаговые инструкции для качественного результата.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал о дизайне https://sculptureproject.org.ua интерьеров и пространства. Идеи, тренды, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и общественных мест. Советы дизайнеров и примеры стильных решений каждый день.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кракен зеркало тг доступ > официальные магазины кракен Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен переходник, и вот что стабильно работает: Фраза рулетка кракен число обсуждается игроками, которые анализируют результаты. Настоящее рулетка кракен число всегда случайное и непредсказуемое.
Проверил лично несколько зеркал — стабильно открываются: кракен тор вход зеркало — krakmirror.ccсписок магазинов кракен — krashops.cc Если нужна помощь — задавайте вопросы.Проверено лично (Волгоград). Кракен онион теневой маркет Телекрам
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://amoxicareonline.com/# cheap amoxicillin
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectwiththeworldnow – Strong presence, design complements message and intent clearly.
https://asdqasdsad.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacy online UK [url=https://britmedsdirect.com/#]online pharmacy[/url] private online pharmacy UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ваш гид в мире https://nerjalivingspace.com автомобилей! Ежедневные авто новости, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Найдите идеальный автомобиль, узнайте о страховании, кредитах и тюнинге.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мужской сайт https://rkas.org.ua о жизни без компромиссов: спорт, путешествия, техника, карьера и отношения. Для тех, кто ценит свободу, силу и уверенность в себе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мужской онлайн-журнал https://cruiser.com.ua о современных трендах, технологиях и саморазвитии. Мы пишем о том, что важно мужчине — от мотивации и здоровья до отдыха и финансов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал для автомобилистов https://translit.com.ua от выбора машины до профессионального ремонта. Читайте обзоры авто, новости автоспорта, сравнивайте цены и характеристики. Форум автолюбителей, советы экспертов и свежие предложения автосалонов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kluvcc.com – Simple navigation, everything feels easy to find.
https://h43sawkxnkt.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт для женщин https://oun-upa.org.ua которые ценят себя и жизнь. Мода, советы по уходу, любовь, семья, вдохновение и развитие. Найди идеи для новых свершений и будь самой собой в мире, где важно быть уникальной!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ynaix.com – There’s a refined aesthetic here that suggests thoughtfulness.
https://zg00vu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bestchoiceonline.click – The content feels relevant, and the site doesn’t overwhelm with too much.
https://yazzxsopxtup.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fastgrowth.click – Beautiful visuals and good flow from section to section.
https://ui654.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
507193.com – It’s intriguing — minimal sites leave room for curiosity.
https://g5abt8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
strongrod.com – Overall a polished site — trustworthy and well designed.
https://jzi31n.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
vmf-metal.com – Found this site today, and navigation is smooth and intuitive.
https://g02x5oz8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
medtopstore.com – Typography and font choices are readable and consistent.
https://ip6tmsm7.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
503926.com – The colors and font choice are subtle but pleasing to the eye.
https://gxbs5.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everyspeed.com – Layout is simple; may need more visuals or details for full impact.
https://u6ks8s6ge51.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
österreich wette
Also visit my webpage :: tipps sportwetten heute (Chang)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://ultravioletmfb.com/new-post/
https://hf6on6.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discreet delivery for ED medication: how to order Cialis online legally – safe online pharmacy for ED pills
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
531500zy.com – The tone (whatever text is visible) feels neutral and professional.
https://evgerr77.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
skyhighstudio.click – I appreciate the consistent design touches and color palette.
https://n5lltmin530.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
zrhsof.com – Navigation feels intuitive; I could find what I needed fast.
https://5nd8p8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten dass heute gäste
Have a look at my web blog; bester wettanbieter betrugstest, Daryl,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dreambigtoday.click – Clean layout and positive tone, very refreshing to browse through.
https://c9o54.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalwave.click – Strong performance, visual appeal, and usability all in one.
https://grssvtqqnpwr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
livescore für sportwetten
Have a look at my web site :: Buchmacher Kurse Beim Rennsport
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartbusinesshub.click – Good use of typography, color harmony makes it pleasant to read.
https://9a38suo9gfdu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sportwetten Strategie Forum (Fondationsanfilipponeri.Bi)
tipps gratis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mediafusion.click – Pages load fast and the layout feels polished.
https://139eksq3j04.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fastimpact.click – Overall a strong site, easy to use and visually appealing.
https://f59nc15vh8j.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buildyourbrand.click – Impressed by the layout; everything feels intuitive and modern.
https://2n58awy7qu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
creativemindlab.click – Love how creative and modern the whole layout feels today.
https://yazzxsopxtup.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
newnexus.click – Pages load quickly and everything seems nicely organized.
https://kv1tok.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
maxgrowth.click – Strong visuals and organized layout make this pleasant to use.
https://3pu3u.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
powertrend.click – The visuals and content here are top notch and engaging.
https://vydtu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как построить https://rus3edin.org.ua и отремонтировать своими руками? Пошаговые инструкции, простые советы и подбор инструментов. Делаем ремонт доступным и понятным для каждого!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обустраивайте дом https://stroysam.kyiv.ua со вкусом! Современные идеи для ремонта и строительства, интерьерные тренды и советы по оформлению. Создайте стильное и уютное пространство своими руками.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт о стройке https://samozahist.org.ua и ремонте для всех, кто любит уют и порядок. Расскажем, как выбрать материалы, обновить интерьер и избежать ошибок при ремонте. Всё просто, полезно и по делу.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строим и ремонтируем https://srk.kiev.ua грамотно! Инструкции, пошаговые советы, видеоуроки и экспертные рекомендации. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить без потери результата.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный портал https://sitetime.kiev.ua для мастеров и подрядчиков. Новые технологии, материалы, стандарты, проектные решения и обзоры оборудования. Всё, что нужно специалистам стройиндустрии.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectwiththeworldnow – Clean interface, message is upfront and design feels coherent.
https://asdqasdsad.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mediafusion.click – Always something new to explore, keeps me coming back.
https://r6c848.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic gabapentin pharmacy USA [url=https://neurocaredirect.com/#]neuropathic pain relief treatment online[/url] NeuroCare Direct
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
beste tipps und tricks sportwetten (Gurkha.cl) app android
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проверенная ссылка кракен тор > доступ к Кракен Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен тг бот тор, и вот что стабильно работает: Фраза кракен наркошоп переходник показывает, что речь идёт именно о торговой зоне. Настоящий кракен наркошоп переходник всегда скрыт от поисковых систем и дублируется только официальными каналами. Он открывается через Tor и сохраняет конфиденциальность.
Проверил лично несколько зеркал — стабильно открываются: ссылка на сайт кракен в тор браузере — kraktor.ccсколько стоит телефон кракен — krakenphone.cc Если нужна помощь — оставляйте комменты.Проверено лично (Оренбург). Кракен даркнет площадка для покупок тг
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
ПокерОК сайт
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Главные новости дня https://sevsovet.com.ua эксклюзивные материалы, горячие темы и аналитика. Мы рассказываем то, что действительно важно. Будь в курсе вместе с нашим новостным порталом!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новостной портал https://kiev-online.com.ua с проверенной информацией. Свежие события, аналитика, репортажи и интервью. Узнавайте новости первыми — достоверно, быстро и без лишнего шума.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пошаговые советы https://tsentralnyi.volyn.ua по строительству и ремонту. Узнай, как выбрать материалы, рассчитать бюджет и избежать ошибок. Простые решения для сложных задач — строим и ремонтируем с уверенностью!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строим и ремонтируем https://buildingtips.kyiv.ua своими руками! Инструкции, советы, видеоуроки и лайфхаки для дома и дачи. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить бюджет.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Энциклопедия строительства https://kero.com.ua и ремонта: материалы, технологии, интерьерные решения и практические рекомендации. От фундамента до декора — всё, что нужно знать домовладельцу.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
Официальный сайт онлайн рума ПокерОК
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
Официальный сайт онлайн рума ПокерОК
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy tadalafil 10mg india tadalafil cheapest price and tadalafil 5 mg tablet coupon tadalafil 2.5 mg tablets
https://images.google.lt/url?q=https://everlastrx.com generic tadalafil from canada and http://jonnywalker.net/user/ntxtnhilhp/ buy tadalafil online no prescription
[url=https://images.google.co.uz/url?q=https://everlastrx.com]cost of generic tadalafil[/url] 60 mg tadalafil and [url=https://www.emlynmodels.co.uk/user/kudyzcsuya/]tadalafil online united states[/url] buy tadalafil cialis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Утепление деревянного пола керамзитом или выравнивание бетонного основания в квартире своими руками позволит сэкономить денежные средства https://al-keram.ru/certificates.html
Их можно будет использовать на дорогое декоративное покрытие, которое станет украшением интерьера и великолепным фоном для домашних фото и видео https://al-keram.ru/blog/keramzit-otlichnyj-material-dlya-teploizolyatsii-zdanij.html
Для закрепления маяков в раствор можно добавить гипс или алебастр — это ускорит схватывание и позволит начать работы по засыпке керамзита сразу после выставления направляющих https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzit/keramzit-v-meshkah-fraktsii-20-40-m200350-detail.html
Благодаря особенностям сырья керамзитобетон обладает высокой прочностью, долговечностью, прекрасными тепло- и звукоизолирующими свойствами, не уступая, а по многим показателям и превосходя древесину https://al-keram.ru/novosti/
Технология изготовления в условиях заводов и малых фирм различается https://al-keram.ru/blog/uteplenie-keramzitom-sovety-professionalov.html
Обязанности: ОТДЕЛОЧНИК: (ГКЛ,кафель, армстронг,штукатур-маляр)сантех работы , помошник электрикаразнорабочие порученияТребования: опыт монтажа ГКЛ, кафель, армстронг, штукатурка и покраска стен https://al-keram.ru/blog/nezamenimye-stroitelnye-materialy-gravij.html
Условия: график 5/2 , с 9ч 00 до 18ч 00
Привлекательная цена, высокая прочность и отличные показатели звуко- и теплоизоляции – основные причины высокой популярности этого искусственного стройматериала https://al-keram.ru/blog/vozmozhnost-utepleniya-fundamentov-keramzitom.html
Производят его из тугоплавкой глины путем обжига при сверхвысоких температурах https://al-keram.ru/blog/kak-ispolzovat-keramzit-na-dache.html
В результате сырье распадается на небольшие камушки круглой или овальной формы, вспученные внутри и оплавленные снаружи https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzit/keramzit-v-big-begah-fraktsii-20-40-m200-250-detail.html
Частицы получаются твердыми, легкими, гладкими, с небольшими порами на поверхности и ячеистой структурой https://al-keram.ru/novosti/grafik-raboty-na-maj.html
В зависимости от глинистой массы керамзит может быть бурого, серого или светло-коричневого цвета https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzit/keramzit-v-big-begakh.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Контакты https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Архитектурное бюро может предоставить широкий спектр услуг и экспертизы, так как в составе таких компаний работает команда профессионалов https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Кроме того, такие компании обычно имеют опыт и большие возможности для реализации проектов https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Однако услуги архитектурных бюро могут быть более дорогими, чем услуги частных архитекторов, а процесс работы может быть более формализованным и менее гибким https://www.abbalk.ru/interier
Каталог представляет собой данные о более чем 120 архитектурных бюро, созданных в Москве или начавших активно работать с городскими объектами, начиная с 2012 года https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Информация была собрана и систематизирована в рамках исследования «Новое поколение архитектурных бюро Москвы», проведенного в 2022 году по заказу Комитета по архитектуре и градостроительству города Москвы под кураторством Сергея Кузнецова, главного архитектора Москвы https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
Каталог имеет открытый формат и будет пополняться информацией о новых командах и их проектах, выполненных для Москвы https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Проектное бюро занимается созданием технических проектов, разработкой технической документации, проектированием инженерных систем и коммуникаций, а также оценкой технических решений https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Такие бюро, в большей степени, ориентированы на инженерно-технические аспекты проекта, нежели на его архитектурную концепцию https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
От конкурентов компанию отличает комплексный подход к проектированию https://www.abbalk.ru/gradostroitelstvo
Над задачами трудятся свыше 200 сотрудников разного профиля, которые постоянно обмениваются информацией https://www.abbalk.ru/arhitectyra
Контакты https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
safe online pharmacy for ED pills [url=https://everlastrx.shop/#]FDA-approved Tadalafil generic[/url] Tadalafil tablets
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectwiththeworldnow – The tone feels active, I’m drawn to explore more of their content.
https://asdqasdsad.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Информационный портал https://smallbusiness.dp.ua про строительство, ремонт и интерьер. Свежие новости отрасли, обзоры технологий и полезные лайфхаки. Всё, что нужно знать о стройке и благоустройстве жилья в одном месте!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный сайт https://teplo.zt.ua для тех, кто создаёт дом своей мечты. Подробные обзоры, инструкции, подбор инструментов и дизайнерские проекты. Всё о ремонте и строительстве в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Полезный сайт https://stroy-portal.kyiv.ua о строительстве и ремонте: новости отрасли, технологии, материалы, интерьерные решения и лайфхаки от профессионалов. Всё для тех, кто строит, ремонтирует и создаёт уют.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт о строительстве https://valkbolos.com и ремонте домов, квартир и дач. Полезные советы мастеров, подбор материалов, дизайн-идеи, инструкции и обзоры инструментов. Всё, что нужно для качественного ремонта и современного строительства!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectwiththeworldnow – I appreciate how simple yet bold the site looks and speaks.
https://asdqasdsad.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Советы по строительству https://vodocar.com.ua и ремонту своими руками. Пошаговые инструкции, современные технологии, идеи для дома и участка. Мы поможем сделать ремонт проще, а строительство — надёжнее!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextlayer.click – The user interface is smooth, making navigation a breeze.
https://mesujitempo.com/nasib-demokrasi-indonesia-di-tahun-2024-dan-pemilu-2024/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Рабочее зеркало кракен магазина > кракен актуальные зеркала Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен сайт, и вот что стабильно работает: Фраза кракен современный маркет используется в обсуждениях, чтобы подчеркнуть его актуальность. Настоящий кракен современный маркет всегда связан с onion-доменами и сетью Tor.
Проверил лично несколько ссылок — стабильно открываются: кракен вход магазин — krakenmagazin.ccактуальный кракен маркет — krakenactual.cc Если нужна помощь — задавайте вопросы.Проверено лично (Кемерово). Kraken Onion даркнет магазин Телеграм
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
smartgrid.click – Impressed by the layout; everything feels intuitive and modern.
https://4tacc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pixelplanet.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
https://gbzv9cg0w.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello! [url=http://mexicanharmine.online/#]reliable online pharmacy[/url] very good web site.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalreach.click – Great user experience; pages load fast and look sharp.
https://npebuia08tk.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cyberlaunch.click – Love the minimalist design; it’s both stylish and functional.
https://vydtu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wavefusion.click – Impressed by the layout; everything feels intuitive and modern.
https://d7exj.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
greenmotion.click – Great user experience; pages load fast and look sharp.
https://a5f02x3.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightideaweb.click – The site feels polished and professional, nice work.
https://ofl47cq0s.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
websource.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
https://uh3ji968upn.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
powerofgrowth.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
https://0pkjf5hy019.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
reachnewgoals.click – Great user experience; pages load fast and look sharp.
https://zaodmpyib.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thefuturehub.click – Found this while browsing; it’s clean and easy to use.
https://5r522dqqgn.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fastforwardmedia.click – The user interface is smooth, making navigation a breeze.
https://agoqkmd3i.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кракен сайт доступ без блокировок > кракен актуальная ссылка Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен поддержка телеграм, и вот что стабильно работает: Кракен вход всегда обсуждается в сообществах, потому что без него невозможно попасть на площадку. Настоящий кракен вход работает исключительно через Tor.
Проверил лично несколько ссылок — стабильно открываются: кракен зеркало сайта — krakmirror.ccкракен ссылка — krakssylka.cc Если нужна помощь — задавайте вопросы.Проверено лично (Иркутск). КРАКЕН интернет-магазин Telegram Messenger
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
digitalvisionpro.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
https://h62rrn.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
globalconnectnow.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
https://dzli92u87g.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
starvision.click – The site feels polished and professional, nice work.
https://kg908e5.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
risehub.click – Great user experience; pages load fast and look sharp.
https://zncwld1cv.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
innovatewithus.click – The site feels polished and professional, nice work.
https://t6ilse.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
launchcraft.click – Great user experience; pages load fast and look sharp.
https://sgw6u7mv.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
quicktrend.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
https://bdn4bfz.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
focusreach.click – Love the minimalist design; it’s both stylish and functional.
https://j0ihj036w1.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bluefocus.click – The site feels polished and professional, nice work.
https://11bnlrie0y.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
brightshift.click – Impressed by the quality of visuals and overall aesthetics.
https://sf464q0kbs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendforge.click – The site feels polished and professional, nice work.
https://m1vms0rqy8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wett tipp vorhersage
Here is my web site: Was ist kombiwette
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Подоконники из искусственного камня https://luchshie-podokonniki-iz-kamnya.ru в Москве. Рейтинг лучших подоконников – авторское мнение, глубокий анализ производителей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-портал про стройку https://donbass.org.ua и ремонт. Новости, проекты, инструкции, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё, что нужно знать о современном строительстве и архитектуре.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный портал https://msc.com.ua о ремонте, дизайне и технологиях. Полезные советы мастеров, обзоры материалов, новинки рынка и идеи для дома. Всё о стройке — от фундамента до отделки. Учись, строй и вдохновляйся вместе с нами!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал про стройку https://keravin.com.ua и ремонт полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры оборудования и материалов. Всё о строительстве домов, дизайне и инженерных решениях
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал про стройку https://dcsms.uzhgorod.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Полезные советы, статьи, технологии, материалы и оборудование. Узнайте о современных решениях для дома и бизнеса.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
order Stromectol discreet shipping USA [url=https://medivermonline.shop/#]generic ivermectin online pharmacy[/url] trusted Stromectol source online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://medivermonline.com/# Mediverm Online
Stromectol ivermectin tablets for humans USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wettquoten heute
Feel free to visit my web blog … beste wettanbieter ohne Oasis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten bonus angebote (Emanuel) gewinnen tipps
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
skyportal.click – Content is engaging and well-organized, makes browsing enjoyable.
https://u6ks8s6ge51.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boldimpact.click – The content is fresh, and the layout is user-friendly.
https://dm7k6eila.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
openlaunch.click – Enjoying the fresher themes, feels like a modern update.
https://5nd8p8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten lizenz kaufen
my web blog – wetten em spiele (https://picopalamagazine.com/beste-tipps-em)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
growwithfocus.click – If you got a link from someone, trace back to source and see if official.
https://bu5ka45la.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextbrand.click – The site feels polished and professional, nice work.
https://p446l.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
worldtrendspace.click – The site feels polished and professional, nice work.
https://6cs8l.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pixelstorm.click – Always find something new and interesting every time I visit.
https://o67rp.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nextgenmarket.click – Always find something new and interesting every time I visit.
https://1jdn050p.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
linkfusion.click – The user interface is smooth, making navigation a breeze.
https://hzvpwj7gj.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
urbanvision.click – The layout here is sleek and modern, very user-friendly.
https://8xpzfxj1uii.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
digitalnest.click – Content is engaging and well-organized, makes browsing enjoyable.
https://qysvmk0q.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cloudmark.click – Loved the recent article, very insightful and well written.
https://enet4iquf.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
goldenwave.click – Solid work — feels like a site made by someone who cares.
https://0vq60.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
linkmaster.click – Great site you’ve got here, the design is crisp and modern.
https://3rni772w5p9.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
futurebeam.click – This place gives a polished, modern impression from first glance.
https://ffwinb.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ideaorbit.click – For now, treat it cautiously — not enough public info to trust confidently.
https://nlgsov.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourbrandzone.click – Really liked the layout here, everything feels smooth and modern.
https://n60t5vd0.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boldspark.click – On mobile it adapts okay, no weird overlaps or broken styling I saw.
https://038y0i57yi.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thinkbeyondtech.click – If you saw this somewhere, I could help check if it’s part of the official firm.
https://x9qpby0.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cloudmatrix.click – Overall gives impression of being in early stage; use caution if sharing personal data.
https://gee-fit.com/product/geefit-honeybee-crop-tee/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный авто портал https://necin.com.ua мир автомобилей в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, сравнения, новости автопрома и советы экспертов. Будь в курсе последних тенденций автоиндустрии
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trendhunter.click – Nice work on design, it’s easy to browse and enjoy.
https://cswjg36btn8b.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Авто портал https://bestsport.com.ua всё об автомобилях: новости, обзоры, тест-драйвы, советы по уходу и выбору машины. Узнайте о новинках автопрома, технологиях и трендах автомобильного мира.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Авто портал https://psncodegeneratormiu.org мир машин в одном месте. Читайте обзоры, следите за новостями, узнавайте о новинках и технологиях. Полезный ресурс для автолюбителей и экспертов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
digitalstorm.click – Navigation is intuitive, found what I was looking for quickly.
https://nnkt9zy21.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Автомобильный портал https://autoguide.kyiv.ua для водителей и поклонников авто. Новости, аналитика, обзоры моделей, сравнения, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту машин разных брендов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн авто портал https://retell.info всё для автолюбителей! Актуальные новости, обзоры новинок, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и полезные советы по эксплуатации и обслуживанию автомобилей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverLastRx: order tadalafil 20mg – FDA-approved Tadalafil generic
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
urbanrise.click – I like the minimalism, pages feel uncluttered and easy to scan.
https://sf464q0kbs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic tadalafil for sale tadalafil 2.5 mg price or cost of tadalafil in canada tadalafil tablets 20 mg buy
http://topsiteswebdirectory.com/gr_domain_list/index.php?domain=pharmaexpressfrance.com generic cialis tadalafil uk or http://dnp-malinovka.ru/user/qcmwbskcdh/?um_action=edit online tadalafil prescription
[url=https://images.google.am/url?q=https://everlastrx.com]online tadalafil prescription[/url] generic tadalafil daily or [url=http://www.88moli.top/home.php?mod=space&uid=969]canadian online pharmacy tadalafil[/url] tadalafil 5mg best price
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://everlastrx.com/# Tadalafil tablets
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
lizenz sportwetten deutschland
Feel free to surf to my blog post – Basketball über unter wetten overtime
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://www.coloredreams.ru Подробные инструкции и пошаговые гайды по использованию. Виртуальный просмотр и 3D-презентации продукции.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
best10data – Might want to proceed with caution until more feedback or details emerge.
https://eak1fi2axfi.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
faquge – Looks good on my phone too, responsive without weird alignment issues.
https://pms9re.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverLastRx [url=https://everlastrx.shop/#]how to order Cialis online legally[/url] discreet delivery for ED medication
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://medivermonline.com/# Stromectol ivermectin tablets for humans USA
trusted Stromectol source online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ivermectin dose for goats with lice ivermectin horse paste for rosacea or ivermectin shampoo for head lice ivermectin for kids
http://go.iranscript.ir/index.php?url=https://medivermonline.com ivermectin 6mg tablet for lice and https://brueckrachdorf.de/user/buxbkxtzqc/ ivermectin horse paste for scabies
[url=http://www.hungryforchange.tv/Redirect.aspx?destination=http://bluepharmafrance.com]where to buy ivermectin pills[/url] what drugs interact with ivermectin and [url=https://forum.expert-watch.com/index.php?action=profile;u=486141]ivermectin for goat lice[/url] doctors who prescribe ivermectin online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Are you minimizing your transaction costs? This article provides a clear run-down of ParaSwap fees and gas, and strategies for low-cost swaps. Full explanation here: [url=https://paraswap.app/blog/paraswap-fees-and-gas-explained/]ParaSwap Fees Guide[/url]. Great advice for saving money.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
oarlop – Could use more in-depth content or blog-type updates to add value.
https://hwc6t0pd.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
x5748 – Fast load, layout’s minimal and doesn’t overwhelm the user.
https://g9oylfwozpc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
246123kj – Navigation links are clear — didn’t struggle to move between pages.
https://1j8ing1x.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bjjxyzp – Quick load and simple layout, overall feels clean and uncluttered.
https://pi6za0.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
660fh – Navigation is intuitive, didn’t struggle to find key sections.
https://o57hsj9e4cw.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский портал https://z-b-r.org ваш источник идей и вдохновения. Советы по красоте, стилю, отношениям, карьере и дому. Всё, что важно знать современной женщине.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
canineaffluent – Content is readable and well spaced, doesn’t feel cluttered.
https://jzi31n.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
goodthingsshare – Footer includes contact and policy links, gives confidence to users.
https://a4jb8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Интересный женский https://muz-hoz.com.ua портал о моде, психологии, любви и красоте. Полезные статьи, тренды, рецепты и лайфхаки. Живи ярко, будь собой и вдохновляйся каждый день!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский портал https://prins.kiev.ua всё о красоте, моде, отношениях, здоровье и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, вдохновение, психология и стиль жизни для современных женщин.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный женский https://novaya.com.ua портал о жизни, моде и гармонии. Уход за собой, отношения, здоровье, рецепты и вдохновение для тех, кто хочет быть красивой и счастливой каждый день.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн женский портал https://replyua.net.ua секреты красоты, стиль, любовь, карьера и семья. Читайте статьи, гороскопы, рецепты и советы для уверенных, успешных и счастливых женщин.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
303sahabat – Search feature returned accurate results, saved me a lot time.
https://si02lqr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
3915t – On mobile it works fine, no weird formatting issues or broken components.
https://9xhls4v5.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
snmm66 – Wish there was more background or about page to learn who’s behind this.
https://h1cm7b0s.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
eggaa – Just stumbled on this, looks clean and loads fast, nice job.
https://pzxoy36si9j7.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
jiandanai520 – No broken links so far, everything I tried worked fine.
https://lrljq.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для этого гидроизоляцию укладывают в промежутки между лагами https://al-keram.ru/blog/page-3.html
Затем засыпают слой керамзита, на который укладывают фольгированную пароизоляцию https://al-keram.ru/zakazat-keramzit-v-mytishchi.html
Для дополнительного тепла сверху можно положить еще слой другого утеплителя (пенопласт, пенополистирол) вровень с верхним краем лаг https://al-keram.ru/blog/nezamenimye-stroitelnye-materialy-gravij.html
Затем настилается деревянный пол, рейки которого прибивают к лагам https://al-keram.ru/blog/kak-ispolzovat-keramzit-na-dache.html
Читайте также: Утепление пола в деревянном доме снизу – как сделать и что использовать https://al-keram.ru/keramzit-s-dostavkoj-v-dmitrov.html
Расход керамзита обусловлен высотой слоя и размером покрываемой площади https://al-keram.ru/novosti/obnovilsya-prays-list.html
Возьмем стяжку толщиной 5 см на площади 20 м3 https://al-keram.ru/price.html
Подставляем эти данные в формулу: 5см х 20м3 х 0,01м3(расход на м2 высотой 1см) = 1 м3 = 1000 л Итого: для заданных параметров потребуется закупить 1000 литров керамзита https://al-keram.ru/contacts.html
Он фасуется в мешки по 50 литров https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzit/keramzit-v-big-begakh.html
Для организации стяжки понадобится 20 мешков данного материала https://al-keram.ru/aktsii/
Это приблизительные расчеты https://al-keram.ru/dokumenty-pokupatelyam.html
Они предоставят возможность оценить ориентировочное количество материалов https://al-keram.ru/blog/5-10.html
Приступая к работам, необходимо учесть некоторые особенности, с которыми сталкиваются строители https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzit/keramzit-v-big-begakh.html
Вам нужны теплые стены в своем загородном доме? Хотите обустроить красивые клумбы или садик? Для этих целей нужен качественный керамзит! Универсальный материал для строительства https://al-keram.ru/blog/primenenie-frakcii-keramzita-10-20-mm.html
Предлагаем продукцию https://al-keram.ru/blog/proizvodstvo-keramzita.html
https://al-keram.ru/blog/kak-vibrat-keramzit.html
https://al-keram.ru/blog/kak-uteplit-dom-keramzitom.html
Также для расчетов важно учитывать и пористость материала https://al-keram.ru/zakazat-keramzit-v-mytishchi.html
Так не стоит использовать очень крупную фракцию для полов, укладываемых на почву, так как он имеет очень высокою теплопроводимость, и конструкция будет нуждаться в дополнительном утеплении https://al-keram.ru/blog/5-10.html
Подготовка основания под засыпку керамзитом начинается с очистки поверхности https://al-keram.ru/blog/uteplenie-keramzitom.html
Чистое основание оценивают на кривизну и перепады плоскости https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzita/catalog-keramzita-v-big-begah.html
Это делают для того, чтобы увидеть, какой слой керамзита нужен для утепления пола, выравнивания поверхности и расчета требуемого количества материала https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzita/catalog-keramzita-rossypyu.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bulkytrader – Found some interesting wholesale items, impressed by the selection.
https://zaodmpyib.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Try to start earning with maximum profit automated trading software based on neural networks, with strong win-rate
https://aitredo.com
TG: @aitredo
WhatsApp: +972557245593
Email: sales@aitredo.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
56089m – Clean layout and fast loading — bookmarked to check updates later.
https://1jdn050p.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
k9c4fzmzxj1 – On my phone it adapts well — mobile view is responsive.
https://9a38suo9gfdu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Check out the full trading pairs list! This detailed overview covers all ParaSwap tokens and pairs. Full tokens and trading pairs list here: [url=https://paraswap.app/blog/paraswap-tokens-and-pairs/]ParaSwap Trading Pairs[/url]. Find the best liquidity for your trade.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yiikr – Looks like there’s potential here, already sharing it with friends.
https://wztbudoox1.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
56089h – Some images are crisp and relevant, not just filler visuals.
https://rnzxszt1.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
8222173 – Tried it on my phone too, works perfectly fine on mobile.
https://x4cncv.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
957420 – Found several useful resources here, will recommend to colleagues soon.
https://k8aim9ydd.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
764585 – No “About” or contact data appears in simple searches, proceed cautiously.
https://0plmu6t.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
instant sports wetten Wett Tipps erfahrungen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten online bonus ohne einzahlung (https://pinoydailynews.altervista.org/) gratis ohne einzahlung
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kytautoparts – Would be nice if they have a filter by make/model for parts.
https://ip6tmsm7.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
top sportwetten anbieter
Here is my web page; neue wettseiten
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten spiel
Look into my site; sportwetten vorhersagen heute
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Актуальный портал https://sinergibumn.com о стройке и ремонте. Современные технологии, материалы, решения для дома и бизнеса. Полезные статьи, инструкции и рекомендации экспертов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dadatudaohang – So far, not enough evidence to trust it fully.
https://m1vms0rqy8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Check the network support list! Read the full article covering all ParaSwap supported networks and tokens. Check the complete list here: [url=https://paraswap.app/blog/paraswap-supported-networks-and-tokens/]ParaSwap Networks List[/url]. Massive compatibility for all DeFi users.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал о стройке https://mr.org.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Статьи, советы экспертов, современные технологии и обзоры материалов. Полезная информация для мастеров, инженеров и владельцев домов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The User Experience (UX) is flawless! This guide covers all ParaSwap wallets and UX integration tips. Wallet integration guide here: [url=https://paraswap.app/blog/paraswap-wallets-and-ux/]ParaSwap Wallets Guide[/url]. Seamless integration with MetaMask.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://www.coloredreams.ru Сравнительные таблицы и подробные описания для удобного выбора. Достоверная информация по всем позициям.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный портал https://repair-house.kiev.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Подробные статьи, обзоры материалов, советы экспертов, новости отрасли и современные технологии для профессионалов и домашних мастеров.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
order gabapentin discreetly: order gabapentin discreetly – order gabapentin discreetly
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten dass quote
Look at my site: Wettanbieter Mit Den Besten Quoten
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I simpky could not go away your web site prior to suggesting that I actually
enjoyed the usual information an individual supply in your guests?
Is gonna be back steadily in order to check up on new
posts
My homepage; Cheap SEO Services
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
This Is The Advanced Guide To Car Key Signal Issue Repair car key ignition switch repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://everlastrx.shop/# EverLastRx
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online pharmacy Prednisone fast delivery [url=http://predniwellonline.com/#]how to get Prednisone legally online[/url] Prednisone tablets online USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В архитектурном бизнесе компания с 2013 года https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
Специализируются в основном на проектировании и строительстве загородных домов https://www.abbalk.ru/
Хотя с локальными задачами по индивидуальным запросам тоже сталкиваются довольно часто https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Среди услуг также реконструкция зданий, конструктивное и инженерное проектирование https://www.abbalk.ru/arhitectyra
Как выбрать архитектурное бюро в Москве https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
Петербургское архитектурное бюро https://www.abbalk.ru/gradostroitelstvo
Специалисты занимаются реконструкцией зданий, проектируют жилые комплексы и крупные арт-объекты https://www.abbalk.ru/arhitectyra
Бюро работает в сферах градостроительной разработки, возведения и реконструкция зданий, а также создает общественные интерьеры https://www.abbalk.ru/arhitectyra
Клиентам доступен предпроектный анализ участка и авторский надзор за строительством https://www.abbalk.ru/interier
Частный дом в Тель-Авиве Фото: архитектурная студия Fas(t)
Создать первое впечатление можно только один раз https://www.abbalk.ru/arhitectyra
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Job Market For Vehicle Keyless Start Repair Professionals Like?
Vehicle keyless start repair (https://articlescad.com/15-reasons-why-you-shouldnt-be-ignoring-car-key-signal-issue-repair-288104.html)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Car Key Sensor Repair: The Intermediate Guide
To Car Key Sensor Repair Car Key Sensor Repair (Mlx.Su)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Car Ignition Repair Tools To Help You Manage Your Everyday Lifethe Only Car Ignition Repair Trick Every Individual
Should Learn car ignition Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
prednisone uk buy prednisone canada prices or prednisone for sale prednisone price
http://www.codetools.ir/tools/static-image/4.php?l=http://pharmalibrefrance.com buy prednisone without rx or https://gikar.it/user/jtvnfheilf/ where to buy prednisone 20mg
[url=http://images.google.co.th/url?q=https://predniwellonline.com]54 prednisone[/url] prednisone no rx or [url=http://lostfilmhd.com/user/kcbkeooqyd/]prednisone 20mg price[/url] prednisone 100 mg
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Current Job Market For Keyless Fob Repair Professionals Like?
Keyless Fob Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Car Key Shell Repair Tools To Streamline Your Everyday
Lifethe Only Car Key Shell Repair Trick That Everybody Should Be Able To Car Key Shell Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
jingcaity – Let me investigate domain history and report useful findings to you.
https://ui654.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
www9tt6 – Let me fetch archival snapshots or server data to see what was there before.
https://9a38suo9gfdu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Prednisone without prescription USA: online pharmacy Prednisone fast delivery – online pharmacy Prednisone fast delivery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
haxorisme – Looks like an unfamiliar domain, didn’t see much credible info.
https://0rvwwsgxbzlr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
See What Car Keyless Start System Repair Tricks The Celebs Are
Making Use Of Car Keyless Start System Repair (Marie)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy generic tadalafil cheap generic tadalafil 5mg or where to buy tadalafil in usa cost of tadalafil generic
http://arcadepod.com/games/gamemenu.php?id=2027&name=idiots+delight+solitaire+games&url=https://everlastrx.com buy cheap tadalafil online and http://orbita-3.ru/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=34690 buy tadalafil europe
[url=https://maps.google.com.kh/url?sa=t&url=https://everlastrx.com]tadalafil 5mg tablets price[/url] buy tadalafil 10mg india and [url=http://ussher.org.uk/user/yabfxvugar/?um_action=edit]buy tadalafil from canada[/url] tadalafil 2.5 mg tablets
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mashoppy – Great first glance, hope shipping is as smooth as design.
https://gbzv9cg0w.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
358799 – Might be parked or under construction, content is minimal.
https://hzvpwj7gj.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
www9tt9 – Better to treat it with suspicion until verified properly.
https://g5abt8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bmrlw – Everything loads well, content seems organized and nicely put together.
https://0cbznj85o3u.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
202496 – It could be dormant or under construction, not clearly active.
https://pw7yu83sg.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://nm5tkpeyvu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
www9tt05 – It may be inactive or used as placeholder; no content found yet.
https://eqgp9xr4q.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
www9tt9 – If someone asks for personal or payment info, verify carefully first.
https://kk3me.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
www9tt04 – Frequent IP changes often point to redirecting or disposable domain usage.
https://942cmhq69k.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dsjy0916 – If you share what you expected this domain to be, I can tailor the check.
https://b1tsztor1.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
www9tt01 – The domain gives minimal trust signals, be careful engaging.
https://rnbme.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mg2jp – The site loading as redirect with “Trust 69 / Privacy 69” is odd.
https://t2h4hnqm.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
hotel-reservation-rome.com – The domain gives mixed feelings, verify credentials before booking.
https://6cs8l.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
832899 – Interesting domain name, loaded quite fast and smooth.
https://359wfi.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
xfbsp666 – Wish there were more examples or case studies though.
https://pdyorv.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
11xhh – Found something cool just by scrolling randomly, nice discovery.
https://woqea9.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ma3wna – I’d love to see more about their mission or about-page details.
https://ctrwdz8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tingshuzu – Clean layout, content is readable and not overwhelming at all.
https://copaf.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bsporttiyu – I wish there were more article variety, but pretty good so far.
https://n5lltmin530.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectwiththeworldnow – I’ll return to this, it seems like a project with real potential.
https://safasf.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
+1
https://sonq93ter.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
affordable Neurontin medication USA: gabapentin capsules for nerve pain – gabapentin spinal surgery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectwiththeworldnow – Every section feels purposeful, style aligns well with the cause.
https://safasf.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
zxjgzxfuzhou – Navigation feels fluid, no broken links so far, thumbs up.
https://c9o54.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Five Killer Quora Answers On Keyless Entry Remote Repair Keyless Entry Remote Repair, Sal,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужна карта? иностранная карта из Киргизии как оформить зарубежную банковскую карту Visa или MasterCard для россиян в 2025 году. Карту иностранного банка можно открыть и получить удаленно онлайн с доставкой в Россию и другие страны. Зарубежные карты Visa и MasterCard подходят для оплаты за границей. Иностранные банковские карты открывают в Киргизии, Казахстане, Таджикистане и ряде других стран СНГ, все подробности смотрите по ссылке.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic gabapentin pharmacy USA [url=https://neurocaredirect.com/#]generic gabapentin pharmacy USA[/url] neuropathic pain relief treatment online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://predniwellonline.shop/# Prednisone tablets online USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The Reasons Why Smart Key Repair Is The Most-Wanted Item In 2025 car smart key repair (output.jsbin.com)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[url=http://coloredreams.ru/]https://coloredreams.ru[/url] Готовые решения и сбалансированные наборы для отдельных категорий. Экономьте время с сформированными пакетами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://predniwellonline.shop/# how to get Prednisone legally online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Смотри аниме онлайн https://anime2027.ru бесплатно и без регистрации! Лучшие сериалы, фильмы и новинки в хорошем качестве — от классики до свежих релизов. Погрузись в мир ярких эмоций, магии и приключений. Удобный плеер, ежедневные обновления и любимые герои ждут тебя прямо сейчас!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Смотри аниме онлайн https://anime2027.store в хорошем качестве — тысячи серий, новые релизы и вечная классика в одном месте! Погрузись в мир приключений, романтики и фантазии, следи за любимыми героями и открывай новые истории. Удобный плеер, обновления каждый день и полное погружение в атмосферу Японии!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
gabapentin burning pain gabapentin lido keto 5 or is gabapentin good for sleep amitriptyline versus gabapentin
https://maps.google.co.nz/url?q=https://neurocaredirect.com gabapentin tablets 300 mg and https://www.trendyxxx.com/user/wtdjqeykbf/videos gabapentin upper back pain
[url=https://images.google.at/url?q=https://neurocaredirect.com]gabapentin tablets 300 mg[/url] using gabapentin for sciatica and [url=https://www.soumoli.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=853073]gabapentin dosage instructions[/url] stability of gabapentin 300 mg capsules repackaged in unit dose containers
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
quote bei wetten dass
Check out my web blog :: sportwetten tipps facebook
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Путешествуйте по Крыму https://м-драйв.рф на джипах! Ай-Петри, Ялта и другие живописные маршруты. Безопасно, интересно и с профессиональными водителями. Настоящий отдых с приключением!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
FDA-approved Tadalafil generic: Tadalafil tablets – FDA-approved Tadalafil generic
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Смотри лучшие китайские https://animelist.ru аниме дунхуа онлайн — эпические битвы, древние легенды и захватывающие приключения! ? Яркая анимация, глубокие сюжеты и дух Востока создают уникальную атмосферу. Погрузись в мир магии и героизма, где каждый кадр — произведение искусства!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wett quoten
Also visit my web-site – Sportwetten Online Mit Lastschrift
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
elmhurstunited – I enjoyed browsing, the flow is smooth and content is engaging.
https://safasf.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
ПокерОК сайт
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
Официальный сайт онлайн рума ПокерОК
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bnnnw – Nice layout, feels clean and pretty easy to navigate.
https://pms9re.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Смотри лучшие турецкие сериалы https://bryansktoday.ru/article/247141 онлайн — истории о любви, предательстве и судьбе, которые не отпускают с первой серии! Погрузись в атмосферу восточного шарма, почувствуй эмоции героев и открой для себя мир, где страсть и честь идут рука об руку. Новые серии каждый день!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт ПокерОК
ПокерОК
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Погрузись в атмосферу китайских дорам https://bryansktoday.ru/article/247115 исторических саг, романтических историй и современных драм! Здесь тебя ждут лучшие сериалы с глубокими сюжетами, красивой картинкой и харизматичными актёрами. Смотри онлайн и окунись в мир восточной любви и вдохновения!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
7392004 – Simple homepage, hope the inner pages bring solid content.
https://nlgsov.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
NeuroCare Direct: Neurontin online without prescription USA – Neurontin online without prescription USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
apphoki – Looks modern, curious what services or apps they offer.
https://qhkjwb.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
п»їwhere to buy stromectol online ivermectin mechanism and tractor supply ivermectin pour-on ivermectin for ringworm
https://www.google.is/url?q=https://medivermonline.com ivermectin treatment and https://pramias.com/profile/lcayqbiiva/ ivermectin pour-on for goat mites
[url=https://maps.google.ro/url?q=https://medivermonline.com]ivermectin covid-19[/url] where to buy ivermectin pills or [url=https://afafnetwork.com/user/tqibdfsidl/?um_action=edit]ivermectin overdose cattle[/url] jr enterprises ivermectin
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Prednisone tablets online USA [url=https://predniwellonline.com/#]PredniWell Online[/url] Prednisone tablets online USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://predniwellonline.com/# online pharmacy Prednisone fast delivery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
schenectadybathroomremodeling – I’ll suggest this to friends needing remodels; it looks well done.
https://dzli92u87g.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
heima999cp – This site feels well-built, no clutter, just good solid information.
https://hyb7203l0a.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
881625 – I visited and the layout seems well structured already.
https://oom8jnr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
031757 – The homepage feels fresh, curious what’s inside.
https://b5o1gh4.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
khawajakhawarrashid – Hope the content is rich and helpful, looks like potential.
https://si02lqr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
selvaluna – Clean design, hope navigation links are easy to find inside.
https://hyb7203l0a.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
btc289 – Clean first look, hope inner pages are equally polished.
https://45h3zla.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
88878qp – If content matches design quality, this will be useful.
https://9xhls4v5.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
9909hd – Nice first impression, I’ll revisit when more content is visible.
https://e5mekv.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
7558app – If content matches the design, this could be a top resource.
https://qqjdxf.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sahabetaff – I’d like to see more blog posts or case studies here.
https://k39jcco67rue.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
hg889988 – Clean homepage design, I’ll check back when content is ready.
https://o67rp.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
16999ys – Clean homepage, makes me want to click further inside.
https://kv1tok.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
zhgsguangning – This site looks interesting, hope content is high quality soon.
https://3ve3h1e.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
122yyy – Good start, hope the content lives up to the design.
https://agoqkmd3i.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Astute reward advise concerning Manta Pacific users: Use the official, sure Manta Connect: [href=https://manta-bridge-app.github.io/]Manta Join App
Highly vouch for as a replacement for sickly fees and hurried execution. Link: https://manta-bridge-app.github.io/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1001-webtest – Minimalist style fits well, waiting for content to appear.
https://pms9re.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
868i – Clean layout, gives a professional first impression.
https://c9o54.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Chance to start earning with super success automated trading software based on neural networks, with huge win-rate
https://aitredo.com
TG: @aitredo
WhatsApp: +972557245593
Email: sales@aitredo.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
togelrejeki – The site loads quickly, and the design is modern.
https://0cbznj85o3u.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
xinyurenedu – An indispensable platform for students pursuing higher education.
https://xpteg0pt0.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello !!
I came across a 139 great site that I think you should explore.
This site is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find valuable.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://consumerhelpunit.org/progressive-slots/jim-morrison-an-icon-of-rock-and-roll/]https://consumerhelpunit.org/progressive-slots/jim-morrison-an-icon-of-rock-and-roll/[/url]
Additionally don’t neglect, guys, which you constantly are able to inside the piece locate answers to address the the absolute confusing questions. Our team attempted — lay out all of the data in an extremely accessible way.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
150 free spins australia, online casino no deposit bonus free spins usa and casinos for
gambling Basic strategy for Craps usa,
or vegas usa casino
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Открой для себя мир китайского аниме https://prokazan.ru/adverting/view/kitajskoe-anime-vzlet-i-razvitie-animacionnoj-industrii захватывающих дунхуа, наполненных магией, древними легендами и невероятной анимацией! ? Смотри лучшие новинки и хиты онлайн, следи за приключениями героев, погружайся в атмосферу Востока и ощути силу настоящего искусства из Китая!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Погрузитесь в мир турецких сериалов https://turkyserial2026.ru ярких эмоций, страстей и неожиданных сюжетных поворотов! Здесь собраны лучшие драмы, мелодрамы и комедии, покорившие сердца зрителей по всему миру. Смотрите онлайн, наслаждайтесь атмосферой восточного колорита и живите историей вместе с героями!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Inaugurate the foremost L2 unite: Employ the decorous, anchor Manta Link: [href=https://manta-bridge-app.github.io/]Manta Join App
It’s fast and fast inasmuch as cross-chain transfers. Connect: https://manta-bridge-app.github.io/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
blur-blur – Helpful tips and insights, makes browsing enjoyable.
https://r6c848.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
0080kk – Consistently good content, keeps me informed and engaged.
https://kbtzcnor6h.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
legal gambling age in united states, the united states casino video and play aristocrat pokies online australia, or win real
money online casino for free usa
Visit my page – mini blackjack side scuttles (http://www.canadaimoveis.net)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
40 mg daily prednisone prednisone without prescription.net and prednisone uk prednisone for sale online
https://www.google.cg/url?q=https://predniwellonline.com prednisone 10 mg over the counter or https://vintage-car.eu/user/hdodxulblb/ prednisone sale
[url=https://images.google.com.co/url?sa=t&url=https://predniwellonline.com]prednisone canada prices[/url] prednisone for sale in canada and [url=http://erooups.com/user/hebiqngmnw/]prednisone 30 mg daily[/url] prednisone in uk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Керамзитовый песок относится к категории сыпучих материалов и используется наравне с щебнем и гравием https://al-keram.ru/blog.html
Он оптимально подходит для обустройства придомовой территории https://al-keram.ru/blog/nezamenimye-stroitelnye-materialy-gravij.html
Также песок незаменим в оформлении https://al-keram.ru/contacts.html
https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzit/keramzit-v-meshkah-fraktsii-20-40-m200350-detail.html
https://al-keram.ru/blog/keramzit-harakteristiki.html
Далее необходимо осуществить смешивание https://al-keram.ru/price.html
Порция должна состоять из 1 части цемента, 2 просеянного песка, 1 воды, а также в зависимости от уровня будущих нагрузок на пол от 3 до 5 долей керамзита https://al-keram.ru/review.html
ООО компании при регистрации был присвоен ОГРН 1134253002597 и ИНН 4253014026 https://al-keram.ru/o-kompanii.html
Начиная с 2013 фирма расположена по адресу 654041, Кемеровская Область, Новокузнецк Город, Транспортная Улица, 77 https://al-keram.ru/blog/keramzit-otlichnyj-material-dlya-teploizolyatsii-zdanij.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Found the most talented L2 cross over: Use the decorous, immovable Manta Connect: [href=https://manta-bridge-app.github.io/]Manta Bridge App
Well vouch for in search unrefined fees and summary execution. Connect: https://manta-bridge-app.github.io/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discreet delivery for ED medication: safe online pharmacy for ED pills – FDA-approved Tadalafil generic
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Testy hint for Manta Pacific users: Employ the official, immovable Manta Connect: [href=https://manta-bridge-app.github.io/]Manta Span App
Strongly recommend for unrefined fees and summary execution. Connect: https://manta-bridge-app.github.io/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Spirited hint in compensation Manta Pacific users: Employ the decorous, anchor Manta Link: [href=https://manta-bridge-app.github.io/]Manta Pacific Bridge
Enthusiastically plug as a replacement for decrepit fees and quick execution. Connect: https://manta-bridge-app.github.io/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis tadalafil tadalafil online australia and tadalafil 10mg coupon tadalafil 5mg tablets in india
https://www.google.com.my/url?sa=t&url=https://everlastrx.com best tadalafil tablets in india or http://erooups.com/user/ixqifldsei/ buy tadalafil online australia
[url=https://maps.google.is/url?q=https://everlastrx.com]tadalafil online india[/url] cost of tadalafil generic and [url=http://www.88moli.top/home.php?mod=space&uid=936]tadalafil from india[/url] tadalafil generic in usa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ilili1oulilil5 – Some pages feel empty, content depth needs work to feel richer.
https://oom8jnr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online pharmacy Prednisone fast delivery: Prednisone without prescription USA – Prednisone without prescription USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
PredniWell Online [url=https://predniwellonline.shop/#]purchase prednisone from india[/url] how to get Prednisone legally online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://medivermonline.com/# generic ivermectin online pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://predniwellonline.com/# PredniWell Online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
allking89 – The site feels intentional, content and structure align nicely together.
https://safasf.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
qi29 – Love how everything works smoothly here, no annoying popups at all.
https://u3fbhw.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
8runner – This site feels legit, and I’d totally come back again soon.
https://nh7pfmc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
xxb00 – Navigation is smooth, and the articles are well-written.
https://8fkiywcma6.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
marlborodoublefusion – Fast loading pages and clean menus, makes browsing a pleasure.
https://hf6on6.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
482429 – Content is informative, love the examples and easy explanations shared.
https://h62rrn.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
accountingservicesgoa – Their team is knowledgeable and always ready to assist.
https://359wfi.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
0250f – This site offers valuable information in a user-friendly format.
https://paar.com.ar/index.php/2022/04/10/service-marketing-in-b2b/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
moviethai4u – Navigation is easy, thumbs up for clear categories and layout.
https://nlgsov.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dancizuci – Nice layout, reading articles here is easy and enjoyable.
https://nb3jn87ai.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
jqdsu – Might revisit later — this feels like a project in progress.
https://0ujn69ntt3lh.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
88878qp – The structure is basic, works for a starting point but needs depth.
https://4f0kndm9nbv3.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Pizza Express liefert wirklich express! In 20 Minuten hatte ich meine Pizza.
Pizzabestellung
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
blossompaperart – Feels like a craft-lover’s spot, creative energy is strong here.
https://39g7fluh.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
78y29h – Some content is vague, hope it becomes more detailed soon.
https://hyb7203l0a.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
powerpres – Content seems meaningful, not just filler, which I respect.
https://l8nd6uub.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thefutureofinnovation – The thematic focus feels coherent, topics tied together nicely overall.
https://grssvtqqnpwr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourtrustedguideforlife – The headings pull me in, content seems thoughtful and real.
https://fc7w2j0iib2.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thebestplacetostarttoday – Images match the topics well, they add value to reading.
https://ypwlo21.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yourjourneytobetterliving – Everything loads nicely and the design feels like quality.
https://fdacht6k6grs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
explorecreativeideasdaily – I kept scrolling and found ideas I actually want to try tonight.
https://5dwtxxw.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
x-xa – Pages sometimes load slowly, but eventually all content shows.
https://4c0nz.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
findwhatyouarelookingfor – This site feels welcoming, I already found something useful.
https://eul2u5zkx1st.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
learnsomethingneweveryday – I enjoy the spacing and margins, nothing feels cramped or messy.
https://ual4hxo.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
everythingyouneedtoknow – The balance of text and visuals is handled nicely throughout.
https://f59nc15vh8j.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nyrw84.top – I hope you’ll build more pages soon — potential for a neat site.
https://nb3jn87ai.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Stromectol ivermectin tablets for humans USA: Stromectol ivermectin tablets for humans USA – Stromectol ivermectin tablets for humans USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discoveramazingthingsonline – Clean visuals, strong presentation, the vibe is positive and inviting.
https://safasf.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
2jasabola.biz – Overall looks promising — I’ll keep an eye on how this evolves.
https://0vq60.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
free casino games in united states, new zealandn online casinos
no deposit and cash freuky casino free chips, or online casino with free mobile no deposit bonus [Hilton] signup bonus
real money usa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
easy-software.online – I checked out your site; the software names are intriguing and concise.
https://rr8jqk.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
awsmining – I like their color scheme and how easy navigation is.
https://sihsu91ka.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Есть металлолом? berulom24 мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг по приему металлолома в Санкт-Петербурге, включая оперативную транспортировку материалов непосредственно на перерабатывающий завод. Особое внимание мы уделяем удобству наших клиентов. Процесс сдачи металлолома организован максимально комфортно: осуществляем вывоз любых объемов металлических отходов прямо с вашей территории.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Хочешь сдать металл? сдать металлолом стоимость наша компания специализируется на профессиональном приёме металлолома уже на протяжении многих лет. За это время мы отточили процесс работы до совершенства и готовы предложить вам действительно выгодные условия сотрудничества. Мы принимаем практически любые металлические изделия: от небольших профилей до крупных металлоконструкций.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
low-cost ivermectin for Americans: ivermectin-pyrantel – generic to heartgard plus – low-cost ivermectin for Americans
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic gabapentin pharmacy USA [url=http://neurocaredirect.com/#]generic gabapentin pharmacy USA[/url] neuropathic pain relief treatment online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello team!
I came across a 139 awesome tool that I think you should dive into.
This resource is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find helpful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://icme09.org/betting/the-strategy-game-of-chess/]https://icme09.org/betting/the-strategy-game-of-chess/[/url]
And do not overlook, guys, that one at all times can inside this particular article find answers for your the very confusing queries. The authors made an effort — explain the complete information via an very accessible manner.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
connectwiththeworldnow – Their mission seems bold, site feels ambitious yet hopeful.
https://safasf.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ivermectin lotion (sklice) п»їwhere to buy stromectol online and ivermectin cream for scabies ivermectin protocol
http://maps.google.co.ls/url?sa=t&url=https://medivermonline.com ivermectin for heartworm prevention or https://vintage-car.eu/user/rbaxdzrvau/ ivermectin ebv
[url=http://maps.google.co.nz/url?q=https://medivermonline.com]ivermectin for humans dosage[/url] ivermectin or [url=http://ragnarokneon.online/home.php?mod=space&uid=4187]ivermectin fda[/url] ivermectin for dogs dosage in mg
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://medivermonline.com/# low-cost ivermectin for Americans
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
the great united statesn casino everett, casinos in ontario canada and free bingo games united
states, or best uk casino offers
Also visit my blog … rent gambling machine (Tyrell)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё о металлообработке https://j-metall.ru и металлах: технологии, оборудование, сплавы и производство. Советы экспертов, статьи и новости отрасли для инженеров и производителей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Neurontin online without prescription USA: gabapentin 400 mg – FDA-approved gabapentin alternative
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
prednisone 5443 prednisone for sale without a prescription and prednisone 50 mg canada buy prednisone online paypal
http://www.kimberleychamber.com/redirect.aspx?destination=http://pharmalibrefrance.com prednisone canada prices or https://www.ipixels.com/profile/169770/xpclnhzbbi buy prednisone tablets online
[url=http://club.dcrjs.com/link.php?url=https://predniwellonline.com::]can you buy prednisone over the counter in mexico[/url] generic prednisone online and [url=http://georgiantheatre.ge/user/ydvocfmrkz/]prednisone 5mg over the counter[/url] prednisone 2.5 mg price
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
diamondescort18 – Looks super polished today, really appreciate the little details added.
https://vbmclu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nyrw84.top – I visited and the layout feels minimal but intriguing.
https://3zzztnlrit5y.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
An intelligent AI ChatBot for generating content, posts, images, and website optimization. Easy installation, flexible settings, and full AI support.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
michaeldfountain – Overall, a strong portfolio site — impressive work and representation.
https://36efmksl.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trackseries – Overall impression is professional and exciting — well done.
https://akd3qlrqehok.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
9hxn2 – Good whitespace usage, nothing feels cramped or overwhelming.
https://pzxoy36si9j7.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
awsmining – I enjoy how simple it is to find what I want.
https://0xxqw.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ureyo – I enjoy how uncluttered everything is, minimal but functional.
https://h1cm7b0s.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
420smokeshop – I like how links are placed logically, no guesswork needed.
https://prmjh.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
charitydriveforservicemembers – It’s great seeing transparency in where funds go and how they help.
https://17479h2tdumr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
linkrootes – Creative touches sprinkled throughout, makes browsing more fun.
https://agoqkmd3i.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
diamondescort18 – Been scrolling for a while, everything looks legit and organized.
https://k8aim9ydd.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
otistaylorjr – I like how your personal style shines through every page.
https://ku0wnli2.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
2jasabola.biz – Your branding stands out, caught my eye almost immediately.
https://5x9o3h0vm.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
easy-software.online – Great typography use—text is readable without harsh strain on eyes.
https://sm3lasas.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
housepartyofhorrors – The copywriting is engaging, pulls me deeper into the concept.
https://k2fnmarvru.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
vuabat – It feels professional yet approachable—nice brand voice.
https://oom8jnr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
knockoutzakk – Found your about section engaging — you’ve got a clear voice.
https://rwu0a.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
erinkristensen – The visuals are striking; your portfolio makes a strong first impression.
https://dm7k6eila.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
are top online pokies and casinos united kingdom open, bet365 united
statesn roulette tips and are there casinos in montreal united kingdom, or $10 deposit usa casinos
My webpage … how far is thunder Valley casino from here
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kruisefest – Overall, a fresh and exciting festival site experience.
https://3zzztnlrit5y.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
maccabeestraders – I like how cleanly the product sections are laid out overall.
https://yphkpql.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
guitargodscollectibles – I’m impressed by the attention to guitar details and specs.
https://b5o1gh4.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fullumandholt – The branding feels elegant, like it fits a high-end design studio.
https://7y61u4.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
blpawards – Seems like a good platform for recognition in creative fields.
https://bscm8ie.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
appytrucksandskulls – The visuals hit hard, gives real personality to the brand.
https://00ehyzv9tt.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
janetfortampa – Excited to see how this evolves in the art community.
https://prmjh.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
successmarketboutique – Browsing through, I can see how this could help artists globally.
https://beco88x.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Prednisone without prescription USA: online pharmacy Prednisone fast delivery – Prednisone without prescription USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
colossal-heart – It’s refreshing to see innovation in the art world like this.
https://samn1b.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
hellgate100nyc – Excited to see how this evolves in the art community.
https://k39jcco67rue.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ouretiquette – Just explored this site; the concept of art verification is intriguing.
https://942cmhq69k.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ukrainianvictoryisthebestaward – Sounds passionate; award concept like this can inspire many.
https://dzli92u87g.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafil soft gel capsule 20mg generic tadalafil in canada or tadalafil free shipping tadalafil online no prescription
https://cse.google.dm/url?q=https://everlastrx.com tadalafil online price and http://georgiantheatre.ge/user/uqhgeismku/ buy tadalafil india
[url=https://images.google.dj/url?sa=t&url=https://everlastrx.com]tadalafil online united states[/url] generic tadalafil medication and [url=https://allchoicesmatter.org/user/glymunqhcu/?um_action=edit]tadalafil online prescription[/url] tadalafil 20 mg price canada
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
redhillrepurposing – Browsing through, I can see how this could help artists globally.
https://1mlcp.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online pokies gambling australia, usa no deposit casino bonus list
and best casino in ms (Deanne) slot sites usa 2021, or paying tax on gambling winnings australia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
whollywoodhalloween – My friends and I loved the decoration tips from your blog.
https://enet4iquf.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Tadalafil tablets [url=https://everlastrx.com/#]safe online pharmacy for ED pills[/url] EverLastRx
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
For hottest news you have to visit the web and on web I found this site as a
finest web site for
latest updates.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://predniwellonline.com/# online pharmacy Prednisone fast delivery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://medivermonline.com/# Mediverm Online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
safe online pharmacy for ED pills: safe online pharmacy for ED pills – FDA-approved Tadalafil generic
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wexfordliteraryartsfestival – The idea of a global art registry feels like a game-changer.
https://nh7pfmc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
theberserkeriscoming – This could really streamline the process of art authentication.
https://sl6oo.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
islingtondesigndistrict – Love how they’re combining technology with art authenticity.
https://gxbs5.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
how to get Prednisone legally online: online pharmacy Prednisone fast delivery – Prednisone without prescription USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trusted Stromectol source online [url=https://medivermonline.shop/#]Mediverm Online[/url] trusted Stromectol source online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[url=http://coloredreams.ru/]https://coloredreams.ru[/url] Удобный интерфейс и мультиустройственная поддержка для просмотра с телефона. Комфортная навигация на всех платформах.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
blegacyfarms – Browsing through, I can see how this could help artists globally.
https://enet4iquf.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
aworldofgin – Love how they’re combining technology with art authenticity.
https://1j8ing1x.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
alixrice – The idea of a global art registry feels like a game-changer.
https://3xfq6z.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shopmaggielindemann – The idea of a global art registry feels like a game-changer.
https://gi9eo7j8x.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
colossal-heart – This could really streamline the process of art authentication.
https://rssbqe6.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ouretiquette – I appreciate the transparency this site offers to artists and buyers.
https://nb3jn87ai.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
redhillrepurposing – Excited to see how this evolves in the art community.
https://eak1fi2axfi.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
hellgate100nyc – The platform’s design is clean and user-friendly.
https://3zzztnlrit5y.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wagisonsncompany – I appreciate how well organized the pages are, navigation flows nicely.
https://safasf.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сайт кракен тор позволяет обойти возможные блокировки и получить доступ к маркетплейсу. [url=https://www.dravidianuniversity.ac.in/]кракен актуальная ссылка на сегодня[/url] необходимо искать через проверенные источники, чтобы избежать фишинговых сайтов. kraken зеркало должно обновляться регулярно для обеспечения непрерывного доступа.
onion – главная особенность Кракен.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Tadalafil tablets: EverLastRx – Tadalafil tablets
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
IPTV форум https://vip-tv.org.ua/ место, где обсуждают интернет-телевидение, делятся рабочими плейлистами, решают проблемы с плеерами и выбирают лучшие IPTV-сервисы. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу интернет-ТВ!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Need porn videos or photos? best ai porn generator – create erotic content based on text descriptions. Generate porn images, videos, and animations online using artificial intelligence.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
crowltheselinks – Offers look vague, would like to see clearer descriptions.
https://ko5sn27g.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
googlerankmaster – Quick loading and smooth scrolling, nice user experience so far.
https://uh3ji968upn.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
live-sex-cam – I’m genuinely impressed with the smooth performance and instant loading.
https://17479h2tdumr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
artvoyage – I spent hours browsing the galleries, truly captivating art pieces.
https://pi6za0.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
liveforextrading – I like how they break down signals and indicators simply.
https://0vq60.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thefreemath – Navigation is smooth, I could move between topics without confusion.
https://t6ilse.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
saltburn – It has potential if they fill it with quality content and visuals.
https://8iaoi63.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dhpb-smile – I visited briefly, the design feels basic but functional so far.
https://wt7aa90btl.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
affordable Neurontin medication USA: neuropathic pain relief treatment online – generic gabapentin pharmacy USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
papamasque – This site exudes elegance and intrigue, I’m eager to see more.
https://safasf.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
low-cost ivermectin for Americans [url=http://medivermonline.com/#]Stromectol ivermectin tablets for humans USA[/url] order Stromectol discreet shipping USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
axin2 – Just found this site, layout is clean and very approachable.
https://ddv8fuznvs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
antsmarket – The domain looks quite young, many pages appear parked or unused so far.
https://z2mqhs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wraoys – Would be nice to see a blog or “about us” to understand its purpose.
https://g0iwzn5it.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cyrusmining – Might be a cloud-mining project, but transparency isn’t clear yet.
https://f59nc15vh8j.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://neurocaredirect.com/# neuropathic pain relief treatment online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
legitimate canadian online casinos, united kingdom online
casinos and run it once poker canada, or casino
chips canada
Also visit my site: odds of winning roulette 30 times in a row
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discreet delivery for ED medication: FDA-approved Tadalafil generic – Tadalafil tablets
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Need TRON Energy? buy tron energy instantly and save on TRX transaction fees. Rent TRON Energy quickly, securely, and affordably using USDT, TRX, or smart contract transactions. No hidden fees—maximize the efficiency of your blockchain.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Seo аудит https://seo-audit-sajta.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
newstoday – Definitely bookmarking this, will visit daily for updates.
https://0plmu6t.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
triple shot pokies united states, no deposit online slots usa and united kingdom internet casino, or canadian online
casino with $5 deposit
My web page – Goplayslots.Net
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
no deposit mobile casino bonus uk, free poker chips no deposit uk and free spins
no deposit casino uk new, or $5 min deposit new casino in south philly
zealandn casinos
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
prednisone 50 mg tablet canada: how to get Prednisone legally online – Prednisone tablets online USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Chance to start earning with superior quality automated trading software based on neural networks, with fenomenal win-rate
https://aitredo.com
TG: @aitredo
WhatsApp: +972557245593
Email: sales@aitredo.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy amoxil [url=https://amoxdirectusa.shop/#]Buy Amoxicillin for tooth infection[/url] Amoxicillin 500mg buy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
best australia odds in casino baccarat – oceanofgames.pk, no deposit bonus, usa casino bonuses and no deposit cash
bonus casino canada, or online uk casino woth 24 hours payout
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
htechwebservice – Found exactly what I was searching for, thanks for sharing.
https://z2mqhs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Clomid price: Clomid price – Generic Clomid
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
u888vn – Informative posts and handy guides make this a go-to site.
https://n60t5vd0.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pacerproes – Smooth navigation, everything is where you expect it to be.
https://sonq93ter.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В отличие от других участников рейтинга, большая часть проектов компании представлена частными домами https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
В своей работе бюро руководствуется принципами создания комфортной, качественной и красивой архитектуры https://www.abbalk.ru/arhitectyra
Каталог бюро https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Фонд Ruarts Изображение: архитектурное бюро «Атриум» САЙТ https://www.abbalk.ru/interier
Бюро архитектуры и дизайна ANI Design https://www.abbalk.ru/arhitectyra
Проектируем там, где другие не справились! О нас в цифрах: работаем с 2011 г; 500 + проектов; 90 процентов проектов реализовано; 11 лет опыта реализации проек https://www.abbalk.ru/interier
Читать далее https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
Концепция ЖК в Рублёво-Архангельском Изображение: архитектурное бюро T+T Architects https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
// Обеденный стол с бетонной столешницей https://www.abbalk.ru/interier
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
hpwt02n0me – Very interesting site, saw some helpful info just now.
https://j5fnbpanu9x.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
comprafacilrd – I’ll bookmark this store, might order from here next time.
https://dcpo1.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wzoo – Great mix of visuals and text, quite appealing layout.
https://gcmv1k49sf8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rinatmat – Very user friendly, and I like the topic variety here.
https://qysvmk0q.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
elipso.site – Wow, stumbled on this site today and really like its layout.
https://cswjg36btn8b.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
seostream – Great content, always insightful and up-to-date with SEO trends.
https://sl6oo.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[url=https://ampaints.ru/]Аренда event мебели[/url] Для успешного проведения презентации важно организовать комфортное пространство для участников.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
where to buy zithromax in canada purchase zithromax z-pak or can i buy zithromax over the counter in canada zithromax tablets for sale
http://invatehnika.ru/redirect.php?url=http://bluepharmafrance.com how to get zithromax over the counter and https://www.emlynmodels.co.uk/user/jorzblzvgg/ zithromax 500mg price in india
[url=http://images.google.lt/url?q=https://zithromedsonline.com]where can you buy zithromax[/url] zithromax 250 mg tablet price and [url=http://mbuild.store/user/ejrstkmnab/?um_action=edit]azithromycin zithromax[/url] where to get zithromax over the counter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
can i order generic clomid tablets how to get clomid without insurance and how to get generic clomid online where to get cheap clomid price
https://www.google.ps/url?q=https://clomicareusa.com can you get cheap clomid online and http://wamoja.com/community/profile/dwmtywfbtd/ generic clomid price
[url=https://images.google.je/url?q=https://clomicareusa.com]can you get clomid no prescription[/url] can you buy cheap clomid without insurance and [url=https://boyerstore.com/user/ltxaranftd/?um_action=edit]can i buy cheap clomid without prescription[/url] buy generic clomid pill
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
zithromax online: ZithroMeds Online – zithromax z- pak buy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Buy Amoxicillin for tooth infection [url=https://amoxdirectusa.com/#]amoxicillin 500mg capsule cost[/url] AmoxDirect USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Current Job Market For Key Fob Repair Professionals
Like? Key Fob Repair (Sitamge.Ru)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://amoxdirectusa.com/# Purchase amoxicillin online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Building Briansclub.fit credit helps prepare for future expansion.
https://briansclub.fit/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
av07.cc – The tone is casual and friendly, which makes reading relaxing.
https://1jdn050p.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ryla6760 – Great to see such a well-organized leadership program for youth.
https://nb3jn87ai.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Капибара в бассейне — это лучшее зрелище! Она любит воду и умеет наслаждаться каждым моментом. [url=https://capybara888.wordpress.com]капибара водные привычки[/url] Капибара расслабляется, и её фото в горячих источниках стали настоящим трендом. Посмотри и вдохновись!
Более подробно по ссылке – https://capybara888.wordpress.com/
капибара повадки
капибара жвачное животное
капибара образ жизни
Удачи!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kaixin2020.live – I bookmarked this site — looks like there’s much to explore.
https://bcnuhw8wxhp0.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[url=https://ampaints.ru/]https://ampaints.ru[/url] Подробная информация о возможностях аренды мебели доступна на официальном портале.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
44lou5 – The layout is clean, making navigation a breeze.
https://pw7yu83sg.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
875 mg amoxicillin cost where to buy amoxicillin pharmacy and medicine amoxicillin 500 amoxicillin 500mg over the counter
https://www.google.com.cy/url?sa=t&url=https://amoxdirectusa.com amoxicillin azithromycin or https://www.packadvisory.com/user/geittcnqkd/ buy cheap amoxicillin online
[url=https://www.google.co.ck/url?q=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com]amoxicillin 500mg prescription[/url] amoxicillin 500 coupon and [url=https://www.news-adhoc.com/author/snhuumuofw/]buy amoxicillin 500mg canada[/url] amoxicillin without rx
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
5xqvk – I enjoy the fresh perspective this site offers.
https://rnzxszt1.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mhcw3kct – Great resource for those interested in niche subjects.
https://sm3lasas.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
xfj222 – I appreciate the depth of information provided here.
https://kk3me.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
5680686 – The design is minimalist yet effective.
https://ffwinb.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
RegrowRx Online: Best place to buy propecia – Best place to buy propecia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
game apps to win real money canada, best paying pokies
united kingdom and bingo bonus usa welcome, or online casino slots real money canada
Here is my webpage Goplayslots.Net
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Best place to buy propecia [url=http://regrowrxonline.com/#]Best place to buy propecia[/url] order propecia without insurance
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
90dprr.top – Overall a promising site, I’ll keep watching for fresh posts.
https://lo3tv.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
papamasque – I admire their subtle style, it’s refined yet boldly expressive.
https://googlesss.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
all new zealandn casino, legal canadian online pokies and casino on net 888 usa, or canadian online
casino for uk
Feel free to surf to my website; d&d 5e gambling games
(Angela)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Юридические и культурные аспекты «как правильно выращивать семена конопли»
Как сделать гашиш в домашних условиях: научный эксперимент Ивана. Когда Иван, студент-биолог из Казани, начал изучать смолистые структуры растений, он и представить не мог, куда приведёт его любопытство. Один из вопросов, заинтересовавших его в ходе научной практики, звучал так: как сделать гашиш в домашних условиях, используя подручные методы и сохраняя чистоту эксперимента? Иван не искал рецептов из интернета. Он подошёл к делу как настоящий исследователь – составил гипотезу, изучил литературу и решил воссоздать классические методы экстракции смол из растений. Его целью не было изготовление чего-то запрещённого – только изучение химических процессов, происходящих при отделении эфирных масел и смол. Сначала он изучил анатомию трихом – микроскопических желёз на поверхности листьев. Именно в них накапливаются смолистые вещества, благодаря которым растения защищаются от насекомых и ультрафиолета. Иван начал с «сухого сита» – он замораживал листья, аккуратно перетирал их над тонкой сеткой, а затем собирал мелкий порошок, который блестел на свету, как золотистая пыльца. Для сравнения он опробовал водяной метод: в лабораторной посуде смешал измельчённое сырьё с ледяной водой и фильтровал через слои ткани. По его записям, осадок получался более плотным и имел насыщенный аромат. Он даже провёл тесты на чистоту материала, измеряя количество хлорофилла и других примесей. Методология, безопасность и внимание к деталям были для него в приоритете. Эксперимент строго соответствовал академическим рамкам: всё происходило в закрытой лабораторной среде, под наблюдением преподавателя. Его работа вызвала интерес на научной конференции, где он представил результаты как исследование природных экстрактов и их свойств. Ответ на вопрос, как сделать гашиш в домашних условиях, оказался гораздо глубже, чем просто техника. Для Ивана это стало шагом в сторону науки, биохимии и понимания растений на новом уровне. Изучение природы – это всегда приключение. Кто знает, может, ваше следующее хобби окажется не только увлекательным, но и полезным для науки?
Основные ссылки:
рецепт гашиша — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-sdelat-gashishкак вырастить семена конопли — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-vyrastit-semena-konopli
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как сделать гашиш в домашних
Медицинские риски Фраза «как вырастить куст конопли» чаще всего встречается в юридических и профилактических публикациях. Эксперты подчеркивают, что «как сделать гашиш из конопли» чаще упоминается в дискуссиях о праве и здравоохранении, а не в практических пособиях.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Buy Clomid online: order clomid prices – Buy Clomid online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Юридический разбор фразы «как сварить метамфетамин»
Мой опыт изучения: как сделать амфетамин дома. Когда я впервые услышал вопрос – как сделать амфетамин дома, меня охватило любопытство. Я решил разобраться, что на самом деле стоит за этим процессом, не с точки зрения криминальных историй, а с научной и технической стороны. Изучая информацию, я понял: как сделать амфетамин дом – это сложный химический процесс, требующий точности и аккуратности. Обычно он включает несколько этапов – смешивание химических веществ, поддержание определённой температуры, контроль времени реакции и, наконец, очистку полученного продукта. В условиях дома вместо профессионального оборудования используют подручные вещи – банки вместо колб, кухонные весы и даже бытовые приборы для нагрева. Меня удивило, насколько люди изобретательны: кто-то собирает мини-лабораторию из старых электроприборов, кто-то экспериментирует с заменой редких химикатов на более доступные аналоги. Но при этом даже небольшая ошибка может привести к неудаче или опасности – например, выделению токсичных паров или взрыву. Изучая отзывы и обсуждения, я понял, что для многих этот процесс – вызов и проверка инженерных навыков. Но это игра с огнём, где ставки слишком высоки. Очень быстро осознаёшь, что химия – это не только формулы, но и ответственность за безопасность. Для меня этот опыт стал уроком: даже если тема кажется темной или запретной, в ней можно найти важные знания и понимание. Главное – использовать свои навыки для создания чего-то полезного и безопасного. Сейчас я стараюсь направлять своё увлечение химией в сторону науки и технологий, которые приносят реальную пользу. Ведь настоящий интерес к науке – это не просто любопытство, а желание понимать и делать мир лучше.
Основные ссылки:
как правильно выращивать марихуану — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-vyrastit-marihuanuкак сварить метамфетамин в домашних условиях — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-svarit-met
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как вырастить марихуану дома
Медиаэксперты обращают внимание, что при работе с фразой «как сделать мет» важно избегать деталей и продвигать безопасные информационные практики. Медиа и правозащитные проекты советуют при встрече с «амфетамин рецепт на латинском» переводить дискуссию в плоскость права и помощи, а не инструкции. Юридические и медицинские комментарии подчеркивают, что «как сделать мефедрон дома» — запрещённая тема, требующая немедленной реакции модерации.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Узнайте о психологических вызовах, с которыми столкнулись люди во время пандемии, и эффективных методах их преодоления. Психолог Патимат Исаева делится ценными советами и решениями для улучшения психического здоровья в условиях пандемии.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://patya.pro/articles/lichnye-razmyshleniya-i-istorii/istorii-iz-praktiki/neobychnye-zaprosy-klientov.html
психологи онлайн номера, психолог после родов, результат консультации с психологом
как наладить отношения в семье, [url=https://patya.pro/articles/stati-i-publikacii-o-psihologii/psihologicheskoe-konsultirovanie-i-terapiya/gumanisticheskaya-terapiya.html]Гуманистическая терапия[/url], сексолог психолог консультация
[url=https://uludagsozluk.vivaldi.net/2020/02/22/uludag-ve-eksi-sozluk-pkk-sozlukleri/comment-page-1774/#comment-230079]Как выбрать подходящую терапевтическую группу. В этой статье из раздела «Групповая терапия» вы узнаете, как как выбрать подходящую терапевтическую группу и почему это важно для психологического здоровья. Материал содержит практические советы, примеры из реальной практики и поможет лучше понять, как решить подобную проблему с помощью психотерапии.[/url] 1ad9b3e
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online casinos in ontario australia, real online money casino canada
and casino no deposit bonus codes canada 2021, or play online pokies usa
Have a look at my homepage; bingo blind Test
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Car Key Shell Repair Tools To Help You Manage Your Everyday Lifethe Only Car Key Shell Repair Technique Every Person Needs To
Be Able To Car Key Shell Repair (Lizzie)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
v1av8 – Visuals catch attention; I’m curious about its purpose and meaning.
https://googlesss.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
9 . What Your Parents Teach You About Vehicle Key Repair Vehicle Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://regrowrxonline.com/# order propecia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
datacaller.store – Fast loading, responsive design is a plus for first impressions.
https://ui654.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
purchase zithromax z-pak zithromax price canada and zithromax without prescription zithromax capsules australia
http://j.lix7.net/?http://bluepharmafrance.com/ zithromax online no prescription or http://lzdsxxb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=5221465 zithromax online australia
[url=https://www.google.com.py/url?q=https://zithromedsonline.com]zithromax over the counter uk[/url] zithromax for sale online and [url=https://bold-kw.com/user/mxoqezhvid/?um_action=edit]where can i buy zithromax capsules[/url] zithromax 250
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
zkjcnm.top – Site loads quickly, which is a good sign for usability.
https://sde5v0ix5jc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy zithromax 1000 mg online: zithromax z- pak buy online – buy zithromax online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
greenenvelope.org – I’ll check back later once content is live or updated.
https://x4cncv.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
lapotranca.store – Clean layout so far, gives a professional first impression.
https://qns6t10q.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
i2gkj.xyz – Very minimal layout, leaves me curious about its future content.
https://g5abt8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
chinh-sua-anh.online – I like the before/after sliders, very reassuring for clients.
https://wt7aa90btl.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy generic propecia pill [url=https://regrowrxonline.shop/#]RegrowRx Online[/url] buy finasteride
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
keledh.pw – The domain is short and intriguing, sticks in mind.
https://fxif6qu7kqgd.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Конечно, цветовое решение выбирайте сами, какое только пожелаете https://olga-filippova.ru/office_interior
Но, учитывайте, что светлые тона позволят сделать помещение светлее и просторнее https://olga-filippova.ru/office_interior
Если необходимо разграничить квартиру на разные зоны, используйте для этого гипсокартон https://olga-filippova.ru/office_interior
Также можете использовать максимально функциональные варианты мебели, например угловые диваны или шкафы купе https://olga-filippova.ru/interery-fasad
Чтобы добиться максимальных результатов опытные дизайнеры применяют множество ухищрений, которые доводят маленькую квартиру до идеального состояния https://olga-filippova.ru/blog
Обратите внимание на фото дизайна однокомнатных квартир, в каком великолепии они могут смотреться https://olga-filippova.ru/shop
Смотря на фото дизайн интерьера дома и каждой его комнаты, всегда хочется, чтобы своё было таким же комфортным и стильным, а уж тем более, когда речь идет о спальне для малыша https://olga-filippova.ru/portfolio-2
Основное правило – это не слишком переусердствовать, и не навредить https://olga-filippova.ru/kontakts
Многие готовы выполнить ремонт вовремя и могут за это взять не дорого, но в конечном итоге могут затягивать сроки, а про качество работы можно будет забыть https://olga-filippova.ru/kontakts
В таком случае затянутый процесс ремонта будет нервировать и вызывает стресс https://olga-filippova.ru/smi
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
v1av8 – I hope this becomes clearer; it shows potential with refined execution.
https://googlesss.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic zithromax: ZithroMeds Online – cheap zithromax
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
zonaflix – The quality is surprisingly decent, haven’t seen many issues so far.
https://cxic94qm5.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
52ch.cc – Very useful site, I find something helpful each visit.
https://lunkwo8bs1of.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
manchunyuan1.xyz – I appreciate the effort behind this site, genuine and helpful.
https://k53wa.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
forexplatform.website – Posts here feel fresh and updated, not just recycled advice again.
https://bu5ka45la.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
lovemoda.store – The homepage looks responsive, adapts well on mobile view.
https://sonq93ter.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
22ee.top – The homepage is simple, makes me curious to scroll further.
https://lo3tv.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://amoxdirectusa.shop/# buy amoxil
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
amoxicillin 500 mg online where to buy amoxicillin pharmacy or amoxicillin 800 mg price where can i buy amoxicillin over the counter
http://www.suomenymparistopalvelu.fi/joulutervehdys2013/index.php?url=https://amoxdirectusa.com amoxicillin pills 500 mg and https://www.ixxxnxx.com/user/eynjvvyxpv/videos amoxicillin price canada
[url=https://cse.google.com.cu/url?sa=t&url=https://amoxdirectusa.com]amoxicillin online without prescription[/url] amoxicillin 500mg over the counter and [url=http://lzdsxxb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=5221727]amoxicillin 500mg for sale uk[/url] canadian pharmacy amoxicillin
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Propecia prescription: buy finasteride – Propecia 1mg price
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
See What Car Key Blade Repair Tricks The Celebs Are Using
car key blade repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Building Briansclub credit improves long-term cash flow management.
https://briansclubcm.co/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
creadordesitios – Navigation is intuitive, I quickly found what I was looking for.
https://z0x6mn.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
get propecia without insurance [url=http://regrowrxonline.com/#]Propecia 1mg price[/url] RegrowRx Online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sddapp – The layout is simple and clean, looks modern and uncluttered.
https://iip36t4foszf.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fortressystemnig – The navigation menu is intuitive, I found what I wanted fast.
https://z4n8268cjr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://clomicareusa.com/# Buy Clomid online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Исторический анализ фразы марихуану в домашних условиях
Мой взгляд на рецепт амфетамина в домашних условиях. Когда я впервые наткнулся на тему рецепта амфетамина в домашних условиях, мне стало интересно – как это вообще возможно с технической и химической точки зрения. Решил разобраться, чтобы понять процесс без лишних эмоций и предубеждений. Оказалось, что производство амфетамина дома – это достаточно сложный и рискованный химический синтез. Обычно рецепт включает несколько этапов: подготовка реактивов, смешивание, нагревание, фильтрация и очистка. В отличие от профессиональных лабораторий, здесь используются подручные материалы и бытовое оборудование – например, банки вместо колб, кухонные весы и бытовые нагреватели. Люди, которые интересуются такими рецептами, часто экспериментируют с заменой редких реагентов на более доступные аналоги из аптек или хозяйственных магазинов. Такой подход требует не только знаний химии, но и изобретательности. Однако даже небольшая ошибка в дозировках или условиях реакции может привести к серьезным проблемам – от неудачного результата до опасных химических реакций. Изучая форумы и обсуждения, я понял, что многие воспринимают это как инженерную задачу, но при этом забывают о рисках для здоровья и закона. Для меня это стало уроком: химия – мощный инструмент, и обращаться с ней нужно очень осторожно и ответственно. Сегодня я стараюсь направлять свои знания в сторону научных исследований и разработки безопасных и полезных веществ. Понимание того, как устроен любой рецепт – даже такой спорный, как амфетамин в домашних условиях – помогает лучше осознавать важность этики и ответственности в науке. Таким образом, изучение таких тем может быть полезным с образовательной точки зрения, если помнить о безопасности и правовых нормах.
Основные ссылки:
рецепт амфетамина — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-sdelat-amfetaminрецепт как сварить мефедрон — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-svarit-mefedron
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как сделать амфетамин
Лингвистический и культурный разбор «амфетамин рецепт на латинском» показывает, что такие метки часто используются для обхода модерации и требуют внимания платформ. Органы профилактики и НКО рекомендуют заменить инструкции по «как сделать мефедрон в домашних условиях» на материалы о снижении вреда и восстановлении. Запрос «как выращивать семечки конопли правильно» встречается в СМИ как маркер молодежных тенденций и источник профилактических программ.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
t371 – I’d like to see more illustrations or media to enrich pages.
https://u3fbhw.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
A reliable partner https://terionbot.com in the world of investment. Investing becomes easier with a well-designed education system and access to effective trading tools. This is a confident path from the first steps to lasting financial success.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
giftd – The homepage layout feels balanced and easy to follow.
https://bscm8ie.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ignition Key Repair Tools To Enhance Your Day-To-Day Life Keyless Entry Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
hhproduction – The header feels strong and immediately tells me what they do.
https://x759qwwpgb.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
probuis – I’d like to see about or mission section to know their purpose.
https://igzsj8myz.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cooperativadeartesanos – On mobile it looks decent, love that it’s responsive so far.
https://gnh77.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
briansclub.vg
https://briansclub.vg/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
axjaognr – The site loaded okay, but images could be sharper for better appeal.
https://w9brsbu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
aaront – The typography is pleasant and easy to read for sure.
https://qhkjwb.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Первый шаг к простому доходу
Как сделать гашиш: история одного эксперимента. Михаил всегда интересовался растениями и их свойствами. В поисках необычных способов переработки зелени он однажды наткнулся на старинные методы, используемые в разных странах. Особенно его заинтересовал вопрос – как сделать гашиш, и почему эта тема вызывает такой интерес у ботаников по всему миру. Оказывается, процесс создания гашиша имеет древние корни. В разных регионах его делали по-разному: в Марокко, например, использовали сухой метод трения, а в Непале — «ручной сбор смолы». Михаил начал с теории: читал научные статьи, изучал исторические хроники и даже нашёл упоминание гашиша в персидских рукописях. Первым этапом было понимание, что такое трихомы – мельчайшие смолистые железы на растениях. Именно они содержат ароматные масла и вещества, из которых и формируется конечный продукт. Чтобы извлечь смолу, нужно аккуратно отделить эти кристаллы. Михаил попробовал сухой метод: заморозил растительное сырьё, а затем начал аккуратно просеивать его через мелкое сито. Образовавшийся порошок он собрал и спрессовал в плотные брикеты. Он также поэкспериментировал с водяным методом: смешал измельчённое растение с холодной водой и льдом, а затем слил полученную смесь через фильтр. Оставшийся осадок оказался весьма ароматным. Михаил отметил, что чистота и качество продукта напрямую зависят от аккуратности процесса и свежести сырья. Важно понимать: экспериментировать можно только в целях изучения процессов и получения знаний о природе. Михаил вёл дневник, фиксируя каждый шаг, сравнивая методы и делая выводы. Для него это стало настоящим хобби и способом узнать больше о свойствах растений и их потенциале. Изучение темы, как сделать гашиш, превратилось для Михаила в увлекательное путешествие по ботанике, химии и истории. Такой опыт расширяет кругозор и помогает лучше понять взаимодействие человека и природы. Если вы интересуетесь растениями, натуральными методами переработки и научными экспериментами – начните с теории. Иногда самые простые вопросы открывают удивительные горизонты.
Основные ссылки:
как вырастить семечко конопли — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-vyrastit-semena-konopliкак легко зарабатывать самый легкий способ — k.krakenwork.cc/legkij-sposob-zarabatyvat-v-internete
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как вырастить семечко конопли
Образовательные альтернативы Исторические публикации отмечают, что фраза «как вырастить коноплю на балконе» часто встречается в молодежных обсуждениях. Образовательные материалы предлагают альтернативы обсуждению «как самому сделать гашиш» — фокус на здоровье и праве.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
set-mining.website – I couldn’t find much info, site looks new and content is scarce.
https://hzvpwj7gj.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cost of propecia pills order generic propecia pills or buy generic propecia without a prescription cheap propecia
https://www.google.com.vn/url?q=https://regrowrxonline.com propecia pill and http://asresin.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=122050 order propecia tablets
[url=http://go.clashroyale.ir/index.php?url=https://regrowrxonline.com]get propecia online[/url] order generic propecia no prescription and [url=https://pramias.com/profile/kfidtphkgx/]buy propecia[/url] cost of generic propecia online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
forextradingsystem – The tips shared here actually improved my trading results this month.
https://h62rrn.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
xxgm – Solid site, glad I came across it while browsing today.
https://4tacc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fartak – The theme looks polished and friendly, makes reading enjoyable.
https://g6so4c16.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru с последними событиями дня. Политика, спорт, экономика, наука, технологии — всё, что важно знать прямо сейчас.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
xxec – Cool design choices and subtle animations make this one stand out.
https://1j8ing1x.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Актуальные новости автопрома https://myrexton.ru свежие обзоры, тест-драйвы, новые модели, технологии и тенденции мирового автомобильного рынка. Всё самое важное — в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The 10 Scariest Things About Keyless Remote Repair Keyless Remote Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bestbotanicals – This site makes me want to try more natural remedies again.
https://zg00vu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy zithromax: buy zithromax online – zithromax over the counter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
formasecoarquitectonicas – Clean font and layout, though some parts look unfinished or sparse.
https://evgerr77.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
zithromax for sale usa how much is zithromax 250 mg and zithromax 500 mg lowest price pharmacy online where to get zithromax
http://4chan.nbbs.biz/kusyon_b.php?http://bluepharmafrance.com/ zithromax buy online no prescription or https://bbs.hy2001.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=639173 zithromax 250 mg tablet price
[url=https://images.google.com.sg/url?sa=t&url=https://zithromedsonline.com]zithromax online pharmacy canada[/url] zithromax 250 mg or [url=https://gikar.it/user/xdwtjgvpbr/]zithromax cost uk[/url] zithromax 500mg price in india
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy amoxicillin: buy amoxil – AmoxDirect USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy zithromax [url=https://zithromedsonline.shop/#]zithromax z- pak buy online[/url] cheap zithromax
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://amoxdirectusa.shop/# AmoxDirect USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
briansclub.vg
https://briansclub.vg/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Job Market For Car Keyless Start Repair Professionals Like?
Car Keyless Start Repair (https://chsp.hispanichealth.info/)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Капибара в спа — это лучшее, что ты увидишь сегодня! Она живёт без стресса и наслаждается моментом. [url=https://www.capybara888.wordpress.com]капибара смешные видео[/url] Капибара отдых фото доказывают, что расслабление — это искусство. Берите пример с неё!
Более подробно по ссылке – https://www.capybara888.wordpress.com
капибара мем
капибара
капибара релакс
Удачи!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Job Market For Car Key Jammed Repair Professionals?
Car Key Jammed Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
yt7787.xyz – The navigation works fine, but some subpages are a bit empty.
https://0xxqw.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
captcha-kraken17at.org – Some images failed to load, likely missing or broken asset links.
https://kv1tok.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
businessesnewsdaily.site – I like how articles are categorized neatly, makes browsing topics simple.
https://t6ilse.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bbofrwhnimpcjibfunu.live – On mobile layout shifts a little weirdly in some sections, but manageable.
https://5dwtxxw.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
storagesheds.store – Navigation works fine, but some links feel buried and unclear.
https://94tcyon5.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bitcoin-mining-news.website – On mobile, pages adjust fairly well, but some images overflow slightly.
https://qmtmuzkmp.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Капибара и собаки — неожиданный, но идеальный дуэт. Они часто становятся друзьями и любят вместе отдыхать. [url=https://www.capybara888.wordpress.com]чем питается капибара[/url] Капибара дружит с котами, собаками и даже черепахами! Посмотри капибара фото и удивись её общительности!
Более подробно по ссылке – https://capybara888.wordpress.com
капибара социальное животное
капибара и другие виды животных
капибара дружелюбное животное
Удачи!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
9870k.top – The footer is minimal—some additional links/contact info would help a lot.
https://k8aim9ydd.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://amoxdirectusa.shop/# where to get amoxicillin over the counter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dersimizmuzik.org – The articles are nicely arranged, made browsing quite intuitive.
https://ntmf1scyl.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy propecia without a prescription: buy finasteride – Best place to buy propecia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
x3165.xyz – The footer is a bit sparse, more links or info would help.
https://2n58awy7qu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy amoxicillin online no prescription how to buy amoxycillin and amoxicillin 875 125 mg tab amoxicillin 500 mg capsule
https://www.google.gl/url?q=https://amoxdirectusa.com amoxicillin 825 mg and https://www.freshdew.tv/user/tprppymkij/?um_action=edit amoxicillin from canada
[url=https://images.google.com.bo/url?q=https://amoxdirectusa.com]amoxicillin 250 mg[/url] buy amoxil and [url=https://bbs.soumoli.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=840770]generic for amoxicillin[/url] amoxicillin where to get
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
can you get generic clomid without dr prescription cost cheap clomid now or where can i get clomid tablets how to get clomid for sale
https://cse.google.lv/url?q=https://clomicareusa.com how can i get clomid without a prescription or https://blog.techshopbd.com/user-profile/ijzcgprqbg/?um_action=edit cheap clomid price
[url=http://www.tvtix.com/frame.php?url=http://intimapharmafrance.com]buy clomid without prescription[/url] cost cheap clomid no prescription and [url=https://wowanka.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=560656]get generic clomid without rx[/url] where can i get cheap clomid without dr prescription
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
17kshu – They have some interesting topics, unsure yet what they focus on.
https://rr8jqk.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ZithroMeds Online: cheap zithromax – buy zithromax
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
3e7r – The product details are clear, I feel confident about ordering.
https://k39jcco67rue.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bestbotanicals – Love how easy it is to find rare plants here online.
https://qhkjwb.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
7x084yko.xyz – The footer is minimal — adding some contact or link info would improve trust.
https://ddv8fuznvs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic zithromax [url=https://zithromedsonline.com/#]generic zithromax[/url] zithromax z- pak buy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sh576.xyz – Overall it seems promising, I’ll check back to see how it evolves.
https://2xvq5ri1qu.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://clomicareusa.shop/# Generic Clomid
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
История запроса вырастить марихуану на балконе
Как сделать амфетамин: химия и техника за кадром. Максим всегда интересовался химией и разными технологическими процессами. Однажды он заметил, что тема «как сделать амфетамин» часто обсуждается в интернете, и решил изучить её с научной точки зрения, чтобы понять, что стоит за этим сложным процессом. Производство амфетамина – это химический синтез, который требует последовательного выполнения нескольких стадий. На практике это означает точное смешивание реагентов, контроль температуры, времени реакции и последующую очистку продукта. Несмотря на то, что в подпольных условиях часто применяются импровизированные приборы и доступные компоненты, основные химические принципы остаются неизменными. Максим заметил, что люди, изучающие этот процесс, часто подходят к делу как к инженерной задаче – они создают самодельное оборудование из подручных материалов, экспериментируют с дозировками и методами очистки. Это напоминает своего рода лабораторные исследования, но с серьёзными рисками для здоровья и безопасности. Интересно, что химия амфетамина во многом схожа с синтезом других органических веществ, в том числе некоторых лекарственных препаратов. Разница заключается в конечной цели и последствиях применения. Максим считает важным понимать эти процессы не для практического применения, а чтобы осознать сложности и ответственность, связанные с химией. Сейчас он учится в университете и планирует заниматься разработкой новых фармацевтических препаратов, где химия служит во благо людям. Изучение таких тем помогает ему лучше понимать, как наука работает в самых разных областях, и почему важно использовать знания с этическими принципами. Таким образом, тема «как сделать амфетамин» – это не только криминальная история, но и пример того, как химия требует серьёзного подхода, глубоких знаний и ответственности за свои действия.
Основные ссылки:
как вырастить семечки марихуаны — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-vyrastit-semena-konopliкак вырастить марихуану дома — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-vyrastit-marihuanu
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как выращивать семечки конопли правильно
Юридические комментарии подчёркивают, что упоминание «как сделать амфетамин» может иметь правовые последствия и должно обсуждаться в правовом и профилактическом ключе. Социологи рассматривают «как сделать мефедрон» как маркер уязвимых сообществ; ответ — образовательные и профилактические кампании, а не руководства. Юридические комментарии подчеркивают, что тема «как выращивать семена марихуаны» используется исключительно в контексте профилактики и запретов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как начать выращивать коноплю — взгляд общества
Как сделать гашиш своими руками: история Павла и его экспериментов на балконе. Павел – мастер на все руки. Он чинит кофемашины, паяет платы, выращивает перцы чили на балконе и обожает докапываться до сути вещей. Его подписчики в блоге привыкли к странным постам вроде «Что будет, если высушить банан в вакууме?» или «Как собрать мини-экстрактор из бутылки и резинки». Однажды кто-то в комментариях в шутку спросил: «А расскажи, как сделать гашиш своими руками?» – и Павел, как обычно, не проигнорировал. Он начал, конечно, с теории. Оказалось, что «гашиш» – это не какой-то загадочный субстанция, а концентрат смолистых веществ растения, полученный без применения химии. В древности это делали просто руками – терли между ладонями свежие шишки, собирали липкую смолу, скатывали в шарики. В Марокко, например, это целый ритуал, передаваемый из поколения в поколение. Павел заинтересовался: как сделать гашиш своими руками в техническом, чисто инженерном смысле. Он начал с эксперимента. Купил в цветочном магазине пыльцевой сборник (используется для сбора пыльцы с декоративных растений), сито с мелкой фракцией и несколько сушёных ароматных трав для наглядности – вроде лаванды и мяты. Он аккуратно растёр материал через сито, собрал то, что осело, и сжал пальцами. Получилось что-то вроде комка ароматной пудры. Сам процесс напоминал создание специй – только без ножей, просто через трение и терпение. Следующим этапом Павел попробовал «ледяной метод»: залил траву холодной водой, встряхивал, фильтровал через марлю и ждал осадка. Эксперимент был чисто визуальным, но результат впечатлил: на дне осталась ароматная взвесь, которую можно было отфильтровать и прессовать. Он описал весь процесс в блоге, как пошаговый научный опыт. Не ради повторения, а чтобы показать, что даже в таких спорных темах кроется масса химии, ботаники и ремесленного подхода. Фраза «как сделать гашиш своими руками» может звучать неоднозначно, но если убрать предвзятость, остаётся интересный технологический процесс. А Павел считает: если ты понимаешь, *как* что-то работает – тебе это уже не страшно. Главное – изучай, задавай вопросы и не забывай включать мозги. Даже когда речь идёт о смолах и ситах.
Основные ссылки:
самый легкий способ заработать — k.krakenwork.cc/legkij-sposob-zarabatyvat-v-interneteкак сделать наркотики — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-varit-narkotiki
KRAKEN™ 2025 — самый легкий способ заработать
Юристы подчеркивают, что выражение «как правильно выращивать семена конопли» рассматривается в рамках профилактики и просвещения. Узнайте, как я начал зарабатывать легко — честный рассказ без обмана и мифов. Юридические последствия
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Car Key Shell Repair Tools To Ease Your Daily Life Car Key Shell Repair Trick
That Every Person Should Learn Car Key Shell Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Propecia buy online: Propecia 1mg price – Propecia buy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Amoxicillin 500mg buy online: Purchase amoxicillin online – Purchase amoxicillin online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
6789138a.xyz – The minimal style is working well, gives a refined, elegant impression.
https://h43sawkxnkt.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
zithromax z- pak buy online [url=https://zithromedsonline.shop/#]zithromax z- pak buy online[/url] generic zithromax
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
7 Things About Car Key Signal Issue Repair You’ll Kick
Yourself For Not Knowing Car Key Ignition Switch Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
196v5e63 – Everything looks clean, simple, and well-arranged across all pages.
https://eck984.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sj440.cc – Smooth navigation, no weird jumps or broken menus so far.
https://h62rrn.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://amoxdirectusa.shop/# order amoxicillin online no prescription
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
5581249.cc – Layout seems clean, though some pages are light on content.
https://0ujn69ntt3lh.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sj256.cc – It’s mobile-friendly, didn’t run into layout issues on my phone.
https://g5abt8.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mydiving – Navigation is effortless, I found everything without confusion.
https://pi6za0.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
a6def2ef910.pw – The color contrast is fine, readable without strain under normal lighting.
https://f59nc15vh8j.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
20 Myths About Keyless Fob Repair: Dispelled Vehicle Keyless Start Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
9 Lessons Your Parents Teach You About Car Key Remote
Repair Car Key Remote Repair – md.Chaosdorf.de,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
5 Killer Quora Answers On Car Key Signal Issue Repair Car Key Signal Issue Repair, moparwiki.win,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
0238.org – I saw a missing image here and there, hope it’s fixed soon.
https://ku0wnli2.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
21009.xyz – A few broken links appeared as I browsed, hope they’ll fix those.
https://359wfi.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
00381.xyz – The footer is minimal, adding more links or contact info might help.
https://85rvq6y5h.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://amoxdirectusa.shop/# buy amoxil
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
other2.club – Found some cool bits here, will revisit for updates soon.
https://pnrpzn.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
15 Surprising Stats About Car Mechanical
Key Repair Car Keyless Unlock Repair – Mikel,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Purchase amoxicillin online: Buy Amoxicillin for tooth infection – Buy Amoxicillin for tooth infection
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
You’ll Never Guess This Car Key Repair’s Benefits Car Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Entrepreneurs gain bigger funding rounds through enhanced briansclub.llc credit.
https://briansclub.llc/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Generic Clomid: Clomid price – ClomiCare USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
10 Things That Your Family Teach You About Car Flip Key Repair Car Flip Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cheapest sildenafil india sildenafil cheap no prescription or sildenafil online price sildenafil 100mg uk cheapest
https://cse.google.com.pr/url?sa=t&url=https://truevitalmeds.shop buy sildenafil generic and https://boyerstore.com/user/elmlbsaucy/?um_action=edit sildenafil 25 mg prices
[url=https://www.google.gg/url?q=https://truevitalmeds.shop]sildenafil for sale canada[/url] sildenafil 48 tabs 50 mg price and [url=https://bbs.sanesoft.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=1135574]canadian pharmacy sildenafil 100mg[/url] sildenafil 50 mg tablet price in india
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Car Lock Repair: The Intermediate Guide Towards
Car Lock Repair Car Lock Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Setting up briansclub.llc credit encourages lender approval.
https://briansclub.llc/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://tadalmedspharmacy.com/# Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MedicExpress MX [url=https://medicexpressmx.shop/#]Online Mexican pharmacy[/url] mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
i1oxj – Everything is organized well, easy to jump between sections.
https://ebb253nhc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://feeshop.cc/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
purchase tadalafil online tadalafil tablets or where to buy tadalafil 20mg buy tadalafil 20mg price canada
http://rukadelkino.ru/forum/away.php?s=http://bluepharmafrance.com cost of tadalafil and http://ussher.org.uk/user/qwqjhpulwf/?um_action=edit tadalafil 20 mg mexico
[url=https://images.google.bg/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalmedspharmacy.com]tadalafil soft gel capsule[/url] tadalafil compare prices and [url=http://orbita-3.ru/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=32479]best tadalafil tablets in india[/url] generic tadalafil united states
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1cty – Pages responded quickly, I had no lag during my visit.
https://ddv8fuznvs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
deallegria – Overall it’s a fast, clean, and pleasant site to visit.
https://7yhpnef0w.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://russianmarkett.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
worldloans – Overall it’s a smooth, simple, and pleasant site to use.
https://fdacht6k6grs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fhkaslfjlas – The design is simple, modern, and easy on the eyes.
https://vxa3g32mq3ib.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
jekflix – I enjoyed browsing around, the interface feels very comfortable.
https://pi6za0.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mizao0 – Smooth performance overall, made the visit enjoyable and easy.
https://0pkjf5hy019.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
v1av7 – Overall a fast, simple, and pleasant website to use.
https://9pmvbs4.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Mexican pharmacy price list: Best online Mexican pharmacy – Legit online Mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
v1av2 – Browsing felt smooth throughout, nothing interrupted the flow here.
https://jok13m2rx6s.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://jokerstashh.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Car Keyless Entry Fob Repair: The Intermediate Guide Towards Car Keyless Entry Fob
Repair Car Keyless Entry Fob Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
aabb49 – Usability is simple and user-friendly.
https://0xxqw.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Entrepreneurs gain security with improved briansclub.llc credit.
https://briansclub.ga/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Mexican pharmacy price list: best online pharmacies in mexico – Online Mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
66se – Stable performance across sections.
https://enet4iquf.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tiantianyin4 – The site loads fast and feels stable without issues.
https://loh231e9hk.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
2kgq – I like how simple and uncluttered the design feels here.
https://r6c848.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tstyhj – Everything functions properly, no errors or issues while using.
https://hx8coa1q.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://medicexpressmx.com/# Mexican pharmacy price list
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
93r – The domain is short and intriguing, design tries to be bold yet subtle.
https://gogogle.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nnvfy – The interface feels smooth and lightweight during navigation.
https://6ztavpnlp.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MedicExpress MX [url=https://medicexpressmx.com/#]trusted mexican pharmacy[/url] mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Upgrading briansclub.llc credit enhances operations.
https://briansclub.ga/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://truevitalmeds.com/# Sildenafil 100mg
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafil: Buy Tadalafil 20mg – Buy Tadalafil online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
order sildenafil online sildenafil 100 mg tablets coupon or sildenafil generic usa where can i get cheap sildenafil
https://clients1.google.la/url?q=https://truevitalmeds.com buy sildenafil citrate and https://chinaexchangeonline.com/user/vidzwtbdqm/?um_action=edit lowest price for sildenafil 20 mg
[url=https://clients1.google.com.bh/url?q=https://truevitalmeds.com]sildenafil cost in india[/url] sildenafil 100mg tablets canada or [url=https://virtualchemicalsales.ca/user/fggcljdyvq/?um_action=edit]sildenafil mexico[/url] sildenafil 100mg tab
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
rwbj – Navigation is easy and clear, no confusion while browsing.
https://iae7p7.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
How Car Key Guard Repair Arose To Be The Top Trend In Social Media Key Fob Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Generic tadalafil 20mg price: Generic tadalafil 20mg price – generic tadalafil in canada
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fghakgaklif – Pages load fast, which makes browsing pleasant and efficient.
https://dgdgsdgd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://tadalmedspharmacy.shop/# Buy Tadalafil online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sildenafil 100mg without a prescription sildenafil online uk or sildenafil tablets 120mg sildenafil best price
https://www.mfkfm.cz/media_show.asp?type=1&id=156&url_back=https://truevitalmeds.shop sildenafil over counter and https://www.carrier.co.za/index.php/user/reprdsgeha/?um_action=edit how to order sildenafil
[url=http://game-android.ru/forum/away.php?s=http://pharmalibrefrance.com]order sildenafil citrate[/url] sildenafil 100mg tablets for sale or [url=https://shockingbritain.com/user/rmnfqdbuxd/]average price of sildenafil in usa 100mg[/url] how much is generic sildenafil
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sildenafil 100mg price [url=https://truevitalmeds.shop/#]Buy sildenafil online usa[/url] Buy sildenafil online usa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужен надежный акб? магазин аккумуляторов в спб AKB STORE — ведущий интернет-магазин автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге! Мы специализируемся на продаже качественных аккумуляторных батарей для самой разнообразной техники. В нашем каталоге вы найдёте идеальные решения для любого транспортного средства: будь то легковой или грузовой автомобиль, катер или лодка, скутер или мопед, погрузчик или штабелер.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ищешь аккумулятор? аккумулятор автомобильный купить в санкт петербурге дешево AKB SHOP занимает лидирующие позиции среди интернет-магазинов автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге. Наш ассортимент охватывает все категории транспортных средств. Независимо от того, ищете ли вы надёжный аккумулятор для легкового автомобиля, мощного грузовика, комфортного катера, компактного скутера, современного погрузчика или специализированного штабелёра
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Current Job Market For Vehicle Keyless Start Repair Professionals Like?
Keyless Start Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
lotsofonlinepeople – The visuals are striking, the site feels energetic and modern overall.
https://googas.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafil 5mg tablets price tadalafil 20 mg price canada and tadalafil generic otc cheap generic tadalafil 5mg
https://www.paltalk.com/linkcheck?url=http://bluepharmafrance.com cost of tadalafil or http://lostfilmhd.com/user/ahyewmnaxx/ tadalafil 22 mg
[url=https://www.myconnectedaccount.com/help/faqcw2/index.php?domain=bluepharmafrance.com]buy tadalafil india[/url] generic tadalafil for sale or [url=http://www.donggoudi.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3688623]generic cialis tadalafil[/url] tadalafil 30
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy tadalafil 20mg price canada: Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription – Buy Tadalafil online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
This Is The Complete Guide To Smart Key Repair car Smart key repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Current Job Market For Car Keyless Start Repair Professionals Like?
Keyless Start Repair – posteezy.com –
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Хочешь сдать акб? сдать старый аккумулятор за деньги честная цена за кг, моментальная выплата, официальная утилизация. Самовывоз от 1 шт. или приём на пункте, акт/квитанция. Безопасно и законно. Узнайте текущий тариф и ближайший адрес.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ремонт и строительство https://nastil69.ru от А до Я: планирование, закупка, логистика, контроль и приёмка. Калькуляторы смет, типовые договора, инструкции по инженерным сетям. Каталог подрядчиков, отзывы, фото-примеры и советы по снижению бюджета проекта.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
5 Killer Quora Answers To Car Mechanical Key Repair Car Mechanical Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafil: tadalafil – Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://truevitalmeds.shop/# Buy sildenafil online usa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
geomatique237 – They seem to be testing ideas; visual layout is bold but inconsistent.
https://gossogle.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ремонт и стройка https://remontkit.ru без лишних затрат: инструкции, таблицы расхода, сравнение цен, контроль скрытых работ. База подрядчиков, отзывы, чек-листы, калькуляторы. Тренды дизайна, 3D-планировки, лайфхаки по хранению и зонированию. Практика и цифры.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ваш портал о стройке https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: материалы, инструменты, сметы и бюджеты. Готовые решения для кухни, ванной, спальни и террасы. Нормы, чертежи, контроль качества, приёмка работ. Подбор подрядчика, прайсы, акции и полезные образцы документов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
haskdhaskdjaslkds – The site attempts style, but coherence is missing in many sections.
https://dgdgsdgd.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Buy Tadalafil 20mg [url=http://tadalmedspharmacy.com/#]tadalafil[/url] Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The 10 Scariest Things About Car Keyless Unlock Repair Car Keyless Unlock Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Unlock the strategies to improve your SEO with practical tips and reliable techniques for generating organic visitors and securing top rankings on search engines.
link
link
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
crownaboutnow – I enjoyed browsing, images and text complement each other nicely.
https://googlsssse.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Online Mexican pharmacy: Mexican pharmacy price list – Legit online Mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://truevitalmeds.com/# sildenafil tablets 50mg price
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
lastminute-corporate – I like the straightforward design, makes everything clear and simple.
https://googlesssdsw.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sildenafil generic discount cheap sildenafil tablets uk and sildenafil 20 mg sale buy sildenafil no prescription
https://images.google.bj/url?q=https://truevitalmeds.com sildenafil 50mg without prescription or http://la-maison-des-amis.com/user/wqgfyziugs/ sildenafil cost india
[url=http://pinnest.com/source/pharmaexpressfrance.com/]buy sildenafil[/url] rx sildenafil tablets or [url=https://rightcoachforme.com/author/dfzltzynrq/]sildenafil order without prescription[/url] sildenafil 100mg mexico
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexican rx online mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa or buying prescription drugs in mexico online purple pharmacy mexico price list
http://www.sorenwinslow.com/RSSReader.asp?TheFeed=http://intimapharmafrance.com/ buying from online mexican pharmacy and https://www.news-adhoc.com/author/dhrphzmwfk/ mexico drug stores pharmacies
[url=http://www.google.com.cu/url?q=https://medicexpressmx.shop/]mexican pharmaceuticals online[/url] medicine in mexico pharmacies or [url=http://www.88moli.top/home.php?mod=space&uid=22735]buying prescription drugs in mexico online[/url] mexico drug stores pharmacies
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Mexican pharmacy price list: Online Mexican pharmacy – mexico drug stores pharmacies
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://truevitalmeds.com/# Sildenafil 100mg
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello! [url=http://provimedsrx.com/#]ProviMedsRX[/url] good web page.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sildenafil brand name india sildenafil online singapore or cheap real sildenafil 1 sildenafil
https://www.google.vu/url?sa=t&url=https://truevitalmeds.shop::: sildenafil 20 mg in mexico or https://bbs.soumoli.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=830716 sildenafil online india
[url=https://maps.google.pt/url?q=https://truevitalmeds.shop]where to buy generic sildenafil[/url] sildenafil nz pharmacy and [url=http://yangtaochun.cn/profile/mgpgfdyjoi/]sildenafil buy online usa[/url] 100mg sildenafil prices
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafil pills 20mg [url=https://tadalmedspharmacy.shop/#]Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription[/url] buy tadalafil europe
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexican pharmacy: Mexican pharmacy price list – Online Mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
eleanakonstantellos – Her brand feels authentic, each detail seems chosen with care and style.
https://googlesss.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discount tadalafil 20mg tadalafil 10mg generic or tadalafil tablet buy online where to buy tadalafil in usa
http://www.virtual-egypt.com/framed/framed.cgi?url==http://bluepharmafrance.com generic tadalafil for sale and http://ussher.org.uk/user/kwqwpgxnup/?um_action=edit tadalafil – generic
[url=http://www.christopheweber.de/homepage/gemeinsam/ext_link.php?url=http://bluepharmafrance.com]tadalafil tablets canada[/url] tadalafil 20 mg mexico or [url=http://la-maison-des-amis.com/user/bvkorrnxji/]tadalafil 30[/url] tadalafil 5 mg coupon
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Buy sildenafil: true vital meds – true vital meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://medicexpressmx.com/# Mexican pharmacy price list
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Первым делом определитесь, какой стиль будете воплощать в реальность https://olga-filippova.ru/interery-medical-study-center
Исходя из этого, будут и дальнейшие действия https://olga-filippova.ru/office_interior
После чего необходимо закупить материалы и инструменты https://olga-filippova.ru/office_interior
После того, как Вы сделаете ремонт, нужно будет выбирать, и покупать необходимую мебель и аксессуары https://olga-filippova.ru/interior_appartment
И, самое главное, полагайтесь на свой вкус и наши рекомендации и тогда у Вас всё получится!
Хотя у них много идей, но при этом, чтобы прийти к окончательному варианту вам придется проявить не дюжинную настойчивость для соблюдения сроков и показа предварительных вариантов https://olga-filippova.ru/
Цветовое решение лучше использовать в светлом и легком тоне – для студии не подойдут темные коричневые, синие, серые цвета https://olga-filippova.ru/blog
Лучше всего – пастельная гамма или классический белый https://olga-filippova.ru/interery-medical-study-center
Нарисуйте или распечатайте планировку своей квартиры и укажите на ней все реальные размеры вашей квартиры https://olga-filippova.ru/portfolio-2
Помечайте на плане коммуникации, проемы, высоты https://olga-filippova.ru/horeca
Используя компас, укажите стороны света https://olga-filippova.ru/interery-medical-study-center
Сервисы, полезные каждому дизайнеру https://olga-filippova.ru/kontakts
И не только Квартблог собрал список полезных ссылок из 70 сервисов, сайтов и книг, которые будут интересны не только дизайнерам интерьеров https://olga-filippova.ru/interery-fasad
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Smart crypto trading https://terionbot.com with auto-following and DCA: bots, rebalancing, stop-losses, and take-profits. Portfolio tailored to your risk profile, backtesting, exchange APIs, and cold storage. Transparent analytics and notifications.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The 10 Most Scariest Things About Car Key Repair car key repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Buy sildenafil [url=https://truevitalmeds.com/#]Buy sildenafil[/url] sildenafil
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Car Remote Start Repair: The Intermediate Guide
To Car Remote Start Repair Car Remote Start Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Current Job Market For Car Key Jammed Repair Professionals Like?
Car Key Jammed Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Best online Mexican pharmacy: Online Mexican pharmacy – Online Mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://medicexpressmx.shop/# mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี ในยุคที่เกมส์สล็อตออนไลน์ มีองค์ประกอบหลายๆอย่าง ที่เป็นตัวทำให้นักลงทุน ตัดสินใจกับการเล่นเกมสล็อตจาก เว็บนี้ มากกว่าที่อื่นๆ การทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี ทำให้ผู้เล่นติดใจ และ กลับมาเล่นกับ สล็อตเว็บตรง ที่นี่ ซ้ำ
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
เดโม่ pg เว็บตรงไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์ มีทดลองเล่นสล็อตค่ายเกมยอดฮิต เดโม่ pg เป็นแหล่งรวมตัวเกมส์ สล็อตยอดฮิต แตกหนัก แตกดี ที่สำคัญคือ การเลือกเว็บสล็อตสายตรงไม่ผ่านเเย่นต์ เชื่อถือได้มั่นคงปลอดภัยแน่นอน และ ตัวเกมส์สล็อตยอดฮิต ก็เป็นหนึ่งในตัวเลือกสำหรับนักลงทุนเช่นกัน
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
รวมโปรสล็อต50% เป็นหนึ่งในจุดขายของค่ายเกมนี้ เป็น สล็อตเว็บตรง อันดับ1หลายแห่งในไทย และ ต่างประเทศ โดยไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์ ผู้เล่นจึงมั่นใจได้ในความปลอดภัย และ อัตราการจ่ายที่ยุติธรรม รวมโปรสล็อต จากเว็บตรงนี้ มีรวมเกมทุกค่าย ที่ผ่านการตรวจสอบ จากองค์กรเกมระดับโลก ทำให้ผู้เล่นมีความมั่นใจว่า เล่นแล้วได้เงินจริง ไม่มีล็อคยูสแน่นอน!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
เกมยิงปลาแตกง่าย ในวงการออนไลน์ นอกจาก สล็อตออนไลน์แล้ว ยังมี คาสิโนออนไลน์ ที่ได้รับความนิยมในหมู่นักเดิมพันเป็นจำนวนมาก สล็อตเว็บตรง ที่มี รวมเกมยิงปลาทุกค่าย ที่เป็นยอดนิยมอีกด้วย ไม่ได้แค่เพราะความสนุกและความตื่นเต้นในการเล่น ยังเป็นเกมที่มีภาพกราฟิกสวยงามอลังการ และสามารถทำกำไรได้จริง ด้วยฝีมือและกลยุทธ์ที่ดี เหมาะสำหรับทั้งมือใหม่และสายล่าโบนัส
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
รวมโปรสล็อต pg 50% เป็นหนึ่งในจุดขายของค่ายเกมนี้ เป็นโปรโมชั่น จากสล็อตเว็บตรง อันดับ1หลายแห่งในไทย และ ต่างประเทศ โดยไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์ ผู้เล่นจึงมั่นใจได้ในความปลอดภัย และ อัตราการจ่ายที่ยุติธรรม ค่ายเกมนี้ ยังผ่านการตรวจสอบ จากองค์กรเกมระดับโลก ทำให้ผู้เล่นมีความมั่นใจว่า รวมโปรสล็อต pg 50% นี้ เล่นแล้วได้เงินจริง ไม่มีล็อคยูสแน่นอน!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
skibumart – Great mix of artistic style and user experience here.
https://gossogle.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Five Killer Quora Answers To Car Mechanical Key Repair Car Mechanical Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://truevitalmeds.com/# true vital meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Buy sildenafil online usa: sildenafil – Sildenafil 100mg price
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
eleanakonstantellos – Very professional feel, I sense a refined but accessible voice behind it.
https://googlesss.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sildenafil 20 mg over the counter sildenafil for daily use or sildenafil soft sildenafil where to buy
https://maps.google.com.np/url?q=https://truevitalmeds.com cost of 100mg sildenafil or https://armandohart.com/user/rncfmqyqai/?um_action=edit sildenafil pills canada
[url=http://jpn1.fukugan.com/rssimg/cushion.php?url=pharmaexpressfrance.com&popup=1]sildenafil 20 mg over the counter[/url] sildenafil online pharmacy uk and [url=http://156.226.17.6/home.php?mod=space&uid=1306285]sildenafil 5 mg price[/url] buy sildenafil in usa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Чаши бассейнов из монолитного железобетона. Устраиваем опалубку сложной геометрии, двойное армирование, заливку за один цикл с вибрированием. Делаем гидроизоляцию, подготовку под плитку или ПВХ-мембрану, вводы коммуникаций, закладные под оборудование и освещение. Контролируем герметичность и ровность чаши. Сдаем объект под отделку с полным комплектом документации. Работаем официально по договору. Гарантия на работы и материалы.
Вся информация на сайте – https://gbistroj.ru/stolbchatii-fundament
свайно-винтовой фундамент, проектирование фундамента цена, фундамент под забор
фундамент для бани под ключ, [url=https://gbistroj.ru/zemluanie-raboti]земляные работы[/url], ленточный фундамент с цоколем под ключ
Удачи!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Online Mexican pharmacy: Mexican pharmacy price list – legit mexican pharmacy without prescription
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sildenafil 100mg [url=https://truevitalmeds.shop/#]Sildenafil 100mg price[/url] Buy sildenafil online usa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Чаши бассейнов из монолитного железобетона. Устраиваем опалубку сложной геометрии, двойное армирование, заливку за один цикл с вибрированием. Делаем гидроизоляцию, подготовку под плитку или ПВХ-мембрану, вводы коммуникаций, закладные под оборудование и освещение. Контролируем герметичность и ровность чаши. Сдаем объект под отделку с полным комплектом документации. Работаем официально по договору. Гарантия на работы и материалы.
Вся арматура на сайте – https://gbistroj.ru/demontah
цокольный этаж под ключ заказать, фундамент на жб забивных сваях цена, разработка котлована под ключ
фундамент утепленная шведская плита цена, [url=https://gbistroj.ru/monolitnii-s-rostverkom]монолитный фундамент с ростверком под ключ[/url], демонтаж фундамента цена
Удачи!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго дня!
Утеплённая отмостка снижает теплопотери и риск пучения. Монтируем экструдированный пенополистирол, усиливаем кромку, делаем бетон с финишным заглаживанием и противоскользящей текстурой. Предусматриваем деформационные швы, капельники и аккуратное примыкание к цоколю. Интегрируем лотки и точечные водоприёмники, подбираем оптимальную ширину и уклон. Предоставляем гарантию на эксплуатацию. Работаем официально по договору.
Вся арматура на сайте – https://gbistroj.ru/zemluanie-raboti
отделка цоколя под ключ, бурение под сваи цена, фундамент под забор под ключ
земляные работы, [url=https://gbistroj.ru/burenie]бурение под сваи[/url], цокольный этаж под ключ заказать
Удачи!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hi! [url=https://mexrxdirect.top/#]buy provigil cheap[/url] beneficial web page.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://truevitalmeds.com/# Sildenafil 100mg price
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
new online canadian casino, usa gambling ranking and golden pokies united states, or play poker in south united states
My homepage: bellagio blackjack (Shani)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MedicExpress MX: Mexican pharmacy price list – mexico drug stores pharmacies
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Монтаж камеры видеонаблюдения цена https://vcctv.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MedicExpress MX: Legit online Mexican pharmacy – real mexican pharmacy USA shipping
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://truevitalmeds.com/# Buy sildenafil
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Mexican pharmacy price list [url=http://medicexpressmx.com/#]Online Mexican pharmacy[/url] MedicExpress MX
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
masquepourvous – Their branding is sophisticated, every detail seems carefully thought out.
https://googlesss.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Поставка и укладка бетона. Заказываем смесь нужной марки и подвижности у проверенных РБУ, учитываем температуру, расстояние и время в пути. Применяем глубинные вибраторы, правила и бетононасосы. Следим за технологическими перерывами и уходом за бетоном: увлажнение, укрытие плёнкой, пропитки. Соблюдаем график и качество, обеспечиваем прочность и морозостойкость конструкции. Работаем официально по договору.
Вся информация на сайте – https://gbistroj.ru/otdelka-cokolua
столбчатый фундамент цена, фундамент для бани цена, фундамент на жб забивных сваях
свайно-ростверковый фундамент, [url=https://gbistroj.ru/svaino-rostverkovii-fundament]свайно-ростверковый фундамент цена[/url], отмостка под ключ
Удачи!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Your writing is a masterpiece that elevates the reader’s experience by offering nuanced perspectives, and it would be riveting to see you explore the intersection of these ideas with innovative breakthroughs, such as artificial intelligence or sustainable development, while leveraging your talent for making complex concepts accessible and consistently providing enlightening content that resonates deeply with your audience.
link
link
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Свайно-ростверковые решения для слабонесущих грунтов и перепадов рельефа. Бурим скважины, армируем, заливаем сваи и объединяем их монолитным ростверком. Тщательно выбираем шаг свай, глубину погружения и класс бетона по итогам инженерного расчёта. Устраиваем песчаную подушку, закладные, гидроизоляцию и продухи. Обеспечиваем минимальную усадку и устойчивость к пучению. Работаем официально по договору.
Более подробно на сайте – https://gbistroj.ru/gidroizolyacia
дренаж фундамента под ключ, фундамент из блоков фбс, фундамент тисэ под ключ цена
фундамент для дома под ключ, [url=https://gbistroj.ru/demontah]демонтаж фундамента под ключ[/url], ленточный фундамент под ключ цена
Удачи!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
200 free spins no deposit usa casinos, online casino Fort pierce united states 1 dollar deposit and $5 deposit online casino canada, or top
online pokies and casinos canadian free games
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
hanacapecoral – I like the structure, navigation is smooth, experience is positive.
https://google.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
giocare Chicken Road gratis o con soldi veri: giocare Chicken Road gratis o con soldi veri – slot a tema fattoria Italia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
play Chicken Road casino online: real money Chicken Road slots – best Indian casinos with Chicken Road
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
giocare Plinko con soldi veri: bonus Plinko slot Italia – Plinko casino online Italia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
vincite e bonus gioco Chicken Road [url=https://chickenroadslotitalia.com/#]Chicken Road slot machine online[/url] giocare Chicken Road gratis o con soldi veri
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
11 “Faux Pas” That Are Actually OK To Use With Your
Experienced Car Key Repair Car key Repair service
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
British online casinos with Chicken Road Chicken Road or Chicken Road UK players free spins Chicken Road
http://scanmail.trustwave.com/?c=6677&d=3eHL2zmR-mSEueRJSdX4UpJhLotL1yEZhefsffMCDw&u=http://bluepharmafrance.com Chicken Road slot UK or http://www.xgmoli.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=14581 Chicken Road slot UK
[url=http://www.johnsongt.com/link.php?name=deezee&addr=bluepharmafrance.com]Chicken Road slot UK[/url] casino promotions Chicken Road game or [url=http://www.psicologiasaludable.es/user/dglqmpupuc/]licensed UK casino sites Chicken Road[/url] real money slot Chicken Road UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте! Как выбрать топовое казино с реальными выплатами. Полезные хаки от “Килограмм казино” в Telegram: https://t.me/KiloGram_club Изучайте рейтинги и документы. Ищите опции с выводом на телефонный баланс. Следите за отдачей. Пробуйте с низких ставок. Кто поделится своими методами для безопасной игры!
Килограм игорный клуб, KiloGram casino отзывы, промокод казино Килограм
Килограм казино бездепозитный, [url=https://t.me/s/KiloGram_Casino]зеркало Килограм казино[/url], 33 фриспина казино Килограм бездепозитный бонус
Удачи и топовых выйгрышей!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://chickenroadslotitalia.com/# giri gratis Chicken Road casino Italia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The 10 Most Scariest Things About Keyless Remote Repair Keyless Remote Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
giocare Plinko con soldi veri: bonus Plinko slot Italia – migliori casinò italiani con Plinko
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
giocare Chicken Road gratis o con soldi veri: slot a tema fattoria Italia – Chicken Road slot machine online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
British online casinos with Chicken Road [url=http://chickenroadslotuk.com/#]Chicken Road slot UK[/url] licensed UK casino sites Chicken Road
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The 10 Most Terrifying Things About Broken Key Repair Broken Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
See What Emergency Key Repair Tricks The Celebs Are Using Emergency Key Repair, https://notes.io/wWuWQ,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
CBD products be undergoing honestly changed my person! I not at all expected something so natural like colorado cbd to convey such equanimity and civil into my commonplace routine. Tension that once felt uncontrollable is moment so much easier to manage, and my snore has develop deeper and more refreshing. Square muscle aches after long days away faster. It feels remarkable to completely suffer with something gentle even now authoritative that supports both heart and mind. I can’t suspect my days without CBD anymore!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
10 Meetups About Car Flip Key Repair You Should Attend Key Fob Repair, Graph.Org,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
free demo Chicken Road game Chicken Road slot game India and play Chicken Road casino online secure online gambling India
https://www.google.com.sg/url?q=https://chickenroadslotindia.com secure online gambling India and https://www.trendyxxx.com/user/oftmhseobj/videos play Chicken Road casino online
[url=http://alfachat.ru/exit.php?linkurl=pharmaexpressfrance.com]free demo Chicken Road game[/url] play Chicken Road casino online and [url=https://gikar.it/user/ckltxzicwd/]free demo Chicken Road game[/url] Chicken Road slot game India
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Key Stuck In Ignition Repair Tools To Help You Manage Your Everyday Lifethe Only
Key Stuck In Ignition Repair Trick That Every Person Must
Know Key Stuck In Ignition Repair (Vania)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
РРЅРѕРіРґР° инженеры замечают: РѕРґРЅР° Рё та же линия выдаёт разное качество продукции РІ зависимости РѕС‚ того, кто Р·Р° ней работает. Формально человек лишь следит Р·Р° процессом, РЅРѕ факт остаётся фактом — «рука мастера» влияет даже РЅР° автоматизацию. Рта загадка заставляет думать Рѕ невидимой энергии, которую человек вкладывает РІ работу, даже РЅРµ осознавая этого.
Полная информация по ссылке – п»їhttps://baltmashstroy.ru/
проектирование приспособлений в машиностроении, промышленное оборудование, автоматизация процессов машиностроения
капитальный ремонт станков, [url=https://baltmashstroy.ru/]Промышленный монтаж и сервис[/url], сайт промышленного швейного оборудования
Удачи и комфорта в жизни!
[url=https://armviewstorm.com/n/All_Files/gallery-images/gallery-images/final]Тайна невидимых корректировок[/url] ad9b3eb
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
real money slot Chicken Road UK: real money slot Chicken Road UK – Chicken Road
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Plinko gioco a caduta palline: Plinko – scommesse Plinko online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pier45attheport – The site feels elegant, content flows with style and great charm.
https://google.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Keyless Remote Repair: 11 Thing You’re Forgetting To Do
emergency key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Chicken Road slot game India [url=http://chickenroadslotindia.com/#]bonus spins Chicken Road casino India[/url] how to win Chicken Road slot game
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Chicken Road slot machine online: slot a tema fattoria Italia – recensione Chicken Road slot
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
slot a tema fattoria Italia giocare Chicken Road gratis o con soldi veri and giocare Chicken Road gratis o con soldi veri giri gratis Chicken Road casino Italia
https://maps.google.mv/url?q=https://chickenroadslotitalia.shop Chicken Road slot machine online or http://www.donggoudi.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3681327 giocare Chicken Road gratis o con soldi veri
[url=https://www.tjarksa.com/ext.php?ref=http://pharmalibrefrance.com]giri gratis Chicken Road casino Italia[/url] casino online italiani con Chicken Road and [url=https://www.ipixels.com/profile/166814/skofxqrwny]slot a tema fattoria Italia[/url] vincite e bonus gioco Chicken Road
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
play Chicken Road casino online UK UK players free spins Chicken Road or Chicken Road slot UK play Chicken Road casino online UK
http://www.teamready.org/gallery/main.php?g2_view=core.UserAdmin&g2_subView=core.UserRecoverPassword&g2_return=https://chickenroadslotuk.com UK players free spins Chicken Road and http://ragnarokneon.online/home.php?mod=space&uid=3246 real money slot Chicken Road UK
[url=https://cse.google.com.et/url?sa=t&url=https://chickenroadslotuk.com]Chicken Road[/url] UK players free spins Chicken Road or [url=https://cyl-sp.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=108587]British online casinos with Chicken Road[/url] Chicken Road
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bonus Plinko slot Italia scommesse Plinko online or giocare Plinko con soldi veri giocare Plinko con soldi veri
https://www.google.ms/url?sa=t&url=https://hollandapotheeknl.com Plinko gioco a caduta palline or https://voicebyjosh.com/user/loigeplxsk/ Plinko demo gratis
[url=https://www.google.com.ph/url?q=https://hollandapotheeknl.com]bonus Plinko slot Italia[/url] Plinko casino online Italia and [url=http://clubdetenisalbatera.es/user/uejyficxcz/]Plinko gioco a caduta palline[/url] giocare Plinko con soldi veri
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Устранение поломок — это не просто временное решение, а способ вернуть ваше оборудование в идеальное состояние. Наши специалисты работают с вниманием к каждой детали, обеспечивая быстрое и качественное восстановление техники. Мы понимаем, как важна надежность на производстве, и поэтому каждый процесс ремонта и диагностики происходит с учетом максимальной безопасности и эффективности. Мы также предлагаем решения для улучшения работы вашего оборудования, чтобы оно не только восстановилось, но и стало лучше.
Полная информация по ссылке – п»їhttps://dag-techservice.ru/
технологическая карта наладки оборудования, ремонт шкафов управления, обслуживание сантехнического оборудования договор
наладка оборудования в логистическом центре, [url=https://dag-techservice.ru/]Промышленный монтаж и сервис[/url], монтаж промышленного оборудования псков
Удачи и комфорта в жизни!
[url=https://wpcure.com/thankyou-inquiry/?inquiry=c7cb218c43f57bb6ff91f9814b1ede95]Каждая деталь имеет значение — заботимся о вашем оборудовании как о своем[/url] 0c81764
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
slot a tema fattoria Italia: Chicken Road slot machine online – giocare Chicken Road gratis o con soldi veri
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
real money Chicken Road slots: secure online gambling India – secure online gambling India
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Push To Start Key Repair: The Intermediate Guide In Push To Start Key Repair Push To Start Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Хочу рассказать полезной находкой организации мероприятий в Москве.
Стояла проблема – оформить деловое мероприятие для расширенного состава. Нужно было больше посадочных мест.
Покупать мебель было слишком дорого для единичного события. Искали другие варианты и попробовали прокат качественной мебели.
Изучал предложения: картинка аренда офисная мебель – детальная информация о услугах.
**Что получили:**
– Сэкономили около 60% бюджета
– Профессиональное обслуживание
– Все организовано профессионально
– Отличные впечатления
– Возможность продления или выкупа
Рекомендуем всем знакомым. В различных ситуациях – это правильный выбор.
А как вы решаете такие задачи? Делитесь в комментариях!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
how to win Chicken Road slot game [url=http://chickenroadslotindia.com/#]real money Chicken Road slots[/url] bonus spins Chicken Road casino India
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Решил поделиться практическим опытом оформления событий в Москве.
Нужно было – организовать корпоратив для большой компании. Помещение требовало дополнительного оснащения.
Приобретение всего необходимого показалось нерациональным для одноразового использования. Искали другие варианты и узнали о прокат качественной мебели.
Изучал предложения: [url=https://stolikus.ru]мебель в аренду на свадьбу [/url] – детальная информация о услугах.
**Результат:**
– Сэкономили около 60% бюджета
– Профессиональное обслуживание
– Бесплатная доставка и сборка
– Гости были в восторге
– Гибкие условия сотрудничества
Рекомендуем всем знакомым. В различных ситуациях – это правильный выбор.
Есть ли опыт у коллег? Делитесь в комментариях!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет! Как найти выгодное казино с выплатами- Советы эксперта из Telegram “Килограмм казино”: https://t.me/KiloGram_Casino Оценивайте рейтинги и сертификаты. Ищите варианты с моментальными выплатами на МИР. Учитывайте RTP. Начинайте осторожно с небольших сумм. Поделитесь своими трюками по выбору казино!
Килограм казино рабочее зеркало, казино Килограм зеркало, казино Килограм
официальный сайт казино Килограм с бонусом, [url=https://t.me/KiloGram_club]играть в Килограм казино[/url], Килограм казино играть
Удачи и персональных выйгрышей!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hi! [url=https://mexrxdirect.top/#]mexrxdirect[/url] excellent site.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Job Market For Mobile Car Key Repair Professionals?
mobile car key repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
banehmagic – Excellent layout and offerings, confidence in their service grows naturally.
https://z2mqhs.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Расскажу о интересным решением обустройства пространства в столице.
Задача была – оформить деловое мероприятие для расширенного состава. Помещение требовало дополнительного оснащения.
Приобретение всего необходимого показалось нерациональным для одноразового использования. Искали другие варианты и узнали о прокат качественной мебели.
Изучал предложения: аренда мебели икеа – детальная информация о услугах.
**Что получили:**
– Существенная экономия средств
– Профессиональное обслуживание
– Бесплатная доставка и сборка
– Положительная обратная связь
– Гибкие условия сотрудничества
Теперь всегда обращаемся к ним. В различных ситуациях – это правильный выбор.
А как вы решаете такие задачи? Жду мнений!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The 10 Scariest Things About Car Keyless Unlock Repair Car Keyless Unlock Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Коллеги!
Решил поделиться практическим опытом оформления событий в Москве.
Нужно было – провести семейное торжество для большой компании. Помещение требовало дополнительного оснащения.
Закупка оборудования показалось нерациональным для разового мероприятия. Искали другие варианты и узнали о компанию по аренде мебели.
Читал информацию: stolikus.ru (аренда мебели фуршета ) – там все подробно.
**Что получили:**
– Сэкономили около 60% бюджета
– Профессиональное обслуживание
– Все организовано профессионально
– Гости были в восторге
– Индивидуальный подход
Теперь всегда обращаемся к ним. Для любых мероприятий – это оптимальный вариант.
А как вы решаете такие задачи? Жду мнений!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет, гемблеры! – –
Хочешь играть и выводить выигрыши без проблем- Вот что проверяю я перед тем, как ставить:
– Наличие международной лицензии
– Скорость вывода на банковскую карту
– Отзывы по выплатам
– Отдачу слотов ищу от 96% и выше!
Все проверенные площадки тут: https://t.me/s/KiloGramcasino
А вы на что смотрите при выборе казино
автоматы Килограм казино, KiloGram казино, Килограм казино онлайн
Килограм казино официальный сайт промокод, [url=https://t.me/s/KiloGram_Casino]автоматы Килограм казино[/url], казино клуб Килограм
Удачи и топовых выйгрышей!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
casino online italiani con Chicken Road: Chicken Road slot machine online – giri gratis Chicken Road casino Italia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
vincite e bonus gioco Chicken Road: giri gratis Chicken Road casino Italia – slot a tema fattoria Italia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всем привет! Сейчас много разговоров про онлайн платформы, но сложно понять, где реально получить выплату. Чтобы не попасть на мошенников, изучайте мнения игроков, проверяйте документы. Я собрал удобный рейтинг с отзывами здесь: https://t.me/KiloGram_Casino Поделитесь, кто-то уже пробовал эти игровые клубы
казино Килограм официальный сайт скачать, казино Килограм бонус за регистрацию, казино игорный клуб Килограм
KiloGram casino сайт, [url=https://t.me/KiloGramcasino]официальный сайт казино Килограм[/url], Килограм казино демо
Удачи и супер выйгрышей!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Plinko demo gratis: migliori casinò italiani con Plinko – scommesse Plinko online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://plinkoslotitalia.com/# Plinko RTP e strategie
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Коллеги!
Хочу рассказать практическим опытом организации мероприятий в столице.
Нужно было – оформить деловое мероприятие для значительного количества гостей. Помещение требовало дополнительного оснащения.
Закупка оборудования не оправдывалось для разового мероприятия. Стали изучать альтернативы и узнали о компанию по аренде мебели.
Читал информацию: москва аренда синей мебели – детальная информация о услугах.
**Что получили:**
– Существенная экономия средств
– Мероприятие прошло на отлично
– Полный сервис включен
– Положительная обратная связь
– Гибкие условия сотрудничества
Взяли на вооружение. В различных ситуациях – это оптимальный вариант.
Кто что использует? Обсуждаем!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Решил поделиться интересным решением организации мероприятий в Москве.
Нужно было – организовать корпоратив для расширенного состава. Нужно было больше посадочных мест.
Покупать мебель показалось нерациональным для разового мероприятия. Стали изучать альтернативы и открыли для себя компанию по аренде мебели.
Изучал предложения: мебель в аренду для переговорной – там все подробно.
**Итог:**
– Существенная экономия средств
– Мероприятие прошло на отлично
– Полный сервис включен
– Гости были в восторге
– Гибкие условия сотрудничества
Теперь всегда обращаемся к ним. В различных ситуациях – это идеальное решение.
Есть ли опыт у коллег? Обсуждаем!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Job Market For Keyless Fob Repair Professionals?
Keyless Fob Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
CBD products experience in good faith changed my subsistence! I not at all expected something so reasonable like [url=https://cobocbd.com/collections/cbd-gummies ]cbd gummies near me[/url] to topple b reduce such hush and compatible into my everyday routine. Highlight that at the same time felt prodigious is second so much easier to manage, and my snooze has happen to deeper and more refreshing. Even muscle aches after long days away faster. It feels amazing to finally have something gentle to this day powerful that supports both essence and mind. I can’t take it as given my days without CBD anymore!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’ve been using https://www.nothingbuthemp.net/collections/mushroom-vapes regular on account of during the course of a month now, and I’m justifiably impressed during the uncontested effects. They’ve helped me judge calmer, more balanced, and less anxious everywhere the day. My saw wood is deeper, I wake up refreshed, and uniform my nave has improved. The trait is famous, and I cherish the accepted ingredients. I’ll positively heed buying and recommending them to everyone I identify!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
how to win Chicken Road slot game [url=https://chickenroadslotindia.shop/#]play Chicken Road casino online[/url] best Indian casinos with Chicken Road
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Расскажу о интересным решением организации мероприятий в столице.
Нужно было – оформить деловое мероприятие для расширенного состава. Нужно было больше посадочных мест.
Закупка оборудования было слишком дорого для одноразового использования. Рассматривали возможности и попробовали компанию по аренде мебели.
Нашел отличный сервис: stolikus.ru (барная мебель в аренду ) – там все подробно.
**Что получили:**
– Существенная экономия средств
– Профессиональное обслуживание
– Полный сервис включен
– Гости были в восторге
– Индивидуальный подход
Рекомендуем всем знакомым. В различных ситуациях – это правильный выбор.
Кто что использует? Жду мнений!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
See What Car Key Blade Repair Tricks The Celebs Are Using Car key blade repair,
md.swk-web.com,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
veilig online apotheek NL: online apotheek nederland – apotheek zonder receptplicht
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Почему некоторые дома стоят веками, а другие рушатся за годы? — Разница кроется не только в материалах, но и в уважении к деталям: старые мастера строили так, будто дом должен пережить их внуков, а современные проекты часто считают метрами и сроками сдачи; секрет долговечности всегда скрывается в мелочах — правильной сушке кирпича, тщательном подборе раствора, глубине заложенного фундамента, и эти мелочи решают всё.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://rosstroy.ru/materials/dveri/shpon.html
названия строительной компаний, строительство, саморезы для дюбеля газобетона
арматура, [url=https://rosstroy.ru/materials/fundamenty/pesok.html]Строительные технологии | Материалы для фундамента: песок[/url], насосы водоснабжения для квартир
Удачи и комфорта в жизни!
[url=https://salamtourslanka.com/hello-world/#comment-9703]Почему строительные планы меняют судьбы людей?[/url] 752325a
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Ркологические следствия глобального роста отходов проявляются РІ том, что свалки становятся новыми ландшафтами планеты: РѕРЅРё занимают территории, отравляют почвы Рё РІРѕРґСѓ, создают новые источники токсинов, Рё именно РІ этой РіРѕСЂРµ РјСѓСЃРѕСЂР° отражается цивилизация, которая превратила саму планету РІ контейнер для собственных ошибок.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://ecodata.ru/basic-concepts-of-ecology/key-ideas-of-ecology/troficheskij-uroven.html
Сообщество чередование стабильных состояний в экологии, конкуренция видов за ресурсы, Проблемы устойчивости лесов в условиях антропогенных нагрузок Специфические проблемы тропических лесов что это
конкуренция РІ популяции, [url=https://ecodata.ru/basic-concepts-of-ecology/key-ideas-of-ecology/ekologicheskaya-izbytochnost.html]Ркология | Ркологическая избыточность[/url], Особенности демографии развитых Рё развивающихся стран определение
Удачи и комфорта в жизни!
[url=https://premier-realty.co.ke/2024/11/12/why-suburban-properties-in-kenya-are-the-best-investment-opportunity/#comment-9021]Тайна «зелёной энергетики»[/url] 17641ad
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
opinioni su farmacia online italiana: ordinare farmaci senza ricetta – farmacia online Italia affidabile
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
10 Websites To Help You To Become A Proficient
In Keyless Entry Remote Repair Car Keyless Entry Remote Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
How To Explain Remote Key Repair To Your Grandparents Broken key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
medicinali generici a basso costo [url=https://farmaciafacileit.com/#]ordinare farmaci senza ricetta[/url] ordinare farmaci senza ricetta
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacia espanola en linea economica: farmacia online Espana fiable – SaludExpress
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita comprare farmaci online all’estero and Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita Farmacia online miglior prezzo
http://images.google.mk/url?q=https://farmaciafacileit.com farmacia online senza ricetta and http://dnp-malinovka.ru/user/lhpugwvtlj/?um_action=edit Farmacie online sicure
[url=https://maps.google.com.gi/url?sa=t&url=https://farmaciafacileit.com]Farmacia online piГ№ conveniente[/url] comprare farmaci online all’estero or [url=https://vintage-car.eu/user/winhedvueh/]Farmacia online miglior prezzo[/url] comprare farmaci online all’estero
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Car Ignition Repair Tools To Improve Your Daily Lifethe One Car Ignition Repair Trick That Everybody Should Know car ignition Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://farmaciafacileit.shop/# ordinare farmaci senza ricetta
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
apotek på nett: reseptfrie medisiner på nett – apotek på nett
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Google This site has strong energy, design feels smooth
and welcoming.
Check out my homepage; Ali Hamza
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
apotek på nett med gode priser: billige generiske legemidler Norge – apotek på nett
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
9 . What Your Parents Teach You About Emergency Car Key Repair Car Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Создание корпоративного сайта под ключ часто подаётся как скучный перечень функций. Но клиенту важно чувствовать, что ресурс будет частью бизнеса. Если текст объясняет: адаптивный дизайн, SEO оптимизация под локальные запросы, интеграция CRM, настройка контекстной рекламы, поддержка, внимание сохраняется. Корпоративный сайт воспринимается не как витрина, а как инструмент отдела продаж.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://ts-web.ru/
аудит сайтов конкурентов Россия, разработка сайтов для бизнеса в России, поддержка интернет-магазинов в России
разработка сайтов для бизнеса в России, [url=https://ts-web.ru/]TS-Web — Лендинг: SEO, разработка, аналитика[/url], SMM продвижение интернет-магазина
Удачи и комфорта в жизни!
[url=http://actingcode.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=tl_qa&wr_id=79]Digital маркетинг в[/url] 52325ab
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
discrete levering van medicijnen [url=https://hollandapotheeknl.shop/#]online apotheek[/url] discrete levering van medicijnen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Proximity Key Repair Tools To Help You Manage Your Daily Lifethe One
Proximity Key Repair Trick That Everybody Should Know Proximity Key Repair; Roberts-Rankin-2.Mdwrite.Net,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
apotek på nett: reseptfrie medisiner på nett – apotek uten resept med levering hjem
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Key Stuck In Ignition Repair Techniques To Simplify Your Everyday Lifethe Only Key Stuck In Ignition Repair Trick That Everyone Should Know
Key Stuck In Ignition Repair; Paulina,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
CBD products be undergoing honestly changed my biography! I not at all expected something so unpremeditated like https://cobocbd.com/blogs/learn/how-to-make-cbd-oil to carry such calm and civil into my daily routine. Highlight that once felt uncontrollable is trendy so much easier to control, and my sleep has happen to deeper and more refreshing. Yet muscle aches after protracted days fade faster. It feels remarkable to finally arrange something light yet dynamic that supports both body and mind. I can’t suspect my days without CBD anymore!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
geneesmiddelen zonder recept bestellen: Holland Apotheek – veilig online apotheek NL
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheek nederland [url=https://hollandapotheeknl.com/#]veilig online apotheek NL[/url] Holland Apotheek
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ordinare farmaci senza ricetta: opinioni su farmacia online italiana – opinioni su farmacia online italiana
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacia online senza ricetta farmaci senza ricetta elenco or farmacie online autorizzate elenco migliori farmacie online 2024
https://maps.google.bg/url?sa=t&url=https://farmaciafacileit.com п»їFarmacia online migliore or http://www.1gmoli.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=209826 farmacia online senza ricetta
[url=https://www.google.so/url?q=https://farmaciafacileit.com]Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita[/url] comprare farmaci online con ricetta and [url=http://nidobirmingham.com/user/catvhidwrx/]farmaci senza ricetta elenco[/url] farmacie online sicure
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacia online España fiable: medicamentos sin receta a domicilio – pedir fármacos por Internet
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
5 Killer Quora Answers On Keyless Ignition Repair Keyless Ignition Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacia barata: pedir fármacos por Internet – SaludExpress
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacia online madrid farmacia online espaГ±a envГo internacional and п»їfarmacia online espaГ±a farmacia online envГo gratis
http://www.collegeboyspank.com/Home.aspx?returnurl=http://bluepharmafrance.com/ farmacias online seguras or https://vintage-car.eu/user/fiveynodeu/ farmacia online madrid
[url=http://www.ohashi-co.com/w3a/redirect.php?redirect=http://bluepharmafrance.com]п»їfarmacia online espaГ±a[/url] farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a or [url=https://bebele.ru/user/kubwspvijn/]farmacia online envГo gratis[/url] farmacia online envГo gratis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
medicamentos sin receta a domicilio [url=https://saludexpresses.shop/#]farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a[/url] farmacias online seguras
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bestille medisiner online diskret: billige generiske legemidler Norge – apotek på nett
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Current Job Market For Car Key Jammed Repair Professionals?
Car Key Jammed Repair, Kazuko,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheek Nederland betrouwbaar Holland Apotheek and online apotheek nederland generieke geneesmiddelen Nederland
https://www.google.cd/url?sa=t&url=https://hollandapotheeknl.com veilig online apotheek NL or https://armandohart.com/user/etgmxzokkh/?um_action=edit HollandApotheek
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.com.nf/url?sa=t&url=https://hollandapotheeknl.com]discrete levering van medicijnen[/url] apotheek zonder receptplicht or [url=http://lenhong.fr/user/byyzqsshfr/]Holland Apotheek[/url] online apotheek Nederland betrouwbaar
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
reseptfrie medisiner på nett: apotek uten resept med levering hjem – apotek uten resept med levering hjem
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Car Keyless Entry Fob Repair: The Intermediate Guide For Car
Keyless Entry Fob Repair Car Keyless Entry Fob Repair – Latrice,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
medicinali generici a basso costo [url=https://farmaciafacileit.shop/#]FarmaciaFacile[/url] farmacia online Italia affidabile
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
spedizione rapida farmaci Italia: Farmacia online miglior prezzo – spedizione rapida farmaci Italia
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
See What Ignition Key Repair Tricks The Celebs Are Using Ignition Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacia online senza ricetta farmacia online or acquisto farmaci con ricetta farmacie online affidabili
https://www.google.co.ck/url?sa=t&url=https://farmaciafacileit.com farmacia online senza ricetta or https://fionadobson.com/user/kqtimfovzk/?um_action=edit farmacie online affidabili
[url=http://www.google.cm/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=w4&source=images&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&docid=IFutAwmU3vpbNM&tbnid=OFjjVOSMg9C9UM:://pharmaexpressfrance.com/pages/about-us]top farmacia online[/url] Farmacia online miglior prezzo and [url=https://dan-kelley.com/user/xkgdcbbqzu/?um_action=edit]comprare farmaci online all’estero[/url] top farmacia online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
CBD products contain in good faith changed my biography! I not under any condition expected something so logical like [url=https://cobocbd.com/products/mood-gummies ]CBD gummies for mood[/url] to bring such tranquil and compatible into my everyday routine. Significance that once felt prodigious is second so much easier to carry on, and my sleep has become deeper and more refreshing. Square muscle aches after long days away faster. It feels extraordinary to at the end of the day force something gentle even now powerful that supports both body and mind. I can’t surmise my days without CBD anymore!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
billige generiske legemidler Norge: apotek uten resept med levering hjem – apotek på nett
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Car Lock Repair: The Intermediate Guide On Car Lock Repair
Car Lock Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacias online seguras farmacia online envГo gratis and farmacia online 24 horas farmacia online barcelona
https://www.repcheckr.com/reviews/bluepharmafrance.com farmacia online espaГ±a envГo internacional and http://nidobirmingham.com/user/vnprkmnast/ farmacia online espaГ±a envГo internacional
[url=https://www.finanzplaner-deutschland.de/fpdeu/inc/mitglieder_form.asp?nr=24&referer=https://saludexpresses.shop::]farmacias direct[/url] farmacia online madrid or [url=https://www.ixxxnxx.com/user/ewmokhcgvi/videos]farmacia online madrid[/url] farmacia online 24 horas
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://nordapotekno.shop/# kundevurderinger av nettapotek
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
SaludExpress [url=https://saludexpresses.shop/#]farmacia online Espana fiable[/url] farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pedir farmacos por Internet: farmacia online barata – farmacia online Espana fiable
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
reseptfrie medisiner på nett: bestille medisiner online diskret – apotek på nett billigst
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте, форумчане! Сейчас хочу обсудить тему, которая долго меня увлекает — Что посетить в Китае.
Этот большой и разнообразный край привлекает
своей богатой культурой, восточной мудростью и потрясающими пейзажами, поэтому хочу поделиться своими мыслями
и обсудить интересные места для путешествий.
Если рассуждать о главных достопримечательностях, нельзя не упомянуть Великую китайскую стену
— поистине впечатляющее сооружение,
которое поражает своей масштабом и историей.
Также стоит посмотреть на древний город Пекин со своей изысканной
архитектурой и дворцами, а для ценителей
природы предлагаются живописные горы Хуаншань,
где восходы солнца дарят впечатляющие сцены.
[b]Культура[/b] и [b]природа[/b] здесь гармонично переплетаются, что
превращает путешествие по Китаю по-настоящему уникальным опытом.
В итоге, Китай — это страна, где
любой обнаружит что-то особенное,
будь то история, природа или современность.
А как вы считаете? Какие места в Китае
произвели на вас максимальное впечатление, и что бы
вы посоветовали обязательно посетить
тем, кто только планирует поездку?
Будет интересно услышать ваше мнение!
http://www.mythmoor.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Тайна некоторых промышленных покрытий заключается в том, что они выдерживают нагрузки и воздействия, которые не предусмотрены ни одним стандартом: химические растворы, экстремальные температуры, удары и вибрации оставляют на них лишь незначительные следы. Загадка в том, что формулы их состава давно известны и кажутся банальными, но отдельные партии проявляют свойства, близкие к чуду, заставляя инженеров думать, что металл сам выбирает, каким быть.
Полная информация по ссылке – п»їhttps://baltmashstroy.ru/
оборудование литейных цехов, автоматизация машиностроительных процессов, сборочный цех машиностроение
промышленное машиностроение, [url=https://baltmashstroy.ru/]Промышленный монтаж и сервис[/url], машина отечественного производства
Удачи и комфорта в жизни!
[url=https://ecotierrasurban.com/hello-world/#comment-7715]Загадка конвейеров: почему они никогда не устают[/url] 2325ab1
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacia online España fiable: pedir fármacos por Internet – farmacia online España fiable
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
10 Things You Learned In Kindergarden They’ll Help You Understand Keyless Entry Remote Repair Car Keyless entry Remote repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Current Job Market For Vehicle Keyless Start Repair Professionals?
Vehicle Keyless Start Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
billige generiske legemidler Norge kundevurderinger av nettapotek and apotek på nett billigst apotek på nett
https://www.google.com.au/url?q=https://nordapotekno.shop NordApotek and http://www.80tt1.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=4019261 NordApotek
[url=http://www.google.st/url?q=https://nordapotekno.shop]kundevurderinger av nettapotek[/url] apotek på nett med gode priser or [url=https://bbsdump.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=32226]apotek på nett billigst[/url] NordApotek
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
medicinali generici a basso costo [url=https://farmaciafacileit.com/#]opinioni su farmacia online italiana[/url] farmacia online Italia affidabile
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
apotek på nett med gode priser: apotek på nett – bestille medisiner online diskret
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Current Job Market For Mobile Car Key Repair
Professionals? car key repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Тайна сверхпрочных покрытий в том, что они выдерживают нагрузки, превышающие расчётные в несколько раз, и в эксплуатации ведут себя как живые щиты, защищающие металл от разрушения. В лабораториях такие свойства не фиксируются, но на производстве они проявляются стабильно. Загадка этих феноменов заставляет инженеров признать: мы ещё не знаем всех возможностей материалов, которыми пользуемся.
Полная информация по ссылке – п»їhttps://baltmashstroy.ru/
диагностика оборудования и трубопроводов, инновационные технологии в машиностроении, группу компаний промышленное оборудование
сервис станков Санкт-Петербург, [url=https://baltmashstroy.ru/]Промышленный монтаж и сервис[/url], машиностроение в технопарках
Удачи и комфорта в жизни!
[url=https://suidea.com.ar/tablero-de-control-solucion-etoolbox-v5/#comment-107639]Тайна старых учебников машиностроения[/url] 7752325
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Key Stuck In Ignition Repair Tools To Improve Your Daily Life Key Stuck In Ignition Repair Technique Every Person Needs To Be Able
To Key Stuck In Ignition Repair (rentry.co)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacia con envío rápido y seguro: comprar medicinas online sin receta médica – SaludExpress
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
farmacias online seguras: farmacia online Espana fiable – farmacia con envio rapido y seguro
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://farmaciafacileit.com/# opinioni su farmacia online italiana
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
opinioni su farmacia online italiana [url=https://farmaciafacileit.shop/#]farmacia online Italia affidabile[/url] FarmaciaFacile
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The 9 Things Your Parents Teach You About Car Key Housing
Repair Car Key Housing Repair (https://funsilo.date/)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kundevurderinger av nettapotek: apotek uten resept med levering hjem – billige generiske legemidler Norge
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выращивание семечек конопли правильно мифы и факты
Мой взгляд на то, как сварить амфетамин: химия и факты изнутри. Когда я впервые столкнулся с темой, как сварить амфетамин, мне было интересно понять – что же на самом деле скрывается за этим загадочным и пугающим процессом. Решил изучить всё подробно, чтобы разобраться без эмоций и стереотипов. С самого начала стало понятно: это сложный химический синтез, требующий точного соблюдения последовательности действий. Обычно речь идёт о нескольких этапах – смешивание реактивов, контроль температуры и времени, а потом отделение и очистка конечного продукта. Конечно, в подпольных условиях часто используют подручные материалы и самодельное оборудование, что добавляет сложности и риска. Мне показалось любопытным, как люди импровизируют: например, заменяют лабораторные приборы бытовыми приборами или используют химикаты из аптек и хозяйственных магазинов. Это своего рода инженерное творчество, но с серьёзными последствиями, о которых часто предупреждают даже сами участники таких обсуждений. Погружаясь в детали, я понял, что процесс далеко не так прост, как иногда кажется. Малейшая ошибка – и реакция может пойти неправильно, что опасно для здоровья и жизни. Это заставляет уважать сложность химии и осознавать всю ответственность за любые эксперименты с подобными веществами. В итоге мой интерес к теме превратился в понимание: химия – мощный инструмент, который можно использовать как для пользы, так и во вред. Сейчас я стараюсь направлять свои знания в научные исследования и разработки, где химия помогает создавать полезные лекарства и материалы. Этот опыт научил меня, что важно подходить к любым темам с осознанием и ответственностью, а не только с любопытством. Знание – это сила, но только если использовать его правильно.
Основные ссылки:
как сделать мефедрон — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-svarit-mefedronкак вырастить семечки марихуаны — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-vyrastit-semena-konopli
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как сделать домашний мефедрон
Юридические комментарии подчеркивают, что тема «как выращивать семена марихуаны» используется исключительно в контексте профилактики и запретов. Исторический разбор показывает, что выражение «как называется человек который выращивает марихуану» стало частью культурных дискуссий. Фраза «как сделать метамфетамин в домашних условиях» часто появляется в опасных публикациях; эксперты подчёркивают необходимость удаления и просвещения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’ve been exploring terpene-based products candy terpenes recently, and I’m really enjoying the experience. The scents are well off, real, and pleasant. They add a nice be a match for to my constantly programmed, helping beat up a compare the mood and atmosphere. A great find after anyone who appreciates perfumed wellness tools.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’ve been using [url=https://www.nothingbuthemp.net/collections/thc-wine ]thc infused wine[/url] regular for all about a month for the time being, and I’m indeed impressed by the positive effects. They’ve helped me judge calmer, more balanced, and less solicitous everywhere the day. My sleep is deeper, I wake up refreshed, and even my pinpoint has improved. The attribute is outstanding, and I worth the accepted ingredients. I’ll positively preserve buying and recommending them to person I be aware!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
beste online-apotheke ohne rezept: Kamagra online bestellen – online apotheke preisvergleich
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Социальные и профилактические подходы к запросу «как самому сделать гашиш»
Как сделать гашиш: история одного эксперимента. Михаил всегда интересовался растениями и их свойствами. В поисках необычных способов переработки зелени он однажды наткнулся на старинные методы, используемые в разных странах. Особенно его заинтересовал вопрос – как сделать гашиш, и почему эта тема вызывает такой интерес у ботаников по всему миру. Оказывается, процесс создания гашиша имеет древние корни. В разных регионах его делали по-разному: в Марокко, например, использовали сухой метод трения, а в Непале — «ручной сбор смолы». Михаил начал с теории: читал научные статьи, изучал исторические хроники и даже нашёл упоминание гашиша в персидских рукописях. Первым этапом было понимание, что такое трихомы – мельчайшие смолистые железы на растениях. Именно они содержат ароматные масла и вещества, из которых и формируется конечный продукт. Чтобы извлечь смолу, нужно аккуратно отделить эти кристаллы. Михаил попробовал сухой метод: заморозил растительное сырьё, а затем начал аккуратно просеивать его через мелкое сито. Образовавшийся порошок он собрал и спрессовал в плотные брикеты. Он также поэкспериментировал с водяным методом: смешал измельчённое растение с холодной водой и льдом, а затем слил полученную смесь через фильтр. Оставшийся осадок оказался весьма ароматным. Михаил отметил, что чистота и качество продукта напрямую зависят от аккуратности процесса и свежести сырья. Важно понимать: экспериментировать можно только в целях изучения процессов и получения знаний о природе. Михаил вёл дневник, фиксируя каждый шаг, сравнивая методы и делая выводы. Для него это стало настоящим хобби и способом узнать больше о свойствах растений и их потенциале. Изучение темы, как сделать гашиш, превратилось для Михаила в увлекательное путешествие по ботанике, химии и истории. Такой опыт расширяет кругозор и помогает лучше понять взаимодействие человека и природы. Если вы интересуетесь растениями, натуральными методами переработки и научными экспериментами – начните с теории. Иногда самые простые вопросы открывают удивительные горизонты.
Основные ссылки:
как вырастить куст конопли — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-vyrastit-konoplyuкак сделать гашиш из марихуаны — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-sdelat-gashish
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как вырастить куст конопли
Запрос «как называют людей которые выращивают коноплю» используется в исследованиях для анализа субкультурных терминов. Модерация и правила площадок направлены на минимизацию доступа к контенту с «как сделать гашиш своими руками». Фраза «как вырастить семечко конопли» анализируется в образовательных материалах как пример языка, отражающего молодежные интересы и мифы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Социальный анализ выражения «как варить мефедрон рецепт»
Рецепт героина: химический пазл без мистики. Встречали когда-нибудь слово «рецепт героина» и задумывались, что же за тайны скрываются за этим термином? Давайте взглянем на это с научной и при этом лёгкой стороны – химия может быть увлекательной! Героин – это продукт химической трансформации морфина, который добывают из опийного мака. Если представить, что морфин – это исходный пазл, то рецепт героина – инструкция, как из этого пазла сделать новый, немного другой. Всё начинается с растения, а заканчивается сложной реакцией в лаборатории. Ключевой этап – ацетилирование. Звучит серьёзно, но проще представить это как «переодевание» молекулы морфина: она меняет свои «аксессуары» – гидроксильные группы – на «шикарные» ацетильные с помощью уксусного ангидрида. Для этого нужен правильный «фонд» – лабораторное оборудование и точные условия, иначе «переодевание» просто не сработает. Почему стоит знать рецепт героина? Не для того, чтобы повторять дома – это опасно и запрещено! А чтобы понять, как химия оживляет молекулы и превращает одни вещества в другие. Это как изучать волшебство науки, только без фокусов и мистики. Кроме того, изучение таких процессов помогает специалистам создавать лекарства и разрабатывать методы борьбы с наркоманией. Химия – это не только формулы, но и возможность менять мир к лучшему. Так что рецепт героина – это не загадка, а просто ещё одна глава в книге химии, которую стоит прочесть с интересом и уважением. Пусть изучение науки будет вашим новым приключением!
Основные ссылки:
как сделать лсд — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-sdelat-lsdкак сделать героин из мака — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-sdelat-geroin
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как сделать лсд
Как сварить меф в домашних условиях — правовой обзор Профилактические проекты направляют обсуждение «как делают наркотик соли» в сторону программ снижения вреда, консультаций и медицинской помощи. Юридические комментарии подчеркивают, что материалы о «как сделать лсд в домашних условиях» должны блокироваться и заменяться профилактическим контентом.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
apotheke online online apotheke versandkostenfrei and online apotheke online apotheke gГјnstig
http://galaxy-at-fairy.df.ru/phpinfo.php?a%5B%5D=i+want+to+buy+viagra online apotheke rezept or http://la-maison-des-amis.com/user/hmzmpzwzol/ eu apotheke ohne rezept
[url=http://www.pinknotora.net/link/?http://pharmaexpressfrance.com]ohne rezept apotheke[/url] medikament ohne rezept notfall and [url=http://clubdetenisalbatera.es/user/wkwhwkjyft/]online apotheke gГјnstig[/url] medikamente rezeptfrei
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tryggt svenskt apotek pa natet: generiska lakemedel online – eu apotheke ohne rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день, коллеги!
Недавно столкнулся с организацией деловой встречи для застройщика. Было важно на статусном оформлении.
Сложность заключалась что офисные помещения не подходили для масштабного мероприятия. Приобретение нецелесообразно.
Помогли специалисты по аренде – взяли качественные столы. Между прочим, недавно читал [url=http://podushechka.net/arenda-mebeli-dlya-b2b-meropriyatij-reshenie-stroyashhee-uspex-v-stroitelnoj-sfere/]полезный материал[/url] про решения для строительных компаний – там дельные идеи.
Клиент остался доволен. Советую коллегам кто проводит деловые мероприятия.
Процветания компаниям!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
diskret leverans av mediciner: NordicApotek – online apotheke gГјnstig
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
п»їshop apotheke gutschein [url=https://vitalapotheke24.shop/#]kamagra oral jelly[/url] online apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacie en ligne france pas cher pharmacie en ligne france fiable or pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance Pharmacie Internationale en ligne
https://maps.google.com.au/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmarapide.com pharmacie en ligne france pas cher and https://vintage-car.eu/user/amxmqzylxu/ pharmacie en ligne
[url=http://clients1.google.com.vn/url?sa=i&url=https://pharmarapide.com]pharmacie en ligne pas cher[/url] acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance and [url=http://bbs.maibu.cc/space-uid-1160616.html]pharmacie en ligne fiable[/url] acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://vitalapotheke24.shop/# eu apotheke ohne rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Роль платформ при материалах «как сварить мефедрон дома»
Как сделать амфетамин: химия и техника за кадром. Максим всегда интересовался химией и разными технологическими процессами. Однажды он заметил, что тема «как сделать амфетамин» часто обсуждается в интернете, и решил изучить её с научной точки зрения, чтобы понять, что стоит за этим сложным процессом. Производство амфетамина – это химический синтез, который требует последовательного выполнения нескольких стадий. На практике это означает точное смешивание реагентов, контроль температуры, времени реакции и последующую очистку продукта. Несмотря на то, что в подпольных условиях часто применяются импровизированные приборы и доступные компоненты, основные химические принципы остаются неизменными. Максим заметил, что люди, изучающие этот процесс, часто подходят к делу как к инженерной задаче – они создают самодельное оборудование из подручных материалов, экспериментируют с дозировками и методами очистки. Это напоминает своего рода лабораторные исследования, но с серьёзными рисками для здоровья и безопасности. Интересно, что химия амфетамина во многом схожа с синтезом других органических веществ, в том числе некоторых лекарственных препаратов. Разница заключается в конечной цели и последствиях применения. Максим считает важным понимать эти процессы не для практического применения, а чтобы осознать сложности и ответственность, связанные с химией. Сейчас он учится в университете и планирует заниматься разработкой новых фармацевтических препаратов, где химия служит во благо людям. Изучение таких тем помогает ему лучше понимать, как наука работает в самых разных областях, и почему важно использовать знания с этическими принципами. Таким образом, тема «как сделать амфетамин» – это не только криминальная история, но и пример того, как химия требует серьёзного подхода, глубоких знаний и ответственности за свои действия.
Основные ссылки:
как сварить метамфетамин — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-svarit-metкак сварить амфетамин — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-sdelat-amfetamin
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как сварить метамфетамин в домашних условиях
Социологи приводят «как сделать амфетамин дома» как пример рискованного онлайн-поведения, требующего образовательных и профилактических ответов. Органы профилактики и НКО рекомендуют заменить инструкции по «как сделать мефедрон в домашних условиях» на материалы о снижении вреда и восстановлении. Запрос «как выращивать семечки конопли правильно» встречается в СМИ как маркер молодежных тенденций и источник профилактических программ.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
günstige online apotheke: Kamagra Deutschland Apotheke – online apotheke günstig
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Почему обсуждают тему «как вырастить коноплю»
Как сделать гашиш в домашних условиях: научный эксперимент Ивана. Когда Иван, студент-биолог из Казани, начал изучать смолистые структуры растений, он и представить не мог, куда приведёт его любопытство. Один из вопросов, заинтересовавших его в ходе научной практики, звучал так: как сделать гашиш в домашних условиях, используя подручные методы и сохраняя чистоту эксперимента? Иван не искал рецептов из интернета. Он подошёл к делу как настоящий исследователь – составил гипотезу, изучил литературу и решил воссоздать классические методы экстракции смол из растений. Его целью не было изготовление чего-то запрещённого – только изучение химических процессов, происходящих при отделении эфирных масел и смол. Сначала он изучил анатомию трихом – микроскопических желёз на поверхности листьев. Именно в них накапливаются смолистые вещества, благодаря которым растения защищаются от насекомых и ультрафиолета. Иван начал с «сухого сита» – он замораживал листья, аккуратно перетирал их над тонкой сеткой, а затем собирал мелкий порошок, который блестел на свету, как золотистая пыльца. Для сравнения он опробовал водяной метод: в лабораторной посуде смешал измельчённое сырьё с ледяной водой и фильтровал через слои ткани. По его записям, осадок получался более плотным и имел насыщенный аромат. Он даже провёл тесты на чистоту материала, измеряя количество хлорофилла и других примесей. Методология, безопасность и внимание к деталям были для него в приоритете. Эксперимент строго соответствовал академическим рамкам: всё происходило в закрытой лабораторной среде, под наблюдением преподавателя. Его работа вызвала интерес на научной конференции, где он представил результаты как исследование природных экстрактов и их свойств. Ответ на вопрос, как сделать гашиш в домашних условиях, оказался гораздо глубже, чем просто техника. Для Ивана это стало шагом в сторону науки, биохимии и понимания растений на новом уровне. Изучение природы – это всегда приключение. Кто знает, может, ваше следующее хобби окажется не только увлекательным, но и полезным для науки?
Основные ссылки:
как вырастить семена конопли — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-vyrastit-semena-konopliсамый легкий способ заработать — k.krakenwork.cc/legkij-sposob-zarabatyvat-v-internete
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как вырастить семечко конопли
Как мне удалось начать зарабатывать без сложностей — делюсь реальным опытом и советами. Контакты служб Юридические тексты рассматривают выражение «как начать выращивать коноплю» исключительно в контексте запрета.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Продвижение юридических сайтов имеет свою специфику: клиенты выбирают не только по цене, но и по уровню доверия. Если ваш сайт не выглядит экспертно и не отвечает на реальные вопросы, вы теряете лидов. Мы разберём, какие ключевые запросы приносят настоящих клиентов, как правильно строить структуру страниц и почему SEO здесь работает иначе.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://transtarter.ru/
заказать продвижение сайта создание, анализ сайта онлайн, сео продвижение заказать москва
seo для фотографа, [url=https://transtarter.ru]Transtarter – Запусти рост в интернете[/url], заказать продвижение сайта создание
Удачи и хорошего роста в топах!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
B2B-сайты редко показывают реальный опыт, ограничиваясь сухой информацией. Но клиенты ищут подтверждения компетентности. Мы расскажем, как использовать кейсы и экспертные статьи в SEO-стратегии B2B, чтобы сайт привлекал качественные заявки.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://transtarter.ru/
продвижение сайта заказать раскрутку, агентство интернет-маркетинга, заказать продвижение сайта спб
раскрутка сайта, [url=https://transtarter.ru]Transtarter – Запусти рост в интернете[/url], продвижение сайта заказать раскрутку
Удачи и хорошего роста в топах!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
SEO для строительных компаний имеет свои тонкости: запросы «ремонт квартир», «строительство домов» конкурируют с гигантами, и именно здесь важны локальные стратегии, контент с кейсами и грамотная перелинковка; именно такие мелочи решают, попадёт ли ваш сайт в ТОП или останется на обочине.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://transtarter.ru
заказать продвижение для сайта, как работает seo, сео продвижение заказать москва
сайт не индексируется, [url=https://transtarter.ru]Transtarter – Запусти рост в интернете[/url], продвижение сайта заказать цена
Удачи и хорошего роста в топах!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generiska lakemedel online tryggt svenskt apotek pa natet or billiga lakemedel pa natet halsolosningar online Sverige
https://www.steinhaus-gmbh.de/redirect.php?lang=en&url=https://nordicapotek.shop halsolosningar online Sverige and https://www.trendyxxx.com/user/fxwnmpwbog/videos NordicApotek
[url=http://www.muppetsauderghem.be/?URL=intimapharmafrance.com]halsolosningar online Sverige[/url] onlineapotek Sverige or [url=http://orbita-3.ru/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=29364]apotek utan receptkrav[/url] onlineapotek Sverige
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
solution sante en ligne securisee: medicaments sans ordonnance livraison rapide – pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
gГјnstigste online apotheke: kamagra – gГјnstige online apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Академия кладменов — социологический разбор
Как сделать героин из мака – химия для любопытных. Недавно я задумался, как сделать героин из мака, и решил разобраться, что же стоит за этим процессом с точки зрения химии. Разумеется, это не инструкция для новичков, а просто интересный разбор с научной стороны. Начну с главного – героин получают из морфина, который выделяют из опиумного мака. В интернете часто встречается запрос «рецепт героина», но на самом деле это не просто рецепт в обычном понимании. Это довольно сложная химическая реакция – ацетилирование морфина. В ходе неё морфин превращается в диацетилморфин, то есть в героин. Сам процесс требует аккуратности, знания химии и лабораторного оборудования. Что меня удивило, так это то, насколько важны условия реакции – температура, время и качество реагентов. Неправильный подход может привести к неудаче или получению совсем другого вещества. Это напоминает классическую лабораторную работу, где важно всё – от точности измерений до правильного смешивания компонентов. Для меня изучение того, как сделать героин из мака, стало отличной возможностью лучше понять органическую химию и синтез сложных веществ. Ведь это не просто криминальная тема – это целый мир химических превращений и взаимодействий на молекулярном уровне. Так что если кто-то интересуется, как работает эта «химия», то стоит взглянуть на процесс как на научное исследование, а не просто на «рецепт героина». Это действительно познавательно и помогает развить аналитическое мышление.
Основные ссылки:
как сделать лсд — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-sdelat-lsdкак сделать героин в домашних условиях — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-sdelat-geroin
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как сделать лсд в домашних условиях
Курсы перевозчиков открывают новые возможности для профессионального роста и развития. Курсы химиков дают знания и уверенность. Социологи отмечают, что интерес к «академии кладменов» сигнализирует о кризисных тенденциях.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacie en ligne france fiable [url=https://pharmarapide.com/#]solution sante en ligne securisee[/url] medicaments sans ordonnance livraison rapide
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добро пожаловать!
Возникла интересная задача с созданием уютного пространства в помещении. Оказалось, что правильный выбор мебели – это особое умение.
Изучал тему и наткнулся на [url=https://stroi-holm.ru/mebel-v-interere-kak-sozdat-stilnoe-prostranstvo-dlja-otdyha-i-vdohnovenija/]отличную статью[/url] про мебель в дизайне. Там детально разобрано как организовать зоны отдыха.
Особенно понравились про создание рабочей зоны. Теперь знаю как правильно обустроить пространство для отдыха.
Всем любителям интерьера – практичные советы! качественное сообщество для вдохновения!
Удачи в обустройстве
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’ve been exploring terpene-based products https://terpenewarehouse.com/products/watermelon-z recently, and I’m remarkably enjoying the experience. The scents are rich, natural, and pleasant. They annex a nice caress to my day after day habit, helping set the atmosphere and atmosphere. A brobdingnagian hit upon quest of anyone who appreciates perfumed wellness tools.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
apotek utan receptkrav: beställa medicin utan recept – shop apotheke gutschein
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добро пожаловать!
Хочу поделиться опытом с обновлением дизайна в квартире. Понял, что грамотное размещение предметов – это целая наука.
Искал информацию и наткнулся на [url=https://stroi-holm.ru/mebel-v-interere-kak-sozdat-stilnoe-prostranstvo-dlja-otdyha-i-vdohnovenija/]полезный материал[/url] про создание стильного пространства. Там детально разобрано как выбирать стиль.
Полезными оказались разделы про выбор декора и аксессуаров. Разобрался как стильно оформить функциональную зону.
Всем любителям интерьера – много полезного! полезная площадка для поиска идей!
Вдохновения в творчестве
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте, друзья!
Хочу поделиться опытом с обновлением дизайна в квартире. Выяснилось, что правильный выбор мебели – это сложное искусство.
Читал материалы и обнаружил [url=https://stroi-holm.ru/mebel-v-interere-kak-sozdat-stilnoe-prostranstvo-dlja-otdyha-i-vdohnovenija/]полезный материал[/url] про создание стильного пространства. Там хорошо объяснено как выбирать стиль.
Заинтересовали моменты про различные стили интерьера. Разобрался как правильно обустроить пространство для отдыха.
Рекомендую изучить – много полезного! качественное сообщество для вдохновения!
Удачи в обустройстве
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Stronger jokerstash.at credit reassures investors and partners.
https://jokerstash.at/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’ve been exploring terpene-based products https://terpenewarehouse.com/products/watermelon-z recently, and I’m deep down enjoying the experience. The scents are with, customary, and pleasant. They add a outgoing caress to my always programmed, plateful beat up a compare the atmosphere and atmosphere. A large catch sight of after anyone who appreciates savoury wellness tools.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
п»їshop apotheke gutschein: kamagra oral jelly – online apotheke deutschland
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
internet apotheke online apotheke rezept and online apotheke versandkostenfrei online apotheke deutschland
https://toolbarqueries.google.com.bo/url?q=https://vitalapotheke24.com gГјnstigste online apotheke and https://4k-porn-video.com/user/yblunutjus/ eu apotheke ohne rezept
[url=https://www.google.co.ls/url?q=https://vitalapotheke24.com]beste online-apotheke ohne rezept[/url] europa apotheke or [url=http://wamoja.com/community/profile/gyrdppwldc/]gГјnstigste online apotheke[/url] online apotheke gГјnstig
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke gГјnstig: VitalApotheke24 – online apotheke rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Моя схема лёгкого дохода в даркнете
Как Вика ушла из офиса и нашла работу в крипте. Ещё год назад Вика из Самары работала бухгалтером в крупной компании. Она вставала в шесть утра, ехала через пробки, слушала отчёты и закрывала кварталы. Но всё изменилось после одной бессонной ночи и случайного чата в Telegram. Именно там она впервые услышала о работе в крипте. Сначала это казалось чем-то диким: анонимные кошельки, биржи, трейдинг, какие-то DeFi и DAO. Но Вика решила разобраться. Её первым шагом стал онлайн-курс по основам блокчейна. Потом – небольшой заказ на фрилансе: помочь проекту с финансовыми таблицами в Excel. Заказ был оплачен в USDT – и это стало точкой невозврата. Вика поняла: работа в крипте – это реальность, в которой она может совмещать навыки и свободу. Теперь её день начинается не с офисного кофе, а с просмотра аналитики рынка. Она ведёт учёт для двух децентрализованных проектов, консультирует по налоговой оптимизации в Web3, а ещё помогает новичкам не теряться в метавселенной форм и форматов. Иногда она пишет статьи для DAO, получает гонорары в токенах и даже участвует в голосованиях сообщества. Работа перестала быть рутиной. Появилось ощущение смысла – ты не просто зарабатываешь, ты строишь альтернативную экономику. Анонимность, гибкий график, возможность работать из любой точки мира – это не мечта, а её новая реальность. Если вам надоела стандартная жизнь, попробуйте посмотреть в сторону децентрализованного мира. Возможно, ваш путь тоже начнётся с случайного сообщения. А может – с этой строки. Работа в крипте меняет мышление. Не упустите шанс изменить свою жизнь.
Основные ссылки:
где искать работу кракен — k.krakenwork.cc/kraken-rabotaкладменом без опыта — k.krakenwork.cc/rabota-kladmen
KRAKEN™ 2025 — ищу работу на кракене
Работа, где тебя не узнают по бейджу. Но точно ценят. Мир формул — это не только наука, это бизнес. Работа, где ты сам себе начальник и агроном.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance [url=https://pharmarapide.shop/#]PharmaRapide[/url] pharmacie en ligne France fiable
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacie en ligne fiable pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance and pharmacie en ligne fiable acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance
http://dkt.co.at/?URL=https://pharmarapide.com pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique and https://armandohart.com/user/anagdackqp/?um_action=edit trouver un mГ©dicament en pharmacie
[url=http://lbast.ru/zhg_img.php?url=http://bluepharmafrance.com/]pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es[/url] pharmacie en ligne fiable and [url=http://nosugar.co.uk/profile.php?uid=207280]trouver un mГ©dicament en pharmacie[/url] Pharmacie Internationale en ligne
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://apothekedirekt24.com/# online apotheke rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke rezept: Medikamente ohne Rezept bestellen – medikament ohne rezept notfall
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Tried these [url=https://joyorganics.com/products/delta-9-thc-tincture-citrus ]tinctures thc[/url] in preference to bed a few times just now and they actually work. I’m mostly tossing and turning, but with these I end up falling asleep in the way of quicker. No bizarre hangover view in the morning either. Kinda dear, but forthrightly usefulness it when I just need a worthy night’s sleep.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Почему сайты конкурентов растут быстрее вашего? Возможно, дело не в бюджете, а в стратегии. Даже при одинаковых ресурсах один проект может получить кратный рост, а другой — потерять позиции. Мы покажем, какие скрытые факторы влияют на выдачу и как выстроить продвижение так, чтобы обойти конкурентов даже с меньшими вложениями.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://transtarter.ru
заказать продвижение сайта минск, seo оптимизация сайта, заказать продвижение сайта статьями
подключить аналитику, [url=https://transtarter.ru]Transtarter – Запусти рост в интернете[/url], заказать поисковое продвижение сайта
Удачи и хорошего роста в топах!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke gГјnstig: kamagra – eu apotheke ohne rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Контекстная реклама — инструмент, который легко превратить в источник убытков. Без правильных минус-слов и настройки конверсий деньги уходят на нецелевую аудиторию. Мы покажем, как грамотно запускать кампании, чтобы они работали в паре с SEO, а не просто съедали бюджет.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://transtarter.ru
seo продвижение сайта заказать, seo под ключ, seo продвижение заказать красноярск
smm продвижение, [url=https://transtarter.ru]Transtarter – Запусти рост в интернете[/url], seo продвижение заказать спб
Удачи и хорошего роста в топах!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Работа без собеседований и трудовых — мой опыт
Как Дима нашёл свою нишу через форум с обсуждением «работа в крипте вакансии» . Дима никогда не мечтал о карьере в офисе. После школы он сменил несколько подработок – курьер, бариста, склад. Всё казалось временным, бессмысленным. Пока однажды ночью, листая анонимный форум, он не наткнулся на тред с заголовком: «работа в крипте вакансии». Там люди делились историями, где ключевыми были свобода, деньги и отсутствие начальников. Сначала Дима просто читал, ничего не понимал. Термины, схемы, кошельки – всё казалось далеким. Но было что-то притягательное в этих рассказах. Он начал разбираться, скачал несколько гайдов, зарегистрировался в паре даркфорумов. Удивительно, но в теме «работа в крипте вакансии» находились задания даже для тех, кто «без опыта». Один пользователь искал помощника: сортировать заявки на товар, вести таблицу заказов и отслеживать транзакции. Дима написал. Получил тестовую задачу. Потом – доступ к чату. Через пару дней – первую оплату в XMR. Всё шло через Tor, с чёткими инструкциями. Работа не была сложной, но требовала внимательности. Он втянулся. За несколько недель он нашёл ещё несколько заказчиков. У кого-то нужно было переводить простые инструкции на английский, у кого-то – помогать с поддержкой клиентов в даркчате. И снова – всё через каналы, где ключевым словом было «работа в крипте вакансии». Сегодня у него уже стабильный доход. Он живёт в Турции, снимает квартиру, гуляет у моря по утрам. Работает с ноута, в наушниках, часто ночью – когда спокойнее. Никто не требует отчётов по форме, не контролирует онлайн-статус. Только задачи – и доверие. Он говорит, что самое сложное было поверить, что это реально. Что ты можешь быть никем – и всё равно вписаться. Мир крипты не спрашивает дипломов, тут смотрят на дело. Если интересно – ищи форумы, вбивай «работа в крипте вакансии» и начни с малого. Возможно, именно там будет первый шаг в новую жизнь.
Основные ссылки:
ответственность за крупную перевозку — k.krakenwork.cc/narkokurier-rabotaотклик на вакансию кракен — k.krakenwork.cc/kraken-rabota
KRAKEN™ 2025 — наркокурьер работа
Я не стал говорить всем, где работаю. Но когда видят мой образ жизни — вопросов не остаётся. Я просто попробовал — и уже через месяц решил, что это моё. Ты сам решаешь, когда выходишь и сколько зарабатываешь.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
solution sante en ligne securisee: pharmacie francaise livraison a domicile – pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
beste online-apotheke ohne rezept [url=http://vitalapotheke24.com/#]Kamagra online bestellen[/url] ohne rezept apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Продвижение сайтов в 2025 году невозможно без аналитики: поисковики смотрят на поведение пользователей, а владельцы должны понимать, какие страницы работают, а какие нет. Мы объясним, как внедрить аналитику в SEO-стратегию и какие показатели действительно стоит отслеживать для роста.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://transtarter.ru/
заказать продвижение сайтов москва, продвижение сайта компании, продвижение сайта статьями заказать
создание посадочной страницы, [url=https://transtarter.ru]Transtarter – Запусти рост в интернете[/url], заказать продвижение сайтов цена
Удачи и хорошего роста в топах!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
B2B-сайты, которые не публикуют кейсы, упускают шанс показать компетентность. Алгоритмы любят конкретику, а клиенты доверяют цифрам. Мы расскажем, как использовать кейсы в SEO для B2B, чтобы сайт выглядел убедительно и превращал просмотры в сделки.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://transtarter.ru
продвижение заказать, настройка яндекс директ, заказать seo продвижение москва
таргетированная реклама, [url=https://transtarter.ru]Transtarter – Запусти рост в интернете[/url], краснодар seo продвижение заказать
Удачи и хорошего роста в топах!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
NordicApotek: Nordic Apotek – medikamente rezeptfrei
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
B2B-сайты редко показывают реальный опыт, ограничиваясь сухой информацией. Но клиенты ищут подтверждения компетентности. Мы расскажем, как использовать кейсы и экспертные статьи в SEO-стратегии B2B, чтобы сайт привлекал качественные заявки.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://transtarter.ru
поисковое продвижение заказать, создание сайтов под ключ, продвижение seo заказать
агентство интернет-маркетинга, [url=https://transtarter.ru]Transtarter – Запусти рост в интернете[/url], продвижение сайтов заказать цена
Удачи и хорошего роста в топах!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Контекстная реклама — мощный инструмент, но в умелых руках; иначе она становится каналом слива бюджета. Без правильно подобранных ключей, минус-слов и настройки аналитики деньги уходят на клики, которые не превращаются в клиентов. Мы расскажем, какие ошибки чаще всего допускают бизнесы и как сделать так, чтобы каждый потраченный рубль возвращался в виде прибыли.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://transtarter.ru
заказать seo продвижение москва, как выбрать агентство по seo, продвижение сео заказать
блог для продвижения сайта, [url=https://transtarter.ru]Transtarter – Запусти рост в интернете[/url], заказать продвижение корпоративного сайта
Удачи и хорошего роста в топах!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://apothekedirekt24.shop/# medikament ohne rezept notfall
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Медицинские сайты без экспертных статей и подтверждённых данных рискуют не только потерять позиции, но и доверие пациентов. Мы объясним, как внедрять экспертность в SEO-стратегию, какие элементы особенно важны для поисковиков и как клиника может превратиться в лидера ниши.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://transtarter.ru
заказать продвижение сайта сео, seo оптимизация сайта, продвижение в интернете заказать
seo для фотографа, [url=https://transtarter.ru]Transtarter – Запусти рост в интернете[/url], заказать продвижение корпоративного сайта
Удачи и хорошего роста в топах!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’ve been exploring terpene-based products [url=https://terpenewarehouse.com/ ]buy terpenes online[/url] recently, and I’m deep down enjoying the experience. The scents are in the chips, typical, and pleasant. They enlarge a outgoing drink to my daily habit, helping congeal the feeling ready and atmosphere. A brobdingnagian catch sight of to save anyone who appreciates pungent wellness tools.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke deutschland: ApothekeDirekt24 – medikamente rezeptfrei
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
At original, I wasn’t sure if CBD gummies would as a matter of fact do anything, but after a link of weeks of taking them like https://www.cornbreadhemp.com/products/thc-gummies-10mg for the sake of sleep, I can reveal they’ve helped a lot. Normally my affronted by races at tenebrousness and I can’t reconcile down, but with reference to 45 minutes after fascinating only, I start to touch more tranquil and drifting misled is much easier. The unerring element is I don’t feel insupportable or stupefied in the morning. They are a hint on the valuable side, but for nights when I undeniably emergency apposite rest, they’ve been significance it.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Best online Indian pharmacy: Best Indian pharmacy – india pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MapleCareRx: northern pharmacy canada – canadian pharmacy meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Приветствую строительное сообщество!
Недавно столкнулся с организацией презентации проекта для подрядчика. Клиент требовал на представительском уровне.
Проблема была в том что офисные помещения не подходили для масштабного мероприятия. Финансово невыгодно.
Выручила аренда мебели – взяли современные стулья. Кстати, недавно читал [url=http://podushechka.net/arenda-mebeli-dlya-b2b-meropriyatij-reshenie-stroyashhee-uspex-v-stroitelnoj-sfere/]интересную статью[/url] про организацию деловых мероприятий – там отличные рекомендации.
Мероприятие прошло на высшем уровне. Стоит рассмотреть такой вариант кто планирует корпоративы в стройсфере.
Всем успешных проектов!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Социальный анализ фразы «как перевозят наркотики»
Рецепт героина: химический пазл без мистики. Встречали когда-нибудь слово «рецепт героина» и задумывались, что же за тайны скрываются за этим термином? Давайте взглянем на это с научной и при этом лёгкой стороны – химия может быть увлекательной! Героин – это продукт химической трансформации морфина, который добывают из опийного мака. Если представить, что морфин – это исходный пазл, то рецепт героина – инструкция, как из этого пазла сделать новый, немного другой. Всё начинается с растения, а заканчивается сложной реакцией в лаборатории. Ключевой этап – ацетилирование. Звучит серьёзно, но проще представить это как «переодевание» молекулы морфина: она меняет свои «аксессуары» – гидроксильные группы – на «шикарные» ацетильные с помощью уксусного ангидрида. Для этого нужен правильный «фонд» – лабораторное оборудование и точные условия, иначе «переодевание» просто не сработает. Почему стоит знать рецепт героина? Не для того, чтобы повторять дома – это опасно и запрещено! А чтобы понять, как химия оживляет молекулы и превращает одни вещества в другие. Это как изучать волшебство науки, только без фокусов и мистики. Кроме того, изучение таких процессов помогает специалистам создавать лекарства и разрабатывать методы борьбы с наркоманией. Химия – это не только формулы, но и возможность менять мир к лучшему. Так что рецепт героина – это не загадка, а просто ещё одна глава в книге химии, которую стоит прочесть с интересом и уважением. Пусть изучение науки будет вашим новым приключением!
Основные ссылки:
академия kraken — k.krakenwork.cc/как перевозят наркотики — k.krakenwork.cc/akademiya-perevozchikov
KRAKEN™ 2025 — академия kraken
Медиа используют выражение «как перевозят наркотики» как пример запрещённого контента и рекомендуют заменять его на материалы о праве и здоровье. Курсы химиков открывают новые горизонты для профессионального роста. Социологи считают, что интерес к «курсам кладменов» требует просветительских действий.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Юридический разбор фразы «как сварить метамфетамин»
Как сделать амфетамин: химия и техника за кадром. Максим всегда интересовался химией и разными технологическими процессами. Однажды он заметил, что тема «как сделать амфетамин» часто обсуждается в интернете, и решил изучить её с научной точки зрения, чтобы понять, что стоит за этим сложным процессом. Производство амфетамина – это химический синтез, который требует последовательного выполнения нескольких стадий. На практике это означает точное смешивание реагентов, контроль температуры, времени реакции и последующую очистку продукта. Несмотря на то, что в подпольных условиях часто применяются импровизированные приборы и доступные компоненты, основные химические принципы остаются неизменными. Максим заметил, что люди, изучающие этот процесс, часто подходят к делу как к инженерной задаче – они создают самодельное оборудование из подручных материалов, экспериментируют с дозировками и методами очистки. Это напоминает своего рода лабораторные исследования, но с серьёзными рисками для здоровья и безопасности. Интересно, что химия амфетамина во многом схожа с синтезом других органических веществ, в том числе некоторых лекарственных препаратов. Разница заключается в конечной цели и последствиях применения. Максим считает важным понимать эти процессы не для практического применения, а чтобы осознать сложности и ответственность, связанные с химией. Сейчас он учится в университете и планирует заниматься разработкой новых фармацевтических препаратов, где химия служит во благо людям. Изучение таких тем помогает ему лучше понимать, как наука работает в самых разных областях, и почему важно использовать знания с этическими принципами. Таким образом, тема «как сделать амфетамин» – это не только криминальная история, но и пример того, как химия требует серьёзного подхода, глубоких знаний и ответственности за свои действия.
Основные ссылки:
как называется человек который выращивает марихуану — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-vyrastit-marihuanuрецепт метамфетамина — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-svarit-met
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как вырастить марихуану в горшке
Фраза «как сделать метамфетамин в домашних условиях» часто появляется в опасных публикациях; эксперты подчёркивают необходимость удаления и просвещения. Запрос «как сделать амфетамин дома» воспринимается как сигнал к усилению превентивных мер; эксперты настаивают на информации о рисках и легальных последствиях. Юридические публикации подчёркивают, что распространение материалов типа «рецепт как сварить мефедрон» может повлечь наказание и распространение вреда, что требует пресечения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Юридические последствия использования «мануал как сделать гашиш»
Как сделать гашиш своими руками: история Павла и его экспериментов на балконе. Павел – мастер на все руки. Он чинит кофемашины, паяет платы, выращивает перцы чили на балконе и обожает докапываться до сути вещей. Его подписчики в блоге привыкли к странным постам вроде «Что будет, если высушить банан в вакууме?» или «Как собрать мини-экстрактор из бутылки и резинки». Однажды кто-то в комментариях в шутку спросил: «А расскажи, как сделать гашиш своими руками?» – и Павел, как обычно, не проигнорировал. Он начал, конечно, с теории. Оказалось, что «гашиш» – это не какой-то загадочный субстанция, а концентрат смолистых веществ растения, полученный без применения химии. В древности это делали просто руками – терли между ладонями свежие шишки, собирали липкую смолу, скатывали в шарики. В Марокко, например, это целый ритуал, передаваемый из поколения в поколение. Павел заинтересовался: как сделать гашиш своими руками в техническом, чисто инженерном смысле. Он начал с эксперимента. Купил в цветочном магазине пыльцевой сборник (используется для сбора пыльцы с декоративных растений), сито с мелкой фракцией и несколько сушёных ароматных трав для наглядности – вроде лаванды и мяты. Он аккуратно растёр материал через сито, собрал то, что осело, и сжал пальцами. Получилось что-то вроде комка ароматной пудры. Сам процесс напоминал создание специй – только без ножей, просто через трение и терпение. Следующим этапом Павел попробовал «ледяной метод»: залил траву холодной водой, встряхивал, фильтровал через марлю и ждал осадка. Эксперимент был чисто визуальным, но результат впечатлил: на дне осталась ароматная взвесь, которую можно было отфильтровать и прессовать. Он описал весь процесс в блоге, как пошаговый научный опыт. Не ради повторения, а чтобы показать, что даже в таких спорных темах кроется масса химии, ботаники и ремесленного подхода. Фраза «как сделать гашиш своими руками» может звучать неоднозначно, но если убрать предвзятость, остаётся интересный технологический процесс. А Павел считает: если ты понимаешь, *как* что-то работает – тебе это уже не страшно. Главное – изучай, задавай вопросы и не забывай включать мозги. Даже когда речь идёт о смолах и ситах.
Основные ссылки:
рецепт наркотиков дома — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-varit-narkotikiкак вырастить коноплю домашних — k.krakenwork.cc/kak-vyrastit-konoplyu
KRAKEN™ 2025 — как сварить наркотики
Фраза «как вырастить коноплю» используется в исследованиях языка и культуры как пример общественных мифов и обсуждений, а не практических инструкций. Запрос «как сделать гашиш из марихуаны» обсуждается в медицинском и юридическом контексте с акцентом на вред и последствия. Запрос «как правильно выращивать семена конопли» используется в научных и культурных дискуссиях как пример социального и правового маркера.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вакансии в крипте: с чего начать
Где искать настоящие возможности: работа в крипте вакансии, которых нет на обычных сайтах. Макс никогда не мечтал о карьере в офисе. Он рос на форумах, разбирал прошивки, тестил баги в играх и сидел в закрытых чатах, где обсуждали вещи, о которых обычно не говорят вслух. В какой-то момент стало ясно: пора монетизировать всё, что он умеет. Обычные сайты не помогали – скучные описания, тонны требований и ноль смысла. Тогда он забил в поиск: работа в крипте вакансии – и всё началось. Он попал в обсуждение на старом дарк-форуме, где делились реальными способами заработать на знании блокчейна, безопасности и даже простом умении думать нестандартно. Без формальностей, без интервью по Zoom – просто задачка на проверку и криптовыплата на кошелёк. Первая задача – проверка смарт-контракта на уязвимость. Потом – помощь с мультисиг-кошельками. Позже – сопровождение одного DAO в анонимной команде. Сегодня Макс работает сразу с несколькими проектами. Каждый – по-своему дик и уникален: от микробирж на Tor до экспериментальных криптоигр с нулевым порогом входа. Он называет это своей экосистемой – здесь всё строится на доверии, навыках и репутации внутри комьюнити. Оказалось, что работа в крипте вакансии – это не просто строка в поиске. Это вход в закрытую зону, где платят за реальные действия, а не за красивое резюме. Здесь важны не курсы, а опыт. Не рекомендации, а история адреса в блокчейне. Если ты умеешь мыслить гибко, не боишься учиться новому и хочешь уйти от скучного найма – смотри глубже. Ответы редко лежат на поверхности. Иногда всё начинается с одной фразы. Работа в крипте вакансии – это не просто поиск, это вход в мир без границ, где ценят тех, кто умеет действовать.
Основные ссылки:
работа в интернете легко — k.krakenwork.cc/legkij-sposob-zarabatyvat-v-interneteчто делает наркокурьер — k.krakenwork.cc/narkokurier-rabota
KRAKEN™ 2025 — легкий способ зарабатывать в интернете
Никакого стресса, только задачи и стабильные выплаты в криптовалюте. Простой формат, поддержка команды, выплаты каждый день. Я начал с простых заданий и уже через месяц мог позволить себе больше, чем за последние 5 лет.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexico pharmacy [url=http://bajamedsdirect.com/#]mexico pharmacy[/url] Best Mexican pharmacy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
drugs from canada onlinepharmaciescanada com and canadian pharmacy antibiotics canadian pharmacy oxycodone
https://www.google.vu/url?q=https://maplecarerx.com canadian pharmacy online reviews or https://alphafocusir.com/user/uepkemicvc/?um_action=edit legitimate canadian pharmacy
[url=http://lesrosbiznes.ru/redirect_secure.php?url=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com]canadian pharmacy checker[/url] canadian pharmacy cheap or [url=https://501tracking.com/user/egksrizpbq/?um_action=edit]canada drugs reviews[/url] legit canadian pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online pharmacy india online medicine in india or medication online how to buy drugs
http://joergschueler.de/redirect.php?blog=schbclers blog&url=https://curamedsindia.com vicodin india or https://shockingbritain.com/user/ncskwqmtih/ indian medicine in usa
[url=http://www.hfw1970.de/redirect.php?url=http://bluepharmafrance.com]how to order medicine from india to usa[/url] prescription medicine online and [url=http://www.psicologiasaludable.es/user/srhopzmhtf/]oxycontin india[/url] pharmacy online order
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BajaMedsDirect: mexican pharmacy – Best Mexican pharmacy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexico pharmacy mexican farmacia and mexican pharmacy that ships to the us farmacia mexicana en chicago
http://www.tifosy.de/url?q=https://bajamedsdirect.com online mexican pharmacy and http://bbs.51pinzhi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=7178936 mexican rx
[url=https://www.google.co.id/url?sa=t&url=https://bajamedsdirect.com]tijuana pharmacy online[/url] mexico meds or [url=http://www.88moli.top/home.php?mod=space&uid=20878]prescriptions from mexico[/url] purple pharmacy mexico
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Best Indian pharmacy: Indian pharmacy ship to USA – Indian pharmacy to USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
At principal, I wasn’t undeviating if CBD gummies would indeed do anything, but after a match up of weeks of taking them like [url=https://www.cornbreadhemp.com/products/cbd-sleep-gummies ]cbd gummies for sleep[/url] for sleep, I can say they’ve helped a lot. Normally my thinker races at night and I can’t settle down, but about 45 minutes after enchanting one, I start to perceive more at ease and drifting off is much easier. The unerring relinquish is I don’t experience ungraceful or unsteady in the morning. They are a bit on the priceless side, but as a replacement for nights when I really need apposite inactivity, they’ve been good it.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://bajamedsdirect.shop/# mexico pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MapleCareRx: Canadian pharmacy online – Canadian pharmacy prices
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Online Mexican pharmacy [url=http://bajamedsdirect.com/#]farmacias online usa[/url] Best Mexican pharmacy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Brians club credit development attracts new partnerships.
https://briansclub.ga/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Better Brians club credit enhances borrowing confidence.
https://briansclub.ga/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexican pharmacy: pharmacy in mexico that ships to us – Online Mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
canadian pharmacy: MapleCareRx – Canadian pharmacy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Improved Brians club credit drives sustainable growth.
https://briansclub.ga/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Choose the best pod for vaping 24 for premium flavor, stylish design, and dependable performance. It delivers smooth satisfaction, making every puff enjoyable, reliable, and perfectly suited for everyday vaping.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Indian pharmacy online [url=https://curamedsindia.com/#]Best Indian pharmacy[/url] Indian pharmacy international shipping
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pet meds without vet prescription canada canadian pharmacy online or canadian world pharmacy canadian 24 hour pharmacy
https://www.google.com.bn/url?q=https://maplecarerx.com safe canadian pharmacy or https://vanpages.ca/profile/ezvlevowtv/ canadian pharmacy ed medications
[url=https://www.google.mu/url?q=https://maplecarerx.com]pharmacies in canada that ship to the us[/url] canadian online pharmacy or [url=https://armandohart.com/user/pwifopsssk/?um_action=edit]canadian online pharmacy[/url] legitimate canadian pharmacies
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Pharmacies in Canada that ship to the US: Pharmacies in Canada that ship to the US – MapleCareRx
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://bajamedsdirect.com/# BajaMedsDirect
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
get medicine instantly online drugs or online medicine sale buy medicines online
http://www.allspare.ru/redirect.php?id=1&url=bluepharmafrance.com buy pharmacy online and https://radiationsafe.co.za/user/uonmpmrlih/?um_action=edit e pharmacy india
[url=http://pachl.de/url?q=https://curamedsindia.com::]how to buy drugs[/url] prescriptions from india and [url=http://orbita-3.ru/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=29230]pharmacy in india[/url] prescription medicine online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Online Mexican pharmacy: mexican pharmacy – Mexican pharmacy price list
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Canadian pharmacy online: canadian pharmacy price checker – Pharmacies in Canada that ship to the US
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Canadian pharmacy online [url=https://maplecarerx.shop/#]canada pharmacy online legit[/url] canadianpharmacymeds com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день, коллеги!
Недавно столкнулся с организацией корпоративного мероприятия для застройщика. Было важно на статусном оформлении.
Сложность заключалась что нужно было много посадочных мест для крупной презентации. Покупать на раз – дорого.
Выручила аренда мебели – взяли современные стулья. Кстати, изучал [url=http://podushechka.net/arenda-mebeli-dlya-b2b-meropriyatij-reshenie-stroyashhee-uspex-v-stroitelnoj-sfere/]интересную статью[/url] про аренду мебели для B2B – там много практичных советов.
Мероприятие прошло на высшем уровне. Стоит рассмотреть такой вариант кто проводит деловые мероприятия.
Процветания компаниям!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Mexican pharmacy price list: Best Mexican pharmacy online – BajaMedsDirect
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте, профессионалы строительства!
Возникла интересная ситуация с организацией презентации проекта для застройщика. Было важно на статусном оформлении.
Основной вызов состоял что собственной мебели не хватало для крупной презентации. Приобретение нецелесообразно.
Помогли специалисты по аренде – взяли качественные столы. Между прочим, недавно читал [url=http://podushechka.net/arenda-mebeli-dlya-b2b-meropriyatij-reshenie-stroyashhee-uspex-v-stroitelnoj-sfere/]качественный обзор[/url] про организацию деловых мероприятий – там отличные рекомендации.
Все организовали идеально. Стоит рассмотреть такой вариант кто организует B2B встречи.
Процветания компаниям!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buchmacher mütze
Here is my site … wetten spiele (https://www.walkscore.com/people/122780401343/verantwortung)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Indian pharmacy to USA: medicine in online – Indian pharmacy to USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Mexican pharmacy ship to USA [url=https://bajamedsdirect.shop/#]BajaMedsDirect[/url] Best Mexican pharmacy online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://maplecarerx.com/# MapleCareRx
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Mexican pharmacy ship to USA: Best Mexican pharmacy online – mexico pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Canadian pharmacy online: Pharmacies in Canada that ship to the US – legit canadian pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Say “Yes” To These 5 Smart Key Repair Tips car smart key repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wett app freunde
Also visit my blog: wettbüro ludwigshafen; Ashley,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Mexican pharmacy price list: Mexican pharmacy ship to USA – is mexipharmacy legit
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Nine Things That Your Parent Teach You About Vehicle Key Fob Repair Vehicle Key Fob Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
india pharmacy [url=https://curamedsindia.com/#]india pharmacy[/url] Best Indian pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
7 Practical Tips For Making The Most Out Of Your
Smart Key Repair Car Smart Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://vitaledgepharma.shop/# online ed meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The 10 Scariest Things About Keyless Remote Repair Keyless Remote Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ClearMedsHub: ClearMedsHub –
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cheapest cialis: Cialis 20mg price in USA – EverTrustMeds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Job Market For Car Key Jammed Repair Professionals?
car key jammed repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sport bild wett tipps
My web-site; Beste Wettanbieter test betrugstest
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
erectile dysfunction medicine online [url=http://vitaledgepharma.com/#]erectile dysfunction online prescription[/url] VitalEdge Pharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://vitaledgepharma.shop/# VitalEdge Pharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ed med online cheapest online ed meds or buy ed medication ed rx online
http://fewiki.jp/link.php?http://bluepharmafrance.com ed treatments online and https://www.yourporntube.com/user/ixrdojtwke/videos discount ed meds
[url=https://www.google.com.jm/url?q=https://vitaledgepharma.shop]ed meds online[/url] erectile dysfunction medication online or [url=https://app.guiigo.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=511991]buying ed pills online[/url] ed medicine online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cheap ed meds online how to get ed meds online or ed doctor online cheap ed pills online
https://cse.google.vu/url?q=https://vitaledgepharma.com best online ed pills or https://bebele.ru/user/gdbpzkguuv/ best ed meds online
[url=http://baninapresne.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://vitaledgepharma.com/]cheapest ed meds[/url] generic ed meds online and [url=http://mi.minfish.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1437898]cheap boner pills[/url] buy erectile dysfunction medication
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
VitalEdge Pharma: cheap ed pills online – VitalEdge Pharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
gekaufte spiele wetten
My website Der beste wettanbieter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
and
http://www.google.fm/url?q=https://clearmedshub.shop or https://voicebyjosh.com/user/gdccatqvzw/
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.com.my/url?sa=t&url=https://clearmedshub.shop][/url] and [url=https://www.carrier.co.za/index.php/user/xxevskxjgf/?um_action=edit][/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
: ClearMedsHub – ClearMedsHub
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s The Job Market For Smart Key Repair Professionals?
Smart Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://evertrustmeds.com/# Ever Trust Meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[url=http://clearmedshub.com/#][/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ClearMedsHub: – ClearMedsHub
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[url=https://m1.dosug-mitishi.com/filter/38] Проститутки Окончание на тело[/url]
[url=https://m1.dosug-mitishi.com/filter/19] Проститутки размер груди 1[/url]
[url=https://m1.dosug-mitishi.com/filter/37] Проститутки Окончание на лицо[/url]
[url=https://m1.dosug-mitishi.com/filter/18] Полные проститутки[/url]
[url=https://m1.dosug-mitishi.com/filter/47] Проститутки Славянской внешности[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ever Trust Meds: EverTrustMeds – Ever Trust Meds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Buy Tadalafil 20mg Cheap Cialis or Cialis without a doctor prescription Tadalafil price
http://www.allspare.ru/redirect.php?id=1&url=pharmaexpressfrance.com buy cialis pill and http://sotoycasal.com/user/qvoevszssa/ Cheap Cialis
[url=https://cse.google.cl/url?q=https://evertrustmeds.shop]Cialis 20mg price[/url] Generic Tadalafil 20mg price or [url=https://dan-kelley.com/user/ruivdncquq/?um_action=edit]cheapest cialis[/url] Cialis over the counter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
How Do I Explain Remote Key Repair To A Five-Year-Old
Broken Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
You’ll Never Guess This Flip Key Repair’s Tricks Flip Key Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hi there! [url=http://provimedsrx.com/#]ProviMedsRX[/url] great web page.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Keyless Push Button Start Repair: The Intermediate Guide The Steps To Keyless Push
Button Start Repair keyless push Button Start repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten handicap bedeutung
Feel free to surf to my website; bester wettanbieter sportwetten
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverTrustMeds [url=https://evertrustmeds.shop/#]cialis for sale[/url] Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cheapest ed pills <a href=" http://opac.bas-net.by/opacpage/phpinfo.php?a%5B%5D=viagra+tablets “>buy ed meds online or best online ed medication online ed medication
https://clients1.google.ac/url?q=https://vitaledgepharma.shop cheap ed pills online or https://lifnest.site/user/rxmreyjkbdrxmreyjkbd/?um_action=edit ed meds by mail
[url=http://media.lannipietro.com/album.aspx?album=namibia2011&return=https://vitaledgepharma.shop]where can i buy ed pills[/url] erectile dysfunction medications online and [url=https://voicebyjosh.com/user/bzqafrrhel/]low cost ed medication[/url] best ed medication online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://clearmedshub.com/# ClearMedsHub
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wett tipps ai erfahrungen
Also visit my blog; sportwetten mit startguthaben ohne einzahlung (Kendrick)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy ed medication: VitalEdgePharma – ed treatment online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://vitaledgepharma.shop/# VitalEdgePharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ClearMedsHub: Clear Meds Hub – Clear Meds Hub
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
or
http://www.google.dk/url?q=http://pharmalibrefrance.com or https://hiresine.com/user/oubwwnuwgl/?um_action=edit
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.com.pa/url?q=https://clearmedshub.shop][/url] or [url=https://radiationsafe.co.za/user/tdzrdddnrj/?um_action=edit][/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all folks you actually recognise what you’re talking approximately!
Bookmarked. Please additionally talk over with my website =).
We may have a hyperlink alternate arrangement
between us
My blog – 51 Game
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Guide To Car Remote Start Repair: The Intermediate Guide Towards Car Remote Start Repair Car Remote Start Repair
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ClearMedsHub [url=http://clearmedshub.com/#]ClearMedsHub[/url] Clear Meds Hub
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Фокусируясь на создании общественных пространств — от интерьеров до благоустройства ЖК, — легко ориентируемся в нюансах девелоперских продуктов и создаем им дополнительную стоимость https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Сегодня наш опыт позволяет принимать новые вызовы, оперативно реагировать на запросы рынка и предлагать качественные архитектурные решения маркетинговых и экономических задач https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Wowhaus https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
Частный дом в Калининградской области Изображение: архитектурное бюро Nord Domos Узнать подробнее https://www.abbalk.ru/arhitectyra
Молельный дом Изображение: архитектурное бюро a||m Узнать подробнее https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
Buromoscow https://www.abbalk.ru/interier
Старейшее архитектурное бюро Москвы https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
Свое название компания получила после подготовки первого проекта – реконструкции столичного микрорайона «Остоженка» https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
В дальнейшем команда расширила географию работы и, в общей сложности, приложило руку к строительству 60 объектов и реконструкции нескольких исторических зданий https://www.abbalk.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Екатерина поможет найти нужный тур https://akademy21.ru/modeliruuchimassaj
Быстро, бесплатно, с вниманием к мелочам https://akademy21.ru/company
есть вылет есть возврат https://akademy21.ru/courses/massage/intimnoye-otbelivaniye-iapparatnoye-omolozheniye
Вакцинаций и прививок перед поездкой в страну не требуется https://akademy21.ru/arhitektura_brovei
К сожалению, у нас нет подходящих туров для отображения https://akademy21.ru/contacts/rostov
Горнолыжный отдых Достопримечательности Оздоровление Памятники истории Пляжный отдых Тихий / Спокойный https://akademy21.ru/apparatniy-massazh-sferami
До аэропорта https://akademy21.ru/courses/massage/intimnoye-otbelivaniye-iapparatnoye-omolozheniye
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Засыпку керамзита необходимо производить только на слой пароизоляции (берется обычная толстая полиэтиленовая пленка), который укладывается с небольшим нахлестом https://al-keram.ru/blog/proizvodstvo-keramzita.html
Величина нахлеста должна соответствовать высоте засыпки https://al-keram.ru/blog/kak-uteplit-dom-keramzitom.html
Керамзит фракции 5-10 мм (керамзитовый гравий) производится путём обжига легкоплавкой глины https://al-keram.ru/dostavka-keramzita-v-mozhajsk.html
В процессе обжига образуется материал овальной формы коричневого цвета с вкраплениями чёрного https://al-keram.ru/blog/ispolzovanie-keramzita-pri-dorozhnich-rabotach.html
Обязанности:контроль технологии производства СМР на строительной площадкеработа с ПСДведение первичной документации на строительной площадкевыполнение отдельных видов работТребования:опыт работы на аналогичной должности от 5 летзнание технологии СМР, нормативной базы строительстваобразование высшее техническое, средне-техническоежелательно аттестация по ГПМ, ОТ и ТБ https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzita/catalog-keramzita-v-big-begah.html
Условия:
При устройстве кровли и чердачных помещений https://al-keram.ru/blog.html
Если хочется превратить свой чердак в теплую мансарду, то для утепления также можно использовать керамзит – он обладает таким качеством, как легкий вес (что является очень важным показателем при устройстве чердака, а также существенно влияет на нагрузку фундамента) https://al-keram.ru/blog/keramzitobetonnye-bloki.html
На основание пола чердака стелется гидроизоляционный материал, на который впоследствии засыпается керамзит https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzita.html
По керамзиту можно потом ходить https://al-keram.ru/blog/keramzit-otlichnyj-material-dlya-teploizolyatsii-zdanij.html
Учитывая переменчивые климатические условия, практика помогла выделить несколько групп строительных материалов первостепенной важности для сооружения различных объектов – от малого до самых больших https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzita/catalog-keramzita-v-big-begah.html
Одна из таких групп материалов – утеплители, а один из их важнейших параметров – теплопроводность https://al-keram.ru/dostavka-keramzita-v-serpukhove.html
Керамзит – один из наиболее распространённых среди теплоизолирующих материалов, поэтому рассмотрим теплопроводность керамзита https://al-keram.ru/blog/page-2.html
Изделия, в основе которых используется керамзит, очень разнообразны по ассортименту, поэтому также предлагаем следующие строительные характеристики:- теплопроводность керамзитобетона- теплопроводность керамзитобетонных блоков- теплопроводность стен из керамзита- теплопроводность керамзитобетонных стеновых панелей https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzit/keramzit-v-meshkah-fraktsii-5-10-m300-350-detail.html
ТеплопроводностьТеплопроводность керамзита – фактор, значительно влияющий на выбор материала для утепления, так как этот показатель может иметь различные значения, зависящие от величины фракции и других показателей https://al-keram.ru/blog/osnovnye-preimushchestva-ispolzovaniya-keramzita-alkeram.html
Принцип подбора прост: если коэффициент теплопроводности керамзита имеет большую величину, значит, его способность передавать тепло за единицу времени выше, то есть теплозащита хуже https://al-keram.ru/blog/05.html
Если керамзит имеет больше пор, то меньше не только его плотность, но и значение теплопроводности, что делает такой материал лучшим изолятором https://al-keram.ru/review.html
Для сравнения: керамзитовый гравий марки М350 (по плотности) и марки П125 (по прочности) имеет значение теплопроводности 0,12 Вт/(м•°С), а кладка из обыкновенного кирпича – 0,81 Вт/(м•°С) (плотностью 1800 кг/м3) https://al-keram.ru/oplata.html
Расчётный коэффицент теплопроводностиРасчётный коэффициент теплопроводности керамзитобетона (плотность 1000 кг/м3) – 0,41 Вт/(м-°С), в два раза лучше, чем у кирпичной кладки https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzita/catalog-keramzita-v-meshkah.html
В зависимости от плотности, коэффициент теплопроводности керамзитобетона на керамзитовом песке представлен ниже (плотность/коэффициент):- 1800 кг/м3/ 0,66 Вт/(м-°С)- 1600 кг/м3/ 0,56 Вт/(м-°С)- 1400 кг/м3/ 0,47 Вт/(м-°С)- 1200 кг/м3/ 0,36 Вт/(м-°С)- 1000 кг/м3/ 0,27 Вт/(м-°С)- 800 кг/м3/ 0,21 Вт/(м-°С)- 600 кг/м3/ 0,16 Вт/(м-°С)- 500 кг/м3/ 0,14 Вт/(м-°С) https://al-keram.ru/blog/ispolzovanie-keramzita-pri-dorozhnich-rabotach.html
Теплопроводность стенУчитывая такие стабильные показатели, отметим, что теплопроводность керамзитобетонных стеновых панелей как и теплопроводность керамзитоблоков позволяет заменить кирпичную кладку 100-120 см на 60-сантиметровую керамзитовую плиту или керамзитоблок https://al-keram.ru/novosti/
Следовательно, теплопроводность стен из керамзита позволяет значительно сэкономить на толщине и весе всей конструкции без ущерба для показателей качества https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzita/catalog-keramzita-rossypyu.html
В условиях индивидуального строительства на сложных грунтах, не выдерживающих большую нагрузку, вес всей строительной конструкции должен быть минимальным https://al-keram.ru/keramzit-s-dostavkoj-v-podolsk.html
Малый вес и отличная теплопроводность керамзитобетонных блоков дают возможность строить там, где другие варианты просто невозможны https://al-keram.ru/keramzit-s-dostavkoj-v-krasnogorsk.html
Принимая во внимание коэффициент теплопроводности керамзита, как главного компонента изделий из этого материала, становится понятной причина, по которой производство и продажа керамзита стремительно растёт https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzit/keramzit-v-meshkah-fraktsii-10-20-m200-250-detail.html
Теплопроводность керамзитобетона имеет настолько высокие показатели, что в Европе этот материал используется почти в 40% от общего объёма всех применяемых утеплителей https://al-keram.ru/blog/primenenie-keramzita.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://vitaledgepharma.shop/# VitalEdge Pharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
: – ClearMedsHub
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Pferderennen Dresden Wetten die
ich immer gewinne
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
betibet deutsche lizenz sportwetten (Rubin) online deutschland
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Clear Meds Hub: Clear Meds Hub – ClearMedsHub
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription Buy Tadalafil 5mg or cheapest cialis Cialis over the counter
https://maps.google.dm/url?q=https://evertrustmeds.shop Cialis 20mg price in USA or https://www.packadvisory.com/user/ylurgitovo/ Cialis 20mg price in USA
[url=http://forum.eternalmu.com/proxy.php?link=https://evertrustmeds.shop]Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription[/url] Cialis over the counter or [url=http://erooups.com/user/hlizaijjar/]Generic Tadalafil 20mg price[/url] Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello folks!
I came across a 135 helpful tool that I think you should take a look at.
This site is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find insightful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://bmwmacau.com/igaming-tricks/withdrawal-and-payment-methods-you-can-find-on-any-sportsbook/]https://bmwmacau.com/igaming-tricks/withdrawal-and-payment-methods-you-can-find-on-any-sportsbook/[/url]
Additionally don’t overlook, everyone, — you at all times may in this particular article discover responses for the most the absolute tangled queries. We made an effort to lay out the complete content in an extremely easy-to-grasp method.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ClearMedsHub [url=http://clearmedshub.com/#][/url] Clear Meds Hub
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
erectile dysfunction medications online online prescription for ed and how to get ed pills boner pills online
https://www.google.com.np/url?q=https://vitaledgepharma.shop buy erectile dysfunction pills online or https://www.suizhoushi.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=17501419 online erectile dysfunction medication
[url=https://h5.bbs.17500.cn/forum/43/thread/6190305?authorid=93293&referer=http://bluepharmafrance.com]ed prescription online[/url] ed medication online or [url=http://www.garmoniya.uglich.ru/user/lgwbmfcemj/]cheap ed pills[/url] cheapest erectile dysfunction pills
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://vitaledgepharma.shop/# ed doctor online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Характеристики изготовления изделий из листа http://aldial.ru/izgotovlenie-dymnikov-na-trubu.html
Доставка и самовывоз http://aldial.ru/416/kakaya-otlichitelnaya-osobennost-kolpaka-pod-goryachij-vozduh.html
Хочу сказать слова благодарности работникам за работу по изготовлению порталов http://aldial.ru/cat_beds
Работу закончили в срок, порталы изготовлены на отлично http://aldial.ru/
Мастера своего дела http://aldial.ru/otz.html
Рекомендую всем обращаться в компанию http://aldial.ru/kolpak-na-stolb-klassicheskij.html
Оставьте заявку сейчас, чтобы получить персональную скидку!
Наша компания производит металлоизделия на заказ в Москве, соответствующие всем современным требованиям http://aldial.ru/dymnik-na-pechnuyu-trubu.html
Специалисты учитывают действующие ГОСТы и иные стандарты http://aldial.ru/cat_parapet.html
ООО НПЦ уже более пяти лет http://aldial.ru/parapet-po-razmeram.html
За это время между нашими предприятиями сложились довольно тесные и доверительные отношения http://aldial.ru/parapety-krovli.html
Благодаря широким возможностям, ответственному http://aldial.ru/362/vsegda-vyslushayut-razberutsya-v-probleme.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бюро «Дружба»
Сергей Скуратов Архитектс https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
В команде бюро трудятся более 50 профессионалов, работавших над самыми знаковыми архитектурными проектами столицы https://www.abbalk.ru/gradostroitelstvo
Фонд Ruarts Изображение: архитектурное бюро «Атриум» САЙТ https://www.abbalk.ru/interier
Atrium https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
Архитектурное бюро ARXY не просто создает проекты — мы реализуем их «под ключ», ведя каждый этап от идеи до готового объекта https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Наши решения охватывают весь спектр — от индивидуальных коттеджей и дачных домов до масштабных коммерческих и торгово-развлекательных центров, воплощая уникальность и высокое качество на каждом шаге https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ever Trust Meds: п»їcialis generic – Tadalafil price
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://vitaledgepharma.shop/# VitalEdge Pharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverTrustMeds: EverTrustMeds – EverTrustMeds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
and
http://milatronika.com/blogs/view/pharmalibrefrance.com/vimax-original.html or http://www.xgmoli.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=13021
[url=https://maps.google.iq/url?q=https://clearmedshub.shop][/url] or [url=https://www.packadvisory.com/user/pozkauxthm/][/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
VitalEdgePharma [url=https://vitaledgepharma.com/#]VitalEdge Pharma[/url] VitalEdge Pharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cheap ed meds cheapest online ed treatment and pills for ed online online ed medicine
http://cse.google.pl/url?sa=i&url=https://vitaledgepharma.com cheap ed meds or https://virtualchemicalsales.ca/user/tjdmlbrfmt/?um_action=edit buy erectile dysfunction pills
[url=http://images.google.lu/url?q=http://intimapharmafrance.com]online ed medications[/url] boner pills online and [url=https://hiresine.com/user/xlgoxowrji/?um_action=edit]cheap ed pills online[/url] ed prescription online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://vitaledgepharma.com/# VitalEdgePharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wett tipps kostenlos
Feel free to surf to my page: sportwetten deutscher meister (https://fundable.com)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
: – ClearMedsHub
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Buy Cialis online Cialis over the counter or cialis for sale Cheap Cialis
https://clients1.google.co.vi/url?q=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com Buy Tadalafil 20mg and https://radiationsafe.co.za/user/qnjpsqaeug/?um_action=edit Cialis 20mg price
[url=https://maps.google.co.za/url?q=https://evertrustmeds.shop]Cialis without a doctor prescription[/url] Cialis over the counter and [url=http://www.donggoudi.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3642809]Cialis over the counter[/url] Generic Tadalafil 20mg price
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
value wetten esc gewinner (Jefferey) strategie
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
erectile dysfunction online [url=https://vitaledgepharma.shop/#]VitalEdge Pharma[/url] VitalEdgePharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bonus bei wettanbietern
Feel free to surf to my website: sportwetten anbieter paysafecard –
Victor,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
erection pills online best ed meds online or erectile dysfunction online order ed meds online
https://images.google.co.ls/url?q=https://vitaledgepharma.shop ed doctor online or http://www.80tt1.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=4001266 ed online treatment
[url=http://clients1.google.ge/url?q=https://vitaledgepharma.shop]ed meds online[/url] cheapest erectile dysfunction pills or [url=https://dongzong.my/forum/home.php?mod=space&uid=41334]cheapest online ed treatment[/url] ed meds by mail
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мягкий климат и богатая культура, утонченное искусство и 3500-летняя история Китая привлекают туристов со всех стран мира https://akademy21.ru/massage_lica_guasha
Уникальные памятники природы, разнообразные ландшафты и оригинальные культурные традиции делают путешествие в эту страну незабываемым https://akademy21.ru/obucheniye-lazernoye-udaleniye-sosudov-kuperoza-varikoza
Пляжные курорты острова Хайнань, горячие источники, морской воздух, оздоровительные центры, где в лучших традициях древней китайской медицины вас наполнят энергией и бодростью https://akademy21.ru/courses
Даже самым взыскательным туристам придется по душе отдых в Китае, ведь каждый здесь найдет то, что искал https://akademy21.ru/klassicheskiimassaj
Кухня https://akademy21.ru/contacts/groznyj
Для въезда на территорию Китая необходимо разрешение – виза https://akademy21.ru/courses/leshmaker
Срок оформления документов в посольстве – от 3 до 7 рабочих дней (может быть увеличен в зависимости от сезонности), без учета времени, необходимого на подготовку и подачу документов https://akademy21.ru/combinirivaniy_manicur
Пекин https://akademy21.ru/courses
Показать все предложения https://akademy21.ru/trener-po-dredam
20 Января , Сб от 7 до 8 ночей от 211 283 руб https://akademy21.ru/classicheskiy_manicur_spa
21 Января , Вс от 7 до 8 ночей от 218 422 руб https://akademy21.ru/contacts/kaliningrad
24 Января , Ср 7 ночей от 208 502 руб https://akademy21.ru/dolgovremenaia_ukladka
25 Января , Чт 7 ночей от 211 398 руб https://akademy21.ru/blog
26 Января , Пт 7 ночей от 216 878 руб https://akademy21.ru/courses/nailservice
27 Января , Сб от 7 до 13 ночей от 203 657 руб https://akademy21.ru/courses/stylist
28 Января , Вс 7 ночей от 212 873 руб https://akademy21.ru/contacts/rostov
29 Января , Пн 7 ночей от 216 839 руб https://akademy21.ru/pervaya_medicinskaya_pomosh
30 Января , Вт 7 ночей от 188 436 руб https://akademy21.ru/kurs_cosmetolog_estet
31 Января , Ср 7 ночей от 243 254 руб https://akademy21.ru/lazernoe-udalenie-permanentnogo-makiyazha
1 Февраля , Чт 7 ночей от 190 440 руб https://akademy21.ru/osnovy_makeiaja
2 Февраля , Пт 7 ночей от 209 705 руб https://akademy21.ru/trener-po-dredam
3 Февраля , Сб 7 ночей от 178 201 руб https://akademy21.ru/obucheniye-lazernoye-udaleniye-sosudov-kuperoza-varikoza
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ed doctor online: VitalEdgePharma – buy erectile dysfunction pills
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
По типу профиля металл бывает штампованным (гофрированным) или прямым http://aldial.ru/kupit-kolpaki-na-metallicheskie-stolby-zabora.html
Изделия из листового металла прямого типа на заказ используются преимущественно в строительной сфере или в машиностроении, но бывают и исключения (причем они нередки) http://aldial.ru/410/idealnye-dobornye-elementy.html
Важно учитывать, что конкретные требования зависят от условий, качеств и нужных характеристик готового изделия http://aldial.ru/otz.html
Токарно-фрезерные работы http://aldial.ru/469/algoritm-raboty-s-ooo-aldial.html
ООО
Основные характеристики изготовления изделий из листа http://aldial.ru/dobornye-ehlementy-krovli.html
Порошковая покраска http://aldial.ru/dymnik-na-pechnuyu-trubu.html
Подготовительный этап требует определиться с углами и точками сгибов, габаритами итогового изделия и конфигурацией http://aldial.ru/347/govoril-chto-nado-srochno-i-poluchal-izdeliya-v-etot-zhe-den.html
Перед гибкой металла, лазерной резкой раскраивается лист http://aldial.ru/dobornye-ehlementy-krovli.html
Лист зажимается на специальном гибочном станке с гидроцилиндрами, за счет которых изделие прижимается http://aldial.ru/cat_izdeliya.html
Гибка металла прессом осуществляется за счет усилия гидравлики http://aldial.ru/cat_front-cassettes
На каждом этапе мы проверяем качество выполненной работы и делаем контрольные замеры перед последующей подачей полной партии заготовок http://aldial.ru/410/idealnye-dobornye-elementy.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello folks!
I came across a 135 great tool that I think you should dive into.
This site is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find insightful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
[url=https://blowthedotoutyourass.com/machines-of-luck/the-power-of-the-link-between-a-slot-machine-and-a-gambler/]https://blowthedotoutyourass.com/machines-of-luck/the-power-of-the-link-between-a-slot-machine-and-a-gambler/[/url]
Additionally do not forget, guys, — you always can within this publication discover responses to your the very confusing queries. The authors attempted to present all data using an extremely understandable way.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
startguthaben ohne einzahlung wetten
my page … sportwetten Tipps und tricks (newsblogsite.Blogolenta.com)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://clearmedshub.shop/# ClearMedsHub
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ever Trust Meds: Ever Trust Meds – EverTrustMeds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wedding venues in gt karnal road Book Farmhouses, Banquet Halls, Hotels for Party places at GT Karnal Road Ever thought of enjoying a multi-theme Wedding Function while being at just one destination? If no then you must not have visited Farmhouses. Wedding Venues GT Karnal Road
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Wedding Venues in Wazirpur & GT Industrial Area. List of Farmhouses in Wazirpur, Banquet Halls, Hotels for Party places in Wazirpur & GT Industrial Area Ever thought of enjoying a multi-theme Wedding Function while being at just one destination? If no
then you must not have visited Wazirpur & GT Industrial Area Farmhouses.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Виртуальный номер навсегда – это надежное решение для защиты ваших данных. Хотите купить постоянный виртуальный номер для смс? Мы предлагаем качественные виртуальные номера с доступом к широким возможностям. Оцените простоту и удобство наших услуг. Выбирайте современный способ связи без лишних забот.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://dallasbaxt39405.bloginwi.com/58632985/virtueel-telefoonnummer
виртуальный номер, купить постоянный виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер навсегда
купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда, купить номер телефона навсегда, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для утепления конструкции пола керамзит может использоваться двумя способами https://al-keram.ru/blog/05.html
В первом варианте он замешивается в раствор для заливки стяжки https://al-keram.ru/dostavka-keramzita-v-khimki.html
Это существенно повышает прочностные и теплоизоляционные свойства образуемой поверхности https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzit/keramzit-v-big-begah-fraktsii-10-20-m250-300-detail.html
Во втором случае засыпка керамзитом входит в состав пирога конструкции пола по грунту или по перекрытию https://al-keram.ru/blog/osnovnye-preimushchestva-ispolzovaniya-keramzita-alkeram.html
В зависимости от способа применения, определяют какая фракция керамзита лучше для пола https://al-keram.ru/blog/uteplenie-keramzitom.html
Мокрый – заключается в предварительном замачивании сырья в больших емкостях, закачке образовавшегося раствора (шликера) в бассейн-отстойник, откуда он насосами подается в печь для термической обработки https://al-keram.ru/zakazat-keramzit-v-mytishchi.html
Разделение глиняной увлажненной массы на отдельные частицы происходит при помощи закрепленных на входе в зону обжига тяжелых цепей https://al-keram.ru/novosti/otsutstvie-rosta-tsen-po-sravneniyu-s-konkurentami.html
При создании газонов и клумб широко используют в качестве дренажа возможности керамзита https://al-keram.ru/catalog-keramzit/keramzit-v-big-begah-fraktsii-20-40-m200-250-detail.html
Лучшим доказательством долговечности изделий из глины служат сохранившиеся части древних видов глиняной посуды https://al-keram.ru/aktsii/skidki-pri-pokupke-keramzita.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Купите виртуальный номер для смс навсегда и забудьте о сложностях с доступностью связи. Постоянный виртуальный номер идеально подходит для бизнеса, личного использования и регистрации. Мы предлагаем только качественные услуги, которые сделают вашу связь стабильной и удобной. Виртуальный номер навсегда – это ваш ключ к современным коммуникациям. Попробуйте наши услуги уже сегодня.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://elliottwpkt49370.tinyblogging.com/het-belang-van-mobiele-nummers-in-duitsland-een-gids-70507404
виртуальный номер навсегда, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда, постоянный виртуальный номер
Купить виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс, купить виртуальный номер навсегда
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hi! [url=https://maps.google.co.jp/url?sa=t&url=https%3A%2F%2Fpropeciafx.com]no presription on line rx[/url] beneficial web site.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://clearmedshub.com/#
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ever Trust Meds [url=https://evertrustmeds.shop/#]EverTrustMeds[/url] buy cialis pill
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Виртуальный номер навсегда – это удобство, которое всегда с вами. Хотите купить постоянный виртуальный номер для смс? Мы предоставляем качественные услуги с гарантией стабильности. Постоянный виртуальный номер – это ваш надежный выбор для общения и работы. Начните пользоваться преимуществами уже сегодня!
Полная информация по ссылке – https://edgarakud96308.blog-a-story.com/6516774/alles-wat-je-moet-weten-over-mobiele-nummers-in-duitsland-een-diepgaande-verkenning
постоянный виртуальный номер для смс, Виртуальный номер навсегда, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда
купить виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Если хотите остаться на связи, лучше постоянный виртуальный номер уже сегодня. Сейчас самое время постоянный виртуальный номер без лишних документов. Наши клиенты рекомендуют постоянный виртуальный номер друзьям и коллегам. С помощью сервиса вы легко сможете постоянный виртуальный номер. Выбирайте наш сервис, чтобы постоянный виртуальный номер с удобством.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://andyndmt35893.total-blog.com/het-belang-van-mobiele-nummers-in-duitsland-een-gids-51905479
купить номер телефона навсегда, купить постоянный виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер
виртуальный номер навсегда, виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverTrustMeds: Ever Trust Meds – Generic Tadalafil 20mg price
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Купите виртуальный номер для смс навсегда и получите стабильное решение для всех своих нужд. Постоянный виртуальный номер подходит для работы, общения и регистрации. Мы предлагаем надежные и качественные услуги с гарантией доступности. Виртуальный номер навсегда – это ваш надежный помощник в цифровом мире. Оцените преимущества наших номеров.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://ericklvdm41852.full-design.com/het-belang-van-een-telegram-telefoonnummer-69615510
купить постоянный виртуальный номер, купить постоянный виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер навсегда
постоянный виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер навсегда, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
VitalEdge Pharma: VitalEdgePharma – VitalEdge Pharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Современные технологии позволяют купить постоянный виртуальный номер за минуту. Каждому нужен купить постоянный виртуальный номер для безопасности личных данных. Сейчас самое время купить постоянный виртуальный номер без лишних документов. купить постоянный виртуальный номер — это цифровая свобода и приватность. Вы можете купить постоянный виртуальный номер для регистрации в любых сервисах.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://trentoncwjn26701.livebloggs.com/30995440/virtueel-nummer-voor-altijd
купить номер телефона навсегда, купить виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс
купить виртуальный номер, виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Нужен постоянный виртуальный номер? Мы предлагаем купить виртуальный номер телефона навсегда, который подойдет для смс, регистрации и работы. Постоянный виртуальный номер – это удобный способ оставаться на связи без лишних хлопот. Наши услуги обеспечивают надежность и конфиденциальность. Делайте выбор в пользу современного общения.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://claytontidx47049.like-blogs.com/26676099/het-belang-van-tijdelijke-mobiele-nummers-een-diepgaande-verkenning
купить номер телефона навсегда, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс
купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда, купить виртуальный номер для смс навсегда
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Виртуальный номер навсегда – это современное и удобное решение для повседневных задач. Хотите купить постоянный виртуальный номер для смс? Наши номера подходят для всех популярных платформ и мессенджеров. Постоянный виртуальный номер – это свобода выбора и стабильная связь. Закажите у нас и оцените качество наших услуг.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://louisvaeh54331.elbloglibre.com/26749839/de-magie-van-telegram-zonder-nummer
постоянный виртуальный номер, купить постоянный виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс
Виртуальный номер навсегда, купить постоянный виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
app für sportwetten
Look at my blog … Item734599967
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kostenlose sportwetten tipps
Feel free to visit my webpage Kombiwetten Booster
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://vitaledgepharma.com/# VitalEdge Pharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://evertrustmeds.com/# cheapest cialis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Виртуальный номер навсегда – это универсальное решение для всех ваших задач. Хотите купить постоянный виртуальный номер для смс? Мы предоставляем надежные номера с гарантией стабильности. Постоянный виртуальный номер – это удобный способ сохранить связь в любой ситуации. Заказывайте у нас и получайте лучшее.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://miloetde02115.jaiblogs.com/51675483/koop-voor-altijd-een-virtueel-nummer
виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер, купить постоянный виртуальный номер
купить виртуальный номер навсегда, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс, виртуальный номер
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverTrustMeds [url=https://evertrustmeds.shop/#]Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription[/url] EverTrustMeds
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Фонд Ruarts Изображение: архитектурное бюро «Атриум» САЙТ https://www.abbalk.ru/page47572771.html
Лучшие студии, мастерские и крупные компании, где проектируют дома и пространства https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
ЖК в Москве Изображение: ГК «Тekta» / архитектурная дизайн-студия GAFA Architects https://www.abbalk.ru/stati
В отзывах компанию хвалят за качественные проекты и опытных сотрудников https://www.abbalk.ru/page47574811.html
Телефон: 8 (499) 397-86-62 Адрес: Москва, Пресненская набережная, 6 https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
Архитектурное бюро https://www.abbalk.ru/page47559287.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Виртуальный номер навсегда – это практичное решение для бизнеса и личного использования. Купите постоянный виртуальный номер и используйте его для регистрации, общения или смс. Мы предлагаем удобные и качественные номера с гарантией надежности. Постоянный виртуальный номер – это свобода и стабильность связи. Выбирайте проверенные услуги.
Полная информация по ссылке – https://milojliy71605.newbigblog.com/32646954/alles-wat-je-moet-weten-over-mobiele-nummers-in-duitsland-een-diepgaande-verkenning
купить виртуальный номер, купить виртуальный номер навсегда, купить виртуальный номер навсегда
виртуальный номер навсегда, постоянный виртуальный номер, постоянный виртуальный номер для смс
Удачи и комфорта в общении!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
deutsche lizenz sportwetten
Here is my homepage: esc-Wettquoten
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://gesunddirekt24.com/# apotheke online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
beste sportwetten anbieter deutschland
Feel free to visit my web site … wettanbieter mit bonus
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Viagra kaufen Apotheke Preis Viagra kaufen ohne Rezept Schweiz or Viagra kaufen ohne Rezept legal Viagra online kaufen legal
https://images.google.gy/url?q=https://intimgesund.com Viagra rezeptfreie Schweiz bestellen or http://lenhong.fr/user/zdjzfvfmgp/ Viagra diskret bestellen
[url=https://www.google.com.np/url?q=http://pharmalibrefrance.com]In welchen europäischen Ländern ist Viagra frei verkäuflich[/url] Viagra Tabletten für Männer or [url=https://www.yourporntube.com/user/tzgnerfqpv/videos]Viagra rezeptfreie Schweiz bestellen[/url] Viagra Generika 100mg rezeptfrei
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
medikament ohne rezept notfall: shop apotheke gutschein – online apotheke versandkostenfrei
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
europa apotheke [url=https://potenzapothekede.com/#]rezeptfreie medikamente fur erektionsstorungen[/url] wirkung und dauer von tadalafil
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Туры в Китай из Иркутска в 2023 году вновь набирают популярность https://akademy21.ru/courses/nutritionology
С возобновлением прямого рейса Иркутск – Хайнань, туры в Китай предполагают значительную экономию средств при заблаговременном бронировании авиа- и жд-билетов и отелей https://akademy21.ru/courses
Туры в Китай 2024 от всех туроператоров, цены https://akademy21.ru/courses/cosmetology
Рейтинг: 4 https://akademy21.ru/contacts/ekaterinburg
0 из 5 https://akademy21.ru/contacts/ixelles
0 https://akademy21.ru/courses/leshmaker
Сэкономьте до 25% от стоимости тура https://akademy21.ru/courses/massage/apparatniy-massazh-tela-lpg
Ищем похожие туры https://akademy21.ru/contacts/volgograd
Гуанчжоу https://akademy21.ru/medsestra_cosmetolog
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Цена может меняться в зависимости от:
Наше производство позволяет изготавливать широкий ассортимент разных элементов металлопроката, а непосредственно технология гибки представлена следующими этапами http://aldial.ru/kupit-kolpaki-na-kirpichnye-stolby-zabora.html
Сатинирование нержавейки http://aldial.ru/dobornye-ehlementy-krovli.html
Изделие из стали 3 мм — подставка под клавиатуру http://aldial.ru/dymnik.html
Лазерная резка и гибка под углом 140° (3)
Высокоточное оборудование для лазерной резки трубы http://aldial.ru/347/govoril-chto-nado-srochno-i-poluchal-izdeliya-v-etot-zhe-den.html
Как происходит производство металлических изделий под заказ?
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
schnelle lieferung tadalafil tabletten: PotenzApotheke – online apotheke gГјnstig
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://gesunddirekt24.com/# ohne rezept apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pferderennen live wetten ergebnisse (newsblogsite.Blogripley.com) regeln
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke rezept beste online-apotheke ohne rezept and internet apotheke п»їshop apotheke gutschein
https://images.google.dz/url?q=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com online apotheke rezept and https://memekrapet.com/user/ceydrjzxqq/videos medikamente rezeptfrei
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.gy/url?q=https://blaukraftde.com]online apotheke deutschland[/url] medikamente rezeptfrei and [url=https://www.ixxxnxx.com/user/jhrocjbwrc/videos]eu apotheke ohne rezept[/url] eu apotheke ohne rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafil erfahrungen deutschland: PotenzApotheke – medikamente rezeptfrei
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
apotheke online [url=https://gesunddirekt24.shop/#]rezeptfreie arzneimittel online kaufen[/url] medikamente rezeptfrei
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://gesunddirekt24.com/# online apotheke rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke: MannerKraft – gГјnstigste online apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten verluste zurückholen österreich
Also visit my webpage comment-274947 (Bob)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
deutsche wettanbieter
my page; merkur sportwetten (https://ext-6834287.Livejournal.com/Profile)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
apotheke online: sildenafil tabletten online bestellen – internet apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
internet apotheke apotheke online and online apotheke preisvergleich online apotheke gГјnstig
https://cse.google.com.sl/url?q=https://potenzapothekede.shop europa apotheke or https://www.bsnconnect.co.uk/profile/ntcvdtglha/ п»їshop apotheke gutschein
[url=http://maps.google.com.gh/url?q=https://potenzapothekede.shop]gГјnstigste online apotheke[/url] internet apotheke and [url=http://www.blackinseattle.com/profile/hbuyulzonk/]apotheke online[/url] europa apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kamagra oral jelly deutschland bestellen: generisches sildenafil alternative – Viagra rezeptfreie Schweiz bestellen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Официальный актуальный сайт кракен доступ > кракен магазин зайти Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен сайт ссылка, и вот что стабильно работает: Многие ищут кракен тг маркетплейс, ведь Telegram остаётся основным каналом для распространения рабочих ссылок. Настоящий кракен тг маркетплейс публикуется администрацией и подтверждается пользователями. Это гарантирует безопасность.
Проверил лично несколько зеркал — стабильно открываются: кракен магазин зеркало — krakenmagazin.ccреклама магазина кракен — krakenmagazin.cc Если нужна помощь — пишите.Проверено лично (Липецк). Kraken Marketplace секретная торговая платформа тг мессенджер
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://potenzapothekede.shop/# tadalafil 20mg preisvergleich
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
gratis bonus sportwetten
Review my web-site; halbzeit wetten strategie (Steven)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Viagra online bestellen Schweiz Erfahrungen [url=http://intimgesund.com/#]kamagra kaufen ohne rezept online[/url] IntimGesund
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Viagra wie lange steht er Viagra Apotheke rezeptpflichtig or Viagra kaufen Apotheke Preis Viagra kaufen ohne Rezept legal
https://www.gamekiller.net/proxy.php?link=https://intimgesund.com Viagra online bestellen Schweiz and http://forum.ttpforum.de/member.php?action=profile&uid=436102 Viagra Generika online kaufen ohne Rezept
[url=https://images.google.com.na/url?sa=t&url=https://intimgesund.com]Viagra kaufen ohne Rezept legal[/url] Sildenafil rezeptfrei in welchem Land and [url=https://4k-porn-video.com/user/cbpsbuelct/]Viagra Alternative rezeptfrei[/url] Viagra verschreibungspflichtig
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
apotheke online online apotheke deutschland and gГјnstige online apotheke ohne rezept apotheke
http://artistsbook.lt/wp-content/plugins/wp-js-external-link-info/redirect.php?url=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com п»їshop apotheke gutschein or https://www.snusport.com/user/dczcvuarxw/?um_action=edit online apotheke
[url=https://www.google.com.eg/url?q=https://blaukraftde.com]gГјnstige online apotheke[/url] online apotheke rezept or [url=https://boyerstore.com/user/ucsyhannlw/?um_action=edit]online apotheke deutschland[/url] medikament ohne rezept notfall
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://mannerkraft.com/# online apotheke deutschland
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke rezept: Viagra online kaufen legal in Deutschland – europa apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кракен сайт позволяет обойти возможные блокировки и получить доступ к маркетплейсу. [url=https://enactusegypt.org/]сайт kraken[/url] необходимо искать через проверенные источники, чтобы избежать фишинговых сайтов. кракен зеркало рабочее на сегодня должно обновляться регулярно для обеспечения непрерывного доступа.
регистрация – главная особенность Кракен.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сайт kraken позволяет обойти возможные блокировки и получить доступ к маркетплейсу. [url=https://gminazlota.pl/]зеркало кракен актуальное[/url] необходимо искать через проверенные источники, чтобы избежать фишинговых сайтов. ссылки на кракен должно обновляться регулярно для обеспечения непрерывного доступа.
Bitcoin – главная особенность Кракен.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
schnelle lieferung tadalafil tabletten: wirkung und dauer von tadalafil – п»їshop apotheke gutschein
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
europa apotheke eu apotheke ohne rezept or gГјnstige online apotheke medikamente rezeptfrei
https://maps.google.dj/url?q=https://mannerkraft.shop gГјnstige online apotheke and http://156.226.17.6/home.php?mod=space&uid=1297664 beste online-apotheke ohne rezept
[url=http://www.gtb-hd.de/url?q=https://mannerkraft.shop]gГјnstige online apotheke[/url] apotheke online or [url=https://gicleeads.com/user/atwvxtwkvc/?um_action=edit]medikamente rezeptfrei[/url] online apotheke versandkostenfrei
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Официальная кракен площадка торговая > кракен сайт маркетплейс Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен безопасный вход, и вот что стабильно работает: Сегодня кракен маркет воспринимается как устойчивый и известный ресурс. Настоящий кракен маркет всегда требует входа через Tor, всё остальное — подделки.
Проверил лично несколько ссылок — стабильно открываются: кракен магазин онлайн — krakenmagazin.ccкракен маркетплейс работа — krakenmarketplaces.cc Если нужна помощь — задавайте вопросы.Проверено лично (Ижевск). Сайт Кракена тор-маркет телега
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke gГјnstig [url=https://mannerkraft.shop/#]MannerKraft[/url] eu apotheke ohne rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
internet apotheke: sildenafil tabletten online bestellen – beste online-apotheke ohne rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
medikamente rezeptfrei: deutsche online apotheke erfahrungen – online apotheke preisvergleich
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten live ergebnisse
My page vergleich wettquoten (Kali)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wahl wetten deutschland
Review my website: comment-494464 (Brenna)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://mannerkraft.com/# apotheke online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://potenzapothekede.com/# wirkung und dauer von tadalafil
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет фортовым игрокам КАЗИНО онлайн!
Играй смело и выигрывай чаще через 1win casino зеркало. Здесь доступны лучшие игры онлайн. Каждый день новые эмоции и шансы на победу. Получай бонусы и призы. 1win casino зеркало всегда рядом с игроками.
Заходите скорее на рабочее 1win casino зеркало – [url=https://t.me/s/onewincasinotoday]1win casino зеркало[/url]
Удачи и быстрых выйгрышей в 1win casino!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
п»їshop apotheke gutschein [url=https://potenzapothekede.com/#]tadalafil erfahrungen deutschland[/url] cialis generika ohne rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Приветствую фортовым игрокам!
1win casino зеркало – это твой шанс на победу каждый день. Здесь можно играть без риска блокировок. Все работает быстро и стабильно. Ты получаешь бонусы и выигрыши. 1win casino зеркало создано для азартных эмоций.
Заходите скорее на рабочее 1win casino зеркало – [url=https://t.me/s/onewincasinotoday]1win casino зеркало[/url]
Удачи и персональных выйгрышей в 1win casino!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
medikament ohne rezept notfall: ohne rezept apotheke – günstige online apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Приветствую фортовым игрокам!
Играй и наслаждайся азартом с помощью 1win casino зеркало. Доступ к играм открыт круглосуточно. Каждый спин – это шаг к победе. Получай бонусы и выигрывай стабильно. 1win casino зеркало всегда работает быстро и надежно.
Заходите скорее на рабочее 1win casino зеркало – [url=https://t.me/s/onewincasinotoday]1win casino зеркало[/url]
Удачи и супер выйгрышей в 1win casino!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke: viagra ohne rezept deutschland – europa apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke gГјnstig beste online-apotheke ohne rezept and eu apotheke ohne rezept apotheke online
https://cse.google.co.ve/url?q=https://mannerkraft.shop medikamente rezeptfrei or https://voicebyjosh.com/user/yjnmvgygze/ gГјnstige online apotheke
[url=http://www.protvino.ru/bitrix/rk.php?id=20&event1=banner&event2=click&goto=http://bluepharmafrance.com]online apotheke versandkostenfrei[/url] eu apotheke ohne rezept or [url=https://cyl-sp.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=104539]online apotheke rezept[/url] online apotheke gГјnstig
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Приветствую фортовым игрокам!
1win casino зеркало – это платформа для настоящих победителей. Играй в рулетку, слоты и карточные игры. Каждый день ты получаешь шанс на выигрыш. Все работает стабильно и безопасно. 1win casino зеркало гарантирует честные выплаты.
Заходите скорее на рабочее 1win casino зеркало – https://t.me/s/onewincasinotoday
Удачи и быстрых выйгрышей в 1win casino!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ссылка на сайт кракен для всех > рабочий кракен шоп Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен официальный сайт, и вот что стабильно работает: Фраза кракен телеграм маркетплейс подчёркивает роль мессенджера как главного источника ссылок и новостей. Настоящий кракен телеграм маркетплейс содержит только проверенные onion-адреса. Любые другие чаты или сайты — рискованные.
Проверил лично несколько адресов — стабильно открываются: кракен магазин тор — krakenmagazin.ccподдержка кракен шоп — krakeshop.cc Если нужна помощь — оставляйте комменты.Проверено лично (Казань). KRN теневой маркет Телекрам
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke rezept [url=https://blaukraftde.com/#]Blau Kraft De[/url] online apotheke versandkostenfrei
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Приветствую фортовым игрокам!
Играй честно и выигрывай вместе с 1win casino зеркало. Платформа дает доступ к играм без блокировок. Ты получаешь шанс сорвать джекпот. Все честно и стабильно. 1win casino зеркало гарантирует комфорт и азарт.
Заходите скорее на рабочее 1win casino зеркало – [url=https://t.me/s/onewincasinotoday]1win casino зеркало[/url]
Удачи и топовых выйгрышей в 1win casino!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke deutschland: online apotheke versandkostenfrei – online apotheke preisvergleich
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
potenzmittel diskret bestellen: IntimGesund – Viagra online kaufen legal in Deutschland
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://intimgesund.shop/# potenzmittel diskret bestellen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke preisvergleich [url=https://blaukraftde.shop/#]sildenafil tabletten online bestellen[/url] online apotheke gГјnstig
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кракен ссылка 2025 позволяет обойти возможные блокировки и получить доступ к маркетплейсу. [url=https://elderpharma.com/]кракен зеркала[/url] необходимо искать через проверенные источники, чтобы избежать фишинговых сайтов. кракен сайт магазин должно обновляться регулярно для обеспечения непрерывного доступа.
авторизация – главная особенность Кракен.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
medikamente rezeptfrei: sicherheit und wirkung von potenzmitteln – internet apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online apotheke deutschland: günstige medikamente direkt bestellen – online apotheke deutschland
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кракен рабочая ссылка позволяет обойти возможные блокировки и получить доступ к маркетплейсу. [url=https://electricall.co/]кракен ссылка переходник[/url] необходимо искать через проверенные источники, чтобы избежать фишинговых сайтов. актуальное зеркало кракен должно обновляться регулярно для обеспечения непрерывного доступа.
доступ – главная особенность Кракен.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
gГјnstige online apotheke [url=https://mannerkraft.com/#]Manner Kraft[/url] beste online-apotheke ohne rezept
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://mannerkraft.shop/# gГјnstige online apotheke
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://short33.site
Линкбилдинг это простыми словами – это способ увеличения ссылочной массы сайта. Он помогает улучшить позиции в поиске. Программы для автоматизации делают процесс быстрым и удобным. Ссылочная масса напрямую влияет на DR. Линкбилдинг это простыми словами ускоряет рост сайта.
николай seo, раскрутка сайта в топ цена, линкбилдинг план
Как увеличить DR сайта, seo в метрике, seo или директ
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от крутых seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://short33.site
Линкбилдинг стратегии позволяют строить долгосрочный план продвижения. Нужно выбирать подходящие площадки и инструменты. Программы для автоматизации ускоряют работу. Стратегия определяет качество ссылочной массы. Линкбилдинг стратегии повышают шансы на топовые позиции.
продвижение сайта по позициям в яндексе, поисковое продвижение сайта раскрутка, Использование Xrumer в 2025
Генерация внешних ссылок быстро, hee seo, предложение продвижения сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
safe online pharmacies in canada drugs from canada or best canadian pharmacy to buy from the canadian pharmacy
https://www.google.com.vn/url?q=https://truenorthpharm.com canadian online drugs or https://chinaexchangeonline.com/user/evttkwzxoi/?um_action=edit canadian pharmacy no scripts
[url=https://maps.google.cd/url?q=https://truenorthpharm.com]safe canadian pharmacy[/url] safe reliable canadian pharmacy and [url=https://kamayegaindia.com/user/afzcwvywnp/?um_action=edit]canadian pharmacies compare[/url] reputable canadian pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от успещных seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://short33.site
Xrumer для оптимизации сайта помогает ускорить линкбилдинг. Программа размещает ссылки на форумах и блогах массово. Это экономит время и силы специалистов. Массовый прогон повышает DR и позиции сайта. Xrumer для оптимизации сайта – современный метод продвижения.
seo и youtube, продвижение интернет сайта договор, линкбилдинг заказать
линкбилдинг интернет магазина, seo планирование сайта, пример сео аудит
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
CuraBharat USA: pharmacies in india – CuraBharat USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy canadian drugs: canadian pharmacy mall – canadian online pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Долго думал как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от крутых seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://short33.site
Прогон ссылок через Xrumer помогает улучшить DR и увеличить показатели Ahrefs. Массовая рассылка ссылок через форумы ускоряет линкбилдинг и улучшает SEO-позиции. Программы для линкбилдинга помогают создать качественные внешние ссылки. Увеличение ссылочной массы с Xrumer помогает повысить видимость сайта. Попробуйте Xrumer для повышения SEO-результатов.
поисковое продвижение сайта постоянно, trend seo, линкбилдинг seo
каталоги линкбилдинг, seo pack pro, seo чек листы
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://curabharatusa.com/# CuraBharat USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://curabharatusa.shop/# buy medicine online india
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от крутых seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://short33.site
Xrumer для оптимизации сайта помогает ускорить линкбилдинг. Программа размещает ссылки на форумах и блогах массово. Это экономит время и силы специалистов. Массовый прогон повышает DR и позиции сайта. Xrumer для оптимизации сайта – современный метод продвижения.
сео аудит сайт, проверить текст на сео оптимизацию, Генерация внешних ссылок быстро
Техники увеличения ссылочной массы, бюджет на продвижение сайта продвижение сайтов, сео копирайтеры
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://polarposti.site
Прогон Хрумер для сайта позволяет быстро увеличить ссылочный профиль. Увеличение ссылочной массы быстро становится возможным через Xrumer. Линкбилдинг через автоматические проги ускоряет продвижение. Xrumer форумный спам облегчает массовый постинг. Эффективный прогон для роста DR экономит время специалистов.
seo org, seo цена в месяц, Генерация ссылок через Xrumer
Как поднять показатели Ahrefs, продвижение сайта с гарантией адвертпро, продвижение автоматическое сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexican pharmacies that ship to us [url=http://saludfrontera.com/#]SaludFrontera[/url] SaludFrontera
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
canada pharmacy world: canadian pharmacy online ship to usa – TrueNorth Pharm
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
adderall online india online medicine site and buy medicine online india pharma online
https://www.google.fi/url?sa=t&url=https://curabharatusa.com india pharmacy of the world or https://raygunmvp.com/user/mfzfvgedvh-mfzfvgedvh/?um_action=edit online pharmacy india
[url=http://www.24subaru.ru/photo-20322.html?ReturnPath=https://curabharatusa.com]п»їindian pharmacy[/url] vicodin in india or [url=https://www.pornzoned.com/user/teatlbeuzc/videos]order medicines from india to usa[/url] medicine online india
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от крутых seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Xrumer – https://short33.site
Линкбилдинг или стратегии зависят от целей проекта. Линкбилдинг работа требует внимательного подхода. Линкбилдинг начать можно с форумов и блогов. Линкбилдинг стратегия ускоряет рост ссылочной массы. Линкбилдинг для англоязычного сайта открывает новые рынки.
seo продвижение это, поисковому продвижению сайта в сети, Увеличение ссылочной массы быстро
Линкбилдинг для продвижения в топ-10, продвижение сайтов в топ цена москва, jin seo lee
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
medication canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy 24h com safe and certified canadian international pharmacy canadian pharmacy uk delivery
http://www.tifosy.de/url?q=https://truenorthpharm.com pharmacy com canada or https://lifnest.site/user/fpfcxympuhfpfcxympuh/?um_action=edit rate canadian pharmacies
[url=http://7ba.ru/out.php?url=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com/]vipps canadian pharmacy[/url] legitimate canadian pharmacies or [url=http://foru1f40m.bunbun000.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=9678414]canadian drugs[/url] legitimate canadian online pharmacies
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexican pharma order medicine from mexico or online pharmacy in mexico mexico pharmacy
http://a-bisu.com/topart161/_m/index.php?a=free_page/goto_mobile&referer=https://saludfrontera.com purple pharmacy and https://www.liveviolet.net/user/suxfbgzkkb/videos mexican pharmacy that ships to the us
[url=https://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.ac/url?q=https://saludfrontera.com]mexico medication[/url] mexican pharmacy and [url=http://www.jdmtube.com/user/qqtpsnzbxm/videos]best mexican online pharmacy[/url] mexican mail order pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://saludfrontera.com/# SaludFrontera
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 47 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
CuraBharat USA: CuraBharat USA – CuraBharat USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
northwest pharmacy canada [url=https://truenorthpharm.shop/#]best canadian pharmacy to order from[/url] buying drugs from canada
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
best mexican pharmacy: SaludFrontera – mexican drug stores
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
canadian 24 hour pharmacy canadian online pharmacy and canadianpharmacymeds com legit canadian pharmacy
https://cse.google.co.zw/url?q=https://truenorthpharm.com buying from canadian pharmacies or http://www.xgmoli.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=12262 buying drugs from canada
[url=https://kirschenmarkt-gladenbach.de/go.php?go=https://truenorthpharm.com]legitimate canadian pharmacies[/url] canada drug pharmacy or [url=http://orbita-3.ru/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=26718]canadian pharmacy tampa[/url] best mail order pharmacy canada
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sport wetten tipps heute
Have a look at my website :: bester copa libertadores wettanbieter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от крутых seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://monstros.site
Линкбилдинг услуга позволяет увеличить ссылочный профиль сайта. Линкбилдинг для интернет магазина помогает улучшить позиции. Линкбилдинг сайт SEO ускоряет рост DR. Линкбилдинг линкбилдинг на запад открывает новые рынки. Линкбилдинг по тематике повышает релевантность ссылок.
оптимизировать сайт seo слова, создание разработка и продвижение интернет сайтов веб, Улучшение DR через Xrumer
Автоматизация создания ссылок, сео продвижение курсы, сайт продвижение тверь
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
live Wett tipps (http://Www.multichain.com) sportwetten strategie
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от крутых seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://imap33.site
Увеличение ссылочной массы быстро возможно только с автоматизацией. Ручная работа занимает слишком много времени. Xrumer помогает справиться с этим за несколько часов. Чем больше линков, тем выше позиции. Увеличение ссылочной массы быстро – ключ к успеху.
сайт dr tubers, самостоятельной раскрутке сайта, линкбилдинг что это простыми словами
Форумные проги для SEO, курсы продвижение сайта спб, продвижение сайта по ключевым словам яндекс
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://curabharatusa.shop/# CuraBharat USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от крутых seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://imap33.site
Xrumer помогает увеличить DR и Ahrefs через автоматический прогон ссылок. Массовые рассылки на форумах ускоряют процесс линкбилдинга. Программы для линкбилдинга помогают создать качественные ссылки для вашего сайта. Увеличение ссылочной массы с Xrumer помогает улучшить SEO-позиции. Используйте Xrumer для эффективного продвижения сайта.
раскрутка сайтов в топ цена в топ, описание в сео, линкбилдинг это что
линкбилдинг сео, бесплатное самостоятельное продвижение сайтов, раскрутка сайтов какой
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://saludfrontera.com/# SaludFrontera
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
TrueNorth Pharm: canadian pharmacy store – online pharmacy canada
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
prescriptions from mexico [url=https://saludfrontera.shop/#]purple pharmacy online[/url] SaludFrontera
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy canadian drugs: canadian king pharmacy – precription drugs from canada
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Долго ломал голову как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://imap33.site
Прогон ссылок Хрумером – это быстрый способ улучшить позиции сайта в поисковой выдаче. Увеличение DR с помощью Xrumer происходит за счёт автоматизации линкбилдинга. Программы для автоматического постинга на форумах создают качественные ссылки. Увеличение показателей Ahrefs даёт положительный эффект на SEO. Прогон ссылок с Xrumer – это эффективный метод продвижения.
сколько стоит продвижение сайта, seo мониторинг сайта, Увеличение трафика с помощью прогона
линкбилдинг стоимость, блоги для продвижения сайта, основы seo и smm
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
online canadian drugstore best canadian online pharmacy reviews and canadian pharmacy checker global pharmacy canada
https://images.google.ci/url?sa=t&url=https://truenorthpharm.com best canadian pharmacy or https://afafnetwork.com/user/xmtvhqabeq/?um_action=edit online canadian drugstore
[url=http://www.vesiletunnecat.com/forum/url.asp?url=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com]online canadian pharmacy[/url] reddit canadian pharmacy and [url=http://www.donggoudi.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3624999]best rated canadian pharmacy[/url] canadian pharmacy antibiotics
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexico city pharmacy mexican pharmacies that ship to us or pharmacy in mexico that ships to us mexican drug stores
https://cse.google.com.cu/url?sa=t&url=https://saludfrontera.com п»їmexican pharmacy and http://dnp-malinovka.ru/user/xebnyddkib/?um_action=edit mexican medicine
[url=https://www.google.by/url?q=https://saludfrontera.com]medication in mexico[/url] mexican pharmacy that ships to the us or [url=https://kherkun.com/user/axiktuzjze/?um_action=edit]prescriptions from mexico[/url] pharmacy delivery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от успещных seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://monstros.site
Прогон Хрумер для сайта позволяет быстро увеличить ссылочный профиль. Увеличение ссылочной массы быстро становится возможным через Xrumer. Линкбилдинг через автоматические проги ускоряет продвижение. Xrumer форумный спам облегчает массовый постинг. Эффективный прогон для роста DR экономит время специалистов.
продвижение сайта в москве топ сайт, title сайта seo, линкбилдинг отзывы
линкбилдинг цена, сео что это такое должность, специалист по продвижению сайтов
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[url=https://z2.anime-hd.online/anime-serials/4699-schastlivaja-semerka-2005.html] смотреть аниме Счастливая семерка (2005) [/url]
[url=https://z2.anime-hd.online/anime-serials/2489-my-ne-mozhem-vyjti-v-prjamoj-jefir-2022.html] смотреть аниме Мы не можем выйти в прямой эфир! (2022) [/url]
[url=https://z2.anime-hd.online/anime-serials/4464-bjek-arrou-2021.html] смотреть аниме Бэк Арроу (2021) [/url]
[url=https://z2.anime-hd.online/anime-serials/8407-voznesshijsja-nad-nebesami-2025.html] смотреть аниме Вознёсшийся над небесами (2025) [/url]
[url=https://z2.anime-hd.online/anime-serials/5020-vmeste-s-gospodinom-tv-1-2010.html] смотреть аниме Вместе с господином [ТВ-1] (2010) [/url]
[url=https://z2.anime-hd.online/anime-serials/1217-agressivnaja-rjecuko-2021-2021.html] смотреть аниме Агрессивная Рэцуко (2021) (2021) [/url]
[url=https://z2.anime-hd.online/anime/8237-ataka-titanov-poslednjaja-ataka-2024.html] смотреть аниме Атака Титанов: Последняя атака (2024) [/url]
[url=https://z2.anime-hd.online/anime-serials/5139-gintama-polufinal-2021.html] смотреть аниме Гинтама: Полуфинал (2021) [/url]
[url=https://z2.anime-hd.online/anime-serials/1925-klass-dlja-geroev-2023.html] смотреть аниме Класс для героев (2023) [/url]
[url=https://z2.anime-hd.online/anime-serials/7636-istorii-mejpl-tauna-tv-2-1987.html] смотреть аниме Рстории Мейпл-тауна [РўР’-2] (1987) [/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Долго думал как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от гуру в seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://imap33.site
Линкбилдинг пример помогает понять, как работают массовые прогоны. Xrumer автоматизирует размещение ссылок на форумах. Массовый линкбилдинг повышает DR. Чем больше качественных ссылок, тем выше позиции сайта. Линкбилдинг пример – полезный инструмент для новичков.
just seo, ssr seo, линкбилдинг seo
линкбилдинг это что, рейтинг сео сайта, раскрутка сайта псков
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от гуру в seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Xrumer – https://monstros.site
Прогон ссылок для роста позиции улучшает видимость сайта. Xrumer: полное руководство помогает новичкам освоить инструмент. Создание ссылок массовыми методами экономит время. Как настроить Xrumer для рассылок становится понятным после инструкции. Генерация ссылок через Xrumer ускоряет продвижение.
seo белая черная, примеры seo статей, стратегии линкбилдинг
Создание ссылок массовыми методами, вопросы по seo оптимизации, article seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://saludfrontera.com/# mexican pharmacy las vegas
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
TrueNorth Pharm [url=https://truenorthpharm.shop/#]canada discount pharmacy[/url] TrueNorth Pharm
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
SaludFrontera: SaludFrontera – online mexican pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://imap33.site
Линкбилдинг под бурж помогает продвигать сайты на зарубежные рынки. Нужно работать с иностранными площадками и форумами. Автоматизация через Xrumer ускоряет процесс. Это увеличивает количество качественных ссылок. Линкбилдинг под бурж – залог успешного международного SEO.
новое seo яндекс, продвижение сайта в топ 5 цена, SEO-прогон для повышения позиций
Xrumer: полное руководство, автоматическая оптимизация seo, pdf в продвижении сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
canada drugs reviews canadapharmacyonline com or canadian pharmacy 365 canadian pharmacy ratings
https://www.google.ws/url?sa=t&url=https://truenorthpharm.com::: best online canadian pharmacy or https://exhibitioncourthotel4.co.uk/user-2/giosslnqdl/?um_action=edit canadian pharmacy
[url=https://www.google.dj/url?q=http://pharmalibrefrance.com]legitimate canadian pharmacy online[/url] reputable canadian online pharmacies or [url=https://vanpages.ca/profile/oofseinfuq/]canadian world pharmacy[/url] canadianpharmacyworld com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
CuraBharat USA: CuraBharat USA – CuraBharat USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
SaludFrontera [url=https://saludfrontera.shop/#]SaludFrontera[/url] farmacia mexicana en chicago
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexican pharma: SaludFrontera – purple pharmacy online ordering
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://saludfrontera.com/# SaludFrontera
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://truenorthpharm.com/# canada pharmacy world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacy online: online mexico pharmacy – SaludFrontera
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sportwetten Tipps Von Experten ohne oasis forum
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
SaludFrontera [url=https://saludfrontera.com/#]mexico pet pharmacy[/url] SaludFrontera
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pharmacies in mexico: SaludFrontera – SaludFrontera
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кракен вход актуальное зеркало > зеркало сайта кракен Сегодня я протестировал несколько как найти сайт кракен, и вот что стабильно работает: Иногда пользователи ищут кракен ссылка онлайн, думая, что можно получить доступ напрямую. На самом деле всё работает иначе: ресурс функционирует исключительно через Tor, а onion-адрес является единственным способом входа. Все предложения кракен ссылка онлайн, которые открываются без Tor, — мошеннические. Поэтому пользователям советуют не доверять случайным ресурсам и использовать только проверенные источники.
Проверил лично несколько ссылок — стабильно открываются: кракен даркнет площадка — kradarknet.ccзеркало сайта кракен — kramirrors.cc Если нужна помощь — оставляйте комменты.Проверено лично (Астрахань). Кракен торговая платформа мессенджер телега
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://truenorthpharm.com/# TrueNorth Pharm
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wir Wetten Internet (Logcla.Com) bonus code
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
CuraBharat USA: medicine online india – buy medicine online in india
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://saludfrontera.shop/# mexico pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mexican pharmacy ship to usa [url=https://saludfrontera.shop/#]SaludFrontera[/url] mexican online pharmacy wegovy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Официальная поддержка сайта кракен > кракен зеркало рабочее Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен реальные отзывы, и вот что стабильно работает: Запрос кракен вход остаётся одним из самых популярных, потому что пользователи хотят получить безопасный доступ к площадке. Настоящий кракен вход осуществляется только через Tor и по onion-адресам. Любые попытки попасть на сайт через обычные поисковики приведут к поддельным ресурсам. Чтобы кракен вход был безопасным, важно проверять подлинность ссылки и использовать только официальные каналы.
Проверил лично несколько зеркал — стабильно открываются: кракен даркнет маркет вход — kradarknet.ccофициальное зеркало кракен — kramirrors.cc Если нужна помощь — пишите.Проверено лично (Сочи). Кракен скрытый маркет тэлега
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кракен сайт ссылка работает > список магазинов кракен Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен сайт маркетплейс, и вот что стабильно работает: Фраза кракен маркет плейс подчёркивает, что речь идёт о полном формате площадки, включающей магазины, сервисы и форумы. Настоящий кракен маркет плейс доступен только в сети Tor и сопровождается onion-доменами. Он не индексируется и не публикуется в открытых источниках. Пользователи обсуждают кракен маркет плейс, чтобы делиться отзывами о работе магазинов и обмениваться опытом. Это стало частью культуры сообщества, которая держится на доверии и проверке.
Проверил лично несколько зеркал — стабильно открываются: кракен зеркало — krakmirror.ccкракен магазины — krashops.cc Если нужна помощь — пишите.Проверено лично (Красноярск). Кракен онион торговая платформа Телеграмм
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
weekend pill UK online pharmacy: IntimaCareUK – cialis cheap price UK delivery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis online UK no prescription cialis cheap price UK delivery or cialis cheap price UK delivery IntimaCareUK
https://www.repcheckr.com/reviews/intimapharmafrance.com cialis online UK no prescription or http://www.xgmoli.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=11987 branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy
[url=http://www.virtual-egypt.com/framed/framed.cgi?url==http://intimapharmafrance.com]branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy[/url] IntimaCare and [url=https://blog.techshopbd.com/user-profile/ndqpabzezj/?um_action=edit]cialis cheap price UK delivery[/url] IntimaCareUK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MediQuick UK MediQuickUK or pharmacy online fast delivery UK generic and branded medications UK
https://www.paginainizio.com/html_iframe/news/rss.php?rssurl=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com/ MediQuick and http://orbita-3.ru/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=25686 MediQuickUK
[url=https://www.anquan.org/seccenter/search/pharmaexpressfrance.com]MediQuickUK[/url] cheap UK online pharmacy or [url=https://alphafocusir.com/user/ptvprtikrp/?um_action=edit]order medicines online discreetly[/url] pharmacy online fast delivery UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BluePillUK [url=https://bluepilluk.com/#]BluePillUK[/url] viagra discreet delivery UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://bluepilluk.com/# BluePillUK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis cheap price UK delivery: weekend pill UK online pharmacy – weekend pill UK online pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
buy ED pills online discreetly UK [url=http://intimacareuk.com/#]cialis online UK no prescription[/url] confidential delivery cialis UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Безопасный вход в кракен онлайн > кракен актуальные зеркала Сегодня я протестировал несколько как зайти на кракен в тор браузере, и вот что стабильно работает: Иногда пользователи ищут кракен ссылка онлайн, думая, что можно получить доступ напрямую. На самом деле всё работает иначе: ресурс функционирует исключительно через Tor, а onion-адрес является единственным способом входа. Все предложения кракен ссылка онлайн, которые открываются без Tor, — мошеннические. Поэтому пользователям советуют не доверять случайным ресурсам и использовать только проверенные источники.
Проверил лично несколько ссылок — стабильно открываются: новости кракен даркнет — kradarknet.ccофициальное зеркало кракен — kramirrors.cc Если нужна помощь — пишите.Проверено лично (Саратов). KRN онлайн-рынок телега
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Зайти на форум кракен > кракен форум Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен телеграм, и вот что стабильно работает: Фраза как работает рулетка на кракене интересует пользователей, которые впервые сталкиваются с функцией. Настоящий принцип основан на генераторе случайных чисел, который обеспечивает честность.
Проверил лично несколько ссылок — стабильно открываются: кракен зеркало — krakmirror.ccссылки форумы кракен — krakeforum.cc Если нужна помощь — оставляйте комменты.Проверено лично (Новосибирск). kraken url маркет мессенджер
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic sildenafil UK pharmacy: fast delivery viagra UK online – viagra discreet delivery UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sportwetten tipps prognosen
My homepage … Wett vorhersage Heute
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy [url=https://intimacareuk.com/#]cialis online UK no prescription[/url] IntimaCareUK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
UK pharmacy home delivery online pharmacy UK no prescription or MediQuick MediQuickUK
http://navstreche.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com/ MediQuickUK and https://501tracking.com/user/nstkoaqvma/?um_action=edit MediQuick
[url=https://images.google.is/url?q=https://mediquickuk.com]pharmacy online fast delivery UK[/url] trusted UK digital pharmacy or [url=http://mail.empyrethegame.com/forum/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=431458]generic and branded medications UK[/url] pharmacy online fast delivery UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sildenafil tablets online order UK viagra online UK no prescription and sildenafil tablets online order UK fast delivery viagra UK online
http://www.activecabarete.com/links/index.php?http://bluepharmafrance.com/ viagra discreet delivery UK and http://wamoja.com/community/profile/erqmhnusxh/ generic sildenafil UK pharmacy
[url=https://www.google.nr/url?sa=t&url=https://bluepilluk.com]generic sildenafil UK pharmacy[/url] viagra discreet delivery UK or [url=https://shipcoasts.com/user/xwdiscoxof/?um_action=edit]order viagra online safely UK[/url] sildenafil tablets online order UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://mediquickuk.shop/# online pharmacy UK no prescription
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
safe ivermectin pharmacy UK [url=https://meditrustuk.com/#]safe ivermectin pharmacy UK[/url] ivermectin without prescription UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic sildenafil UK pharmacy http://bluepilluk.com/# BluePill UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MediQuick: cheap UK online pharmacy – MediQuickUK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://monstros.site
Линкбилдинг через программы упрощает работу специалистов. Форумные проги для SEO автоматизируют размещение ссылок. Оптимизация ссылочного профиля повышает авторитетность сайта. Как прокачать сайт через Xrumer становится понятнее с опытом. Автоматизированный линкбилдинг экономит силы и время.
что seo аудит, продвижение сайтов стоит, курс линкбилдинг
линкбилдинг план, продвижение сайтов самара, seo сайта заказать спб
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от успещных seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://imap33.site
Увеличение ссылочной массы быстро возможно только с автоматизацией. Ручная работа занимает слишком много времени. Xrumer помогает справиться с этим за несколько часов. Чем больше линков, тем выше позиции. Увеличение ссылочной массы быстро – ключ к успеху.
рыбинск продвижение сайтов, самые лучшие сео, многоуровневый линкбилдинг
Техники увеличения ссылочной массы, анализ и продвижение сайтов, продвижение сайтов в москве и россии
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Xrumer – https://imap33.site
Увеличение трафика с помощью прогона Xrumer ускоряет продвижение сайта. Форумный линкбилдинг с Xrumer делает создание ссылочной массы системным. Массовая рассылка ссылок экономит время специалистов. Постинг на блогах для SEO помогает закрепить позиции. Xrumer для оптимизации сайта повышает DR.
сео с нуля бесплатно, seo применение, Линкбилдинг через комментарии
линкбилдинг сео, оптимизация сайтов и продвижение сайтов, агрегаторы для продвижения сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://intimacareuk.shop/# buy ED pills online discreetly UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wetten com erfahrungen
my blog … comment-1849913
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MediTrust [url=http://meditrustuk.com/#]MediTrust[/url] trusted online pharmacy ivermectin UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
UK pharmacy home delivery trusted UK digital pharmacy or trusted UK digital pharmacy trusted UK digital pharmacy
https://maps.google.com.kw/url?sa=t&url=https://mediquickuk.com MediQuick UK or https://rightcoachforme.com/author/uqfqbrvvdo/ UK pharmacy home delivery
[url=http://images.google.ee/url?q=https://mediquickuk.com]MediQuickUK[/url] UK pharmacy home delivery or [url=http://www.blackinseattle.com/profile/iijoghnciw/]MediQuickUK[/url] trusted UK digital pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BluePill UK https://intimacareuk.shop/# IntimaCare
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проверенная кракен ссылка для входа > кракен зеркало тг Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен ссылка, и вот что стабильно работает: Сегодня кракен маркет стал центром обсуждений и поиска рабочих ссылок. Сообщество делится инструкциями, как правильно входить, какие onion-домены использовать и как защитить данные. Настоящий кракен маркет подтверждается администрацией.
Проверил лично несколько адресов — стабильно открываются: рабочее зеркало кракен — krakmirror.ccкракен тор вход зеркало — krakmirror.cc Если нужна помощь — пишите.Проверено лично (Уфа). Кракен тор площадка для покупок телега
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BluePillUK fast delivery viagra UK online and BluePill UK generic sildenafil UK pharmacy
https://www.adoptimist.com/?URL=http://bluepharmafrance.com BluePillUK or https://app.guiigo.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=484866 fast delivery viagra UK online
[url=https://cse.google.lt/url?sa=t&url=https://bluepilluk.com]generic sildenafil UK pharmacy[/url] viagra discreet delivery UK and [url=http://foru1f40m.bunbun000.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=9676230]viagra discreet delivery UK[/url] generic sildenafil UK pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://mediquickuk.shop/# UK pharmacy home delivery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
you’re truly a good webmaster. The web site loading velocity is incredible.
It sort of feels that you are doing any unique trick.
Also, The contents are masterpiece. you’ve done a fantastic job
on this subject!
my web blog; Proxy Servers
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
IntimaCare [url=http://intimacareuk.com/#]tadalafil generic alternative UK[/url] IntimaCare UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy IntimaCare and IntimaCare UK cialis online UK no prescription
https://cse.google.com.tr/url?sa=i&url=http://intimapharmafrance.com buy ED pills online discreetly UK and https://vedicnutraceuticals-uk.com/user/amntpsquxd/?um_action=edit cialis online UK no prescription
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.com.my/url?q=https://intimacareuk.com]IntimaCareUK[/url] IntimaCareUK or [url=http://80tt1.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3973417]confidential delivery cialis UK[/url] IntimaCare UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BluePill UK https://bluepilluk.com/# fast delivery viagra UK online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
trusted online pharmacy ivermectin UK generic stromectol UK delivery and ivermectin without prescription UK MediTrustUK
http://clients1.google.com.ni/url?q=https://meditrustuk.com:: stromectol pills home delivery UK or https://forum.expert-watch.com/index.php?action=profile;u=467656 ivermectin without prescription UK
[url=http://scanmail.trustwave.com/?c=6677&d=3eHL2zmR-mSEueRJSdX4UpJhLotL1yEZhefsffMCDw&u=http://pharmalibrefrance.com]ivermectin tablets UK online pharmacy[/url] generic stromectol UK delivery or [url=https://vedicnutraceuticals-uk.com/user/nhdqbnifks/?um_action=edit]ivermectin tablets UK online pharmacy[/url] ivermectin tablets UK online pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
IntimaCare UK: IntimaCare – weekend pill UK online pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://intimacareuk.com/# weekend pill UK online pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ivermectin tablets UK online pharmacy [url=https://meditrustuk.shop/#]MediTrustUK[/url] MediTrust UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
fast delivery viagra UK online https://meditrustuk.com/# generic stromectol UK delivery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
generic and branded medications UK pharmacy online fast delivery UK and generic and branded medications UK generic and branded medications UK
http://www.a-31.de/url?q=https://mediquickuk.com MediQuick UK and https://vintage-car.eu/user/temdebcbxz/ pharmacy online fast delivery UK
[url=https://toolbarqueries.google.com.bh/url?q=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com]generic and branded medications UK[/url] trusted UK digital pharmacy and [url=https://www.hapkido.com.au/user/aaar58fastmailonii-org/]pharmacy online fast delivery UK[/url] trusted UK digital pharmacy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от успещных seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=%D1%82%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%84+bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD+%D1%85%D1%80%D1%83%D0%BC%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC
Автоматизация создания ссылок с Xrumer помогает поддерживать стабильность профиля. Xrumer: настройка и запуск линкбилдинг обеспечивает удобство работы. Линкбилдинг где брать ссылки становится очевидным через базы. Линкбилдинг под ключ экономит время веб-мастеров. Линкбилдинг это что помогает новичкам понять процесс.
продвижение сайтов по поисковикам, seo проверка яндекс, Xrumer рассылка форумов
Оптимизация ссылочного профиля, seo оптимизация ютуба, метод продвижения сайтов
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
https://kozas.site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
MediQuickUK: order medicines online discreetly – generic and branded medications UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://bluepilluk.com/# fast delivery viagra UK online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://intimacareuk.com/# IntimaCare UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ԍood post. І certaiinly aρpreciate tһis website. Kеep writing!
Мy webpage Where to buy mdma pills darknet
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
viagra online UK no prescription [url=http://bluepilluk.com/#]viagra online UK no prescription[/url] order viagra online safely UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BluePill UK https://bluepilluk.com/# BluePill UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добрый день!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=%D1%82%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%84+bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD+%D1%85%D1%80%D1%83%D0%BC%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC
Линкбилдинг под бурж помогает выходить на зарубежные рынки. Качественный линкбилдинг обеспечивает стабильный рост DR. Линкбилдинг вакансии открывают возможности для специалистов. Линкбилдинг купить можно через надежные компании. Компания линкбилдинг форум предоставляет доступ к большим базам ссылок.
seo проектов, лучшие сайты раскрутки, линкбилдинг форум
Линкбилдинг через программы, по для продвижения сайта, seo продвижение яндекс seo fortuna
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
https://kozas.site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wettanbieter mit lizenz in deutschland
my web site … darts wettquoten erklärung
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
safe ivermectin pharmacy UK: MediTrust – trusted online pharmacy ivermectin UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://bluepilluk.shop/# sildenafil tablets online order UK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
viagra online UK no prescription https://intimacareuk.shop/# IntimaCareUK
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как играть в Кракен: правила > кракен телеграмм отзывы Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен телеграм маркетплейс, и вот что стабильно работает: Запрос площадка кракен используется всё чаще, так как именно через него новички ищут доступ к основным разделам. Настоящая площадка кракен — это центральная точка, где собраны инструменты, разделы и возможности. Люди подчёркивают, что площадка кракен работает стабильно только при использовании проверенных зеркал.
Проверил лично несколько зеркал — стабильно открываются: кракен тг бот тор — kraktor.ccкракен телеграмм отзывы — krareview.cc Если нужна помощь — задавайте вопросы.Проверено лично (Сургут). kraken link онлайн-площадка Телеграм
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis generic overnite cialis coupon code
http://noexcuselist.com/li/?url=http://bluepharmafrance.com blue sky peptide tadalafil review
[url=https://maps.google.co.mz/url?sa=t&url=https://evergreenrxusas.shop]cheap cialis for sale[/url] prices of cialis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://evergreenrxusas.shop/# EverGreenRx USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverGreenRx USA: EverGreenRx USA – buying cialis online canadian order
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://evergreenrxusas.com/# EverGreenRx USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafil hong kong [url=http://evergreenrxusas.com/#]EverGreenRx USA[/url] canadian cialis
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
wette ohne einzahlung
My web page basketball wetten verlängerung
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverGreenRx USA: EverGreenRx USA – EverGreenRx USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Актуальная ссылка кракен в торе > кракен в телеграме Сегодня я протестировал несколько бесплатный прокрут рулетки на кракен, и вот что стабильно работает: Фраза кракен в телеграме стала обыденной, ведь почти все пользователи полагаются на этот источник. Настоящий кракен в телеграме дублируется администрацией и подтверждается активным сообществом, которое заботится о том, чтобы новички не ошиблись.
Проверил лично несколько зеркал — стабильно открываются: кракен тор — kraktor.ccкракен поддержка телеграм — kratg.cc Если нужна помощь — пишите.Проверено лично (Архангельск). Kraken Marketplace даркнет маркет мессенджер Телеграм
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverGreenRx USA: cialis over the counter usa – cialis 100mg
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://evergreenrxusas.shop/# EverGreenRx USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverGreenRx USA [url=http://evergreenrxusas.com/#]EverGreenRx USA[/url] EverGreenRx USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis 80 mg dosage cialis drug interactions
https://images.google.com.vn/url?sa=t&url=https://evergreenrxusas.com order cialis online no prescription reviews
[url=https://cse.google.sc/url?sa=t&url=https://evergreenrxusas.com]original cialis online[/url] cialis 30 day free trial
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis 20 milligram cialis for daily use
http://ewin.biz/jsonp/?url=https://evergreenrxusas.shop:: cialis recommended dosage
[url=http://www.hotel.pieniny.com/pl/entity/add/memory?anons=353&refurl=https://evergreenrxusas.shop]tamsulosin vs. tadalafil[/url] cheap cialis with dapoxetine
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis super active: EverGreenRx USA – EverGreenRx USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://evergreenrxusas.com/# EverGreenRx USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cialis tadalafil 10 mg how to take liquid tadalafil
https://www.google.sc/url?q=https://evergreenrxusas.shop cialis recommended dosage
[url=https://www.google.com.cu/url?q=https://evergreenrxusas.shop]tadalafil liquid review[/url] buy tadalafil no prescription
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
how much is cialis without insurance: EverGreenRx USA – best price on generic tadalafil
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverGreenRx USA [url=http://evergreenrxusas.com/#]EverGreenRx USA[/url] EverGreenRx USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://evergreenrxusas.com/# EverGreenRx USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
EverGreenRx USA: cialis prescription online – EverGreenRx USA
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Цена Кракен телефона — дешево? > адрес сайта Кракена Сегодня я протестировал несколько кракен по какому каналу сегодня, и вот что стабильно работает: Фраза кракен смотреть бесплатно без регистрации звучит заманчиво, но сообщество предупреждает: реальный доступ возможен лишь частично. Настоящий кракен смотреть бесплатно без регистрации открывает обзорные страницы и новости, но чтобы пользоваться функциями полноценно, нужна регистрация.
Проверил лично несколько адресов — стабильно открываются: кракен тг бот тор — kraktor.ccвход в кракен — krakenlogin.cc Если нужна помощь — оставляйте комменты.Проверено лично (Омск). Кракен даркнет теневой маркет Телеграмм
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://sparklymaidnyc.com
https://www.sparklymaidnyc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[url=https://h1.hentai-xxx.top/anime.php?id=572] смотреть аниме Потерять Девственость в первую очередь[/url]
[url=https://h1.hentai-xxx.top/anime.php?id=545] смотреть аниме Секретное путешествие[/url]
[url=https://h1.hentai-xxx.top/anime.php?id=283] смотреть аниме Запретные прелести[/url]
[url=https://h1.hentai-xxx.top/anime.php?id=334] смотреть аниме Касание девственницы[/url]
[url=https://h1.hentai-xxx.top/anime.php?id=745] смотреть аниме Легенда о принудительном чпоке Куноити Адзисай[/url]
[url=https://h1.hentai-xxx.top/anime.php?id=278] смотреть аниме Время соблазнений[/url]
[url=https://h1.hentai-xxx.top/anime.php?id=146] смотреть аниме Остров оплодотворения[/url]
[url=https://h1.hentai-xxx.top/anime.php?id=625] смотреть аниме Такая идеальная леди, как я, ни за что не опустится на колени и не превратится в мазохистку![/url]
[url=https://h1.hentai-xxx.top/anime.php?id=267] смотреть аниме Кембриец[/url]
[url=https://h1.hentai-xxx.top/anime.php?id=82] смотреть аниме Я верю ей![/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://sparklymaidnyc.com
https://www.sparklymaidnyc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bataraslot alternatif: situs slot batara88 – situs slot batara88
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=%D1%82%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%84+bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD+%D1%85%D1%80%D1%83%D0%BC%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC
Увеличение DR с помощью Xrumer возможно через автоматический постинг ссылок. Массовый прогон форумов с Xrumer помогает быстро улучшить SEO-позиции. Программы для линкбилдинга ускоряют процесс создания ссылок. Прогон ссылок Хрумером повышает показатели Ahrefs. Используйте Xrumer для качественного продвижения.
создание и продвижение сайтов в казани, seo запрос это, линкбилдинг купить
Повышение авторитетности домена, книги по продвижения сайтов, частный сео продвижение сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
https://kozas.site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://sparklymaidnyc.com
https://www.sparklymaidnyc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
เว็บ PG เกมสล็อตแตกง่าย!
รวยได้ทุกวัน แค่ปลายนิ้วก็รวยได้!,เบื่อเกมสล็อตยากๆ?
ต้อง PGSLOT เลย! ทำเงินได้ไว ทำกำไรเน้นๆ,โอกาสทองมาแล้ว!
PGSLOT ให้ไม่อั้น ทุก User,ไม่ต้องมีทุนเยอะก็เล่นได้!
PGSLOT สล็อตทุนน้อย แตกหนัก จ่ายเต็ม,เข้าเล่น PGSLOT ตอนนี้!
ทำเงินมหาศาล ไม่ต้องรอ,ที่สุดของความบันเทิงและรางวัลใหญ่ มีแค่ PGSLOT ที่เดียว!,
พีจีสล็อต: มีคืนยอดเสียให้!
เล่นเสียก็ยังได้คืน คุ้มค่าเกินคุ้ม,สมัครวันนี้ รับเลย!
พีจีสล็อต แจกโบนัสแรกเข้า รับเองง่ายๆ,ห้ามพลาดเด็ดขาด!
พีจีสล็อต โปรโมชั่นโดนใจ คุ้มสุดๆ,ลงทุนน้อยได้มากกับ PGSLOT!
โปรโมชั่นดีๆ รอคุณอยู่เพียบ,พีจีสล็อต แนะนำเพื่อน ได้เงินง่ายๆ แค่ชวนเพื่อน!,สุดยอดความคุ้มค่า!
เล่น PGSLOT มีแต่ได้กับได้ แจกกระจาย!,
สนุกกับ PGSLOT ได้ทุกที่!
ใช้งานง่ายทุกอุปกรณ์ มือถือ คอมพิวเตอร์ ครบจบในที่เดียว,มั่นใจ
100%! PGSLOT เว็บตรง ไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์
ฝาก-ถอนออโต้ รวดเร็วทันใจ,บริการประทับใจ 24 ชม.!
ทีมงาน PGSLOT พร้อมดูแลและแก้ไขปัญหาให้คุณ,พีจีสล็อต เว็บสล็อตยอดนิยม มั่นคงและเชื่อถือได้,เริ่มเล่น PGSLOT ได้เลย เล่นผ่านเว็บบราวเซอร์ เล่นผ่านเว็บได้เลย,
เล่นเกมไม่มีกระตุก!
พีจีสล็อต เล่นมันส์ไม่มีเบื่อ,
ลองมาแล้ว พีจีสล็อต จ่ายจริงทุกยอด!
ห้ามพลาด!,บริการ
PGSLOT ดีเยี่ยม! ทำรายการรวดเร็ว
ทันใจทุกครั้ง,เจอแล้วเกมสล็อตที่ใช่!
PGSLOT กราฟิกสวย เล่นเพลิน ทำกำไรได้เยอะ!,รีวิวจากผู้เล่นจริง!
พีจีสล็อต ตอบโจทย์ทุกการเดิมพัน ไม่ผิดหวังแน่นอน,ใครยังไม่ลอง PGSLOT ถือว่าพลาดมาก!
โอกาสสร้างรายได้ อยู่ตรงนี้แล้ว,เว็บสล็อตที่ดีที่สุดในตอนนี้!
พีจีสล็อต เกมแตกง่าย เล่นได้ไม่เบื่อ
Review my web site :: สล็อตพีจี
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tadalafil 20 mg en ligne: tadalafil prix – Intima Pharma
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Wһen someone writes an piece of writing he/she kеeps the thoսght of a user іn his/һer mind that how a uѕer can bbe aware օf
it. Thus thаt’ѕ whу tһis piece оf writing is perfect.
Thanks!
Loоk at my web site … Order fentanyl powder with discreet shipping
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for mutual promotion. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://sparklymaidnyc.com
https://www.sparklymaidnyc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
It’s fantastic that you ɑre getting tһoughts fom tһis
post ass weell аs fгom oսr discussion mɑԁe at this plɑсe.
Stop bʏ my site;purity 4-mmc pure crystal powder online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I гeally like it when individuals come tоgether ɑnd share ideas.
Great website, continue the good work!
Αlso visiit my web-site; Desmetramadol powder for chemical synthesis studies
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Здравствуйте!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от крутых seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Увеличение трафика с помощью прогона возможно через массовое размещение ссылок. Форумы и блоги дают естественные линкбэксы. Xrumer ускоряет процесс автоматизации. Чем больше качественных ссылок, тем выше DR. Увеличение трафика с помощью прогона помогает SEO-продвижению.
продвижение сайтов основные направления, продвижение стоит сайтов, Автоматизированный линкбилдинг
Программное обеспечение для постинга, seo книга купить, seo продвижения стоимость
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
https://drtop.site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доброго!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг стратегия должна быть продуманной. Использование Xrumer позволяет автоматизировать процесс прогона ссылок. Массовый линкбилдинг повышает DR. Автоматизация экономит силы специалистов. Линкбилдинг стратегия – основа эффективного продвижения.
интернет магазин seo оптимизация, заказать продвижение сайтов москва топ, Как поднять DR сайта за неделю
линкбилдинг форум, раскрутка сайтов гарантия, сео как переводится
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
https://drtop.site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
native united statesn casino rights, real pokies australia and free imatant spins no deposit bonus united
states, or united kingdom casino slots
Feel free to visit my homepage … number of indian casinos in the us (Anderson)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Dry Cleaning in New York city by Sparkly Maid NYC
https://www.sparklymaidnyc.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
gambling advertising canada, united states online casino slots and online slots australia paypal, or 2021 usa
online casino no deposit bonus codes
my web blog: casinos lake charles hurricane laura (Rosalind)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Wonderful post however ,I was wanting to know if youu could write
a litte more on this topic? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit further.
Thank you!
my web site; Dream Proxies (https://dreamproxies.com/free-proxies-and-discounts)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Quality cleaning fair prices, economical without cutting corners. Budget-friendly quality found. Quality without overpaying.
mmkk.free-blogz.com/83779192/lily-maids-house-cleaning-service-of-nyc
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Its like you learn my mind! You appear to grasp a lot about this, like you wrote the e book in it or something.
I feel that you simply can do with a few percent to force the message house a little bit, but other than that, this is wonderful
blog. An excellent read. I will definitely be back.
my homepage ramatogel
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Bespoke cleaning professionals, bespoke service excellence. Personalized professionals. Bespoke service.
sites.google.com/view/apartmentcleaningservicelongis/home
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hi, I do think this is a great web site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to revisit once
again since I saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the best way to change,
may you be rich and continue to guide others.
Stop by my site; Welcome to Lotus365 – Avail 100% Guaranteed Bonus Now!
(lotus365.diy)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Привет всем!
Долго анализировал как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от крутых seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг или стратегии зависят от целей проекта. Линкбилдинг работа требует внимательного подхода. Линкбилдинг начать можно с форумов и блогов. Линкбилдинг стратегия ускоряет рост ссылочной массы. Линкбилдинг для англоязычного сайта открывает новые рынки.
лучшие раскрутка сайтов, анализ сайта раскрутки, Эффективность прогона Xrumer
Как увеличить показатели домена, seo на авито, seo crm
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Quality cleaning fair prices, fits our NYC budget perfectly. Value cleaning champions. Smart choice made.
http://www.penzu.com/p/794032c98a2b925c
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Here to join conversations, exchange ideas, and gain fresh perspectives as I go.
I enjoy hearing diverse viewpoints and contributing whenever I can. Happy to hear fresh thoughts and meeting like-minded people.
That’s my website-AutoMisto24
https://automisto24.com.ua/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Superb cleaning job, transformed our home completely. Can’t imagine using anyone else. Keep up the great work.
http://www.semfirms.com/profile/lily-maids-house-cleaning-service-nyc
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Greetings from Los angeles! I’m bored to death at work so I decided to browse your blog on my iphone during lunch break.
I love the knowledge you present here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home.
I’m shocked at how quick your blog loaded on my phone ..
I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, very good blog!
Take a look at my blog – denisonhs.net, http://G.Ra.nc.E.rnmn@.R.os.p.E.r.Les.c@pezedium.free.fr,
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I do believe all of the ideas you have introduced in your
post. They’re really convincing and will certainly work.
Nonetheless, the posts are very short for novices. May you please lengthen them
a little from next time? Thank you for the post.
My webpage :: Amazing Proxies
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I am truly thankful to the holder of this website who has shared this impressive piece of writing at at this time.
Also visit my page Reliable Proxies
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks on your marvelous posting! I genuinely enjoyed reading it, you’re a great author.
I will ensure that I bookmark your blog and will
often come back at some point. I want to encourage you to continue your great work, have a nice weekend!
my web site; Proxies Cheap
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello friends, its enormous article on the topic of
cultureand completely explained, keep it up all the
time.
my web page; slot deposit pulsa tanpa potongan
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Great website. Lots of helpful information here. I’m sending it to a
few pals ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks on your effort!
Look into my web blog; Twitter Proxy
Hi there, after reading this remarkable piece of writing i am also glad to share
my knowledge here with colleagues.
Also visit my site – slot anti kalah
Hurrah! At last I got a weblog from where I be capable of really take valuable facts concerning my study and knowledge.
Review my website – slot mpo terbaru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks for the auspicious writeup. It in reality was a amusement account it.
Look complex to far delivered agreeable from you! By the way, how
could we communicate?
Feel free to surf to my blog: animal care services bexar county
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Having read this I thought it was rather enlightening.
I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this content together.
I once again find myself spending a lot of time both reading and posting
comments. But so what, it was still worth it!
Here is my homepage – Diesel
I enjoy what you guys are up too. This type of clever
work and exposure! Keep up the amazing works guys I’ve added you guys to our blogroll.
My web blog – Emas
Hello! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I really enjoy
reading through your blog posts. Can you recommend
any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same subjects?
Thank you!
Look at my site slot deposit pulsa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Today, I went to the beach with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed.
There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear.
She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally
off topic but I had to tell someone!
Here is my site; Aplikasi Trading
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
If some one wishes to be updated with newest technologies afterward he
must be visit this site and be up to date every day.
Also visit my website; slot anti kalah
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Howdy! This is kind of off topic but I need some guidance from an established blog.
Is it tough to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things
out pretty quick. I’m thinking about setting up my own but I’m not sure
where to begin. Do you have any ideas or suggestions?
Many thanks
Here is my webpage … buy rare
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
If some one needs to be updated with most up-to-date technologies
therefore he must be pay a quick visit this website and be up
to date daily.
Also visit my site :: gampang scatter
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hey just wanted to give you a quick heads up.
The text in your article seem to be running off the screen in Ie.
I’m not sure if this is a formatting issue or something to do with browser compatibility but
I thought I’d post to let you know. The layout look great though!
Hope you get the issue fixed soon. Thanks
Here is my website: aborsi anak
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I was curious if you ever considered changing the structure of your site?
Its very well written; I love what youve got to say.
But maybe you could a little more in the way of content
so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for
only having 1 or 2 pictures. Maybe you could space it out better?
Also visit my web page … windows vps online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I every time emailed this web site post page to all my contacts,
since if like to read it after that my links will too.
My web-site … Elite private proxy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ffantastic issues altogether, у᧐u simply received а neew reader.
What migһt yоu suɡgest about үouг submit tһat yoᥙ made ɑ feѡ days in thе past?
Any positive?
Ꮋere is my web site: buy ecstasy pills with bitcoin
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
This paragraph will assist the internet users for building
up new weblog or even a blog from start to end.
Also visit my web page :: slot 4d
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Fantastic Glasses
unit 401 235 Milligan Dr
Okotoks, AB T1S 0B8
info@fantasticglasses.ca
587-997-EYES(3937)
Okotoks eyecare
https://www.fantasticglasses.ca/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Yes! Finally something about slot anti kalah pasti profit anti kalah.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’m not that much of a online reader to be honest but your sites really nice, keep it up!
I’ll go ahead and bookmark your site to come back down the
road. All the best
Stop by my blog post slot mpo
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
of course like yoᥙr website һowever yⲟu need
to check tthe spelling օn quіte a few of yoսr posts.
Severаl of them are rife with spelling problеmѕ and Ι to find it
vеry troublesome to tеll thee truth on the other hand I’ll definitelү сome
Ьack again.
my hⲟmepage andractim dht gel f᧐r sale ussa (https://sfcc-chemicals.com)
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Excellent items from you, man. I’ve take into account your
stuff prior to and you are just too excellent.
I really like what you have received right here, really
like what you are saying and the way in which wherein you assert it.
You make it enjoyable and you still take care of to
keep it smart. I cant wait to read far more from you. That is really a wonderful site.
Check out my website pulseras magneticas
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find It
really useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give
something back and aid others like you aided me.
Check out my site; ramatogel
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Cabinet IQ
8305 Ⴝtate Hwwy 71 #110, Austin,
TX 78735, United Ꮪtates
254-275-5536
Remodelbudget
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Cabinet IQ
8305 Staate Hwy 71 #110, Austin,
TX 78735, United Ꮪtates
254-275-5536
Homeimprovement
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I think this is one of the most important information for
me. And i am glad reading your article. But wanna remark
on few general things, The web site style is great, the articles is really excellent : D.
Good job, cheers
Also visit my blog … asha777.godaddysites.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Lookіng for affordable storage containers?
Check ߋut Container Storage Units for affordable options ɑcross
Kent and Surrey. Ideal fⲟr domestic and business use.
My web blog: storage unit
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Every weekend i used to pay a quick visit this web site, because i want enjoyment, for the
reason that this this website conations actually nice funny stuff too.
my blog :: link slot 4d
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
It’s really very complex in this active life to listen news on Television, therefore
I only use internet for that purpose, and
take the hottest information.
Feel free to surf to my homepage :: slot anti kalah bet receh
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thank you for any other informative blog. Where else could I am getting that kind of info written in such an ideal way?
I’ve a undertaking that I’m just now running on, and I’ve been at
the glance out for such information.
Look into my homepage: mpo slot deposit pulsa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Cabinet IQ
8305 Stаte Hwy 71 #110, Austin,
TX 78735, United Տtates
254-275-5536
Space
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’m really impressed with your writing skills and also
with the layout on your blog. Is this a paid
theme or did you modify it yourself? Anyway keep up the nice quality writing,
it’s rare to see a great blog like this one these days.
Look at my website … japan pocket wifi
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello, i think that i noticed you visited my site thus i came
to return the want?.I’m trying to to find issues to improve my web site!I suppose its ok
to make use of a few of your ideas!!
My website :: תומר מרואני
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
An outstanding share! I’ve just forwarded this
onto a coworker who had been conducting a little research on this.
And he in fact ordered me dinner because I discovered it for him…
lol. So let me reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending the time to talk
about this topic here on your internet site.
Have a look at my website: Online Phonics middle school Grade Program
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What i don’t realize is if truth be told how you are now not really a lot more
neatly-preferred than you might be now. You’re so intelligent.
You already know therefore significantly on the
subject of this topic, made me in my view consider it from a lot of varied angles.
Its like women and men aren’t fascinated unless it is something to accomplish with Lady gaga!
Your personal stuffs nice. At all times care for it up!
Feel free to visit my webpage :: wordpress
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Fantastic Glasses
unit 401 235 Milligan Dr
Okotoks, AB T1S 0B8
info@fantasticglasses.ca
587-997-EYES(3937)
reading glasses Okotoks
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Today, I went to the beachfront with my kids. I found a
sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed
the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear.
She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally off topic but
I had to tell someone!
⭐ http://maltaeng.com
— Learn English in Malta at the best language center with special pricing — Elevate your English
abilities…
⭐ English courses in Malta for adults
— Learn and practise English language in Malta — the country where it’s
spoken.
http://F.R.A.G.Ra.NC.E.Rnmn%40.R.OS.P.E.R.LES.C@Pezedium.Free.fr/?a%5B%5D=%3Ca+href%3Dhttps%3A%2F%2Flinks.gtanet.com.br%2Fmargart72b19%3EEnglish+language+classes+in+Malta%3C%2Fa%3E%3Cmeta+http-equiv%3Drefresh+content%3D0%3Burl%3Dhttp%3A%2F%2F4mostpopular.com%2F__media__%2Fjs%2Fnetsoltrademark.php%3Fd%3D20Trsfcdhf.Hfhjf.Hdasgsdfhdshshfsh%2540Forum.Annecy-Outdoor.com%252Fsuivi_forum%252F%253Fa%25255B%25255D%253D%25253Ca%252Bhref%25253Dhttps%25253A%25252F%25252Fthedigitalbusinesscards.store%25252F2025%25252F06%25252F01%25252Fwhy-choose-malta-for-english-language-studies-debunking-myths-and-seizing-opportunities%25252F%25253EEnglish%252Blanguage%252Bcourses%252Bin%252BMalta%252Bfor%252Binternational%252Bstudents%25253C%25252Fa%25253E%25253Cmeta%252Bhttp-equiv%25253Drefresh%252Bcontent%25253D0%25253Burl%25253Dhttps%25253A%25252F%25252Fwifidb.science%25252Fwiki%25252FImmerse_Yourself_In_The_English_Language_By_Studying_In_Malta%252B%25252F%25253E+%2F%3E —
English programs in Malta, english language schools
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Howdy! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against
hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any recommendations?
socleads.com
Let’s get emails from social media with no effort!!
email list scraper —
best email scraper software, business, email data scraper
http://rlu.ru/58Vrz
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hi, just wanted to mention, I liked this post. It was inspiring.
Keep on posting!
Feel free to surf to my website: Aplikasi trading emas
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Just wish to say your article is as astounding. The clearness on your
put up is just excellent and i could suppose you’re a professional on this subject.
Fine together with your permission allow me to clutch your feed to stay up to date with coming
near near post. Thank you one million and please keep up the gratifying work.
SOCLEADS.COM
Gain emailing addresses from social networks just like that!
email scraper website — best email scraping tools free, email scraping services,
email scraper software
http://WWW.Kepenk%20trsfcdhf.hfhjf.hdasgsdfhdshshfsh@forum.annecy-outdoor.com/suivi_forum/?a%5B%5D=%3Ca+href%3Dhttps%3A%2F%2Fwww.intermoda.ru%2Fredirect%3Furl%3DaHR0cDovL3MuQWxlb2tsb3AuQXRhcmdldD0lNUMlMjJfQmxhbmslNUMlMjIlMjBocmVmbWFpbHRvOmVARWhvc3Rpbmdwb2ludC5jb20vaW5mby5waHA%2FYSU1QiU1RD0lM0NhK2hyZWYlM0RodHRwcyUzQSUyRiUyRmZyZWV3b3JsZC5nbG9iYWwlMkZjb21tdW5pdHklMkZwcm9maWxlJTJGdml2aWVuMzMzMjM5OTY1JTJGJTNFZW1haWwrc2NyYXBlcit0b29sJTNDJTJGYSUzRSUzQ21ldGEraHR0cC1lcXVpdiUzRHJlZnJlc2grY29udGVudCUzRDAlM0J1cmwlM0RodHRwcyUzQSUyRiUyRnNlY3VyaXR5aG9sZXMuc2NpZW5jZSUyRndpa2klMkZVc2VyJTNBRW1pbGllNTdSNzExMjcxKyUyRiUzRQ%3Eemail+scraper+from+gmaps%3C%2Fa%3E%3Cmeta+http-equiv%3Drefresh+content%3D0%3Burl%3Dhttp%3A%2F%2FWww.kepenk%2520trsfcdhf.Hfhjf.hdasgsdfhdshshfsh%40forum.annecy-outdoor.com%2Fsuivi_forum%2F%3Fa%255B%255D%3D%253Ca%2Bhref%253Dhttp%253A%252F%252Fhttps%25253A%25252folv.e.L.U.pc%2540haedongacademy.org%252Fphpinfo.php%253Fa%25255B%25255D%253D%25253Ca%252Bhref%25253Dhttps%25253A%25252F%25252Fethiofarmers.com%25252Fe-mail-scraping-web-scraping-tools-for-finding-prospects-on-google-maps-and-social-media-without-even-trying%25252F%25253Efree%252Bwebsite%252Bemail%252Bscraper%25253C%25252Fa%25253E%25253Cmeta%252Bhttp-equiv%25253Drefresh%252Bcontent%25253D0%25253Burl%25253Dhttps%25253A%25252F%25252Fmyhomemypleasure.co.uk%25252Fwiki%25252Findex.php%25253Ftitle%25253DUser%25253ADamionA2306%252B%25252F%25253E%253Ebest%2Bemail%2Bscraping%2Btools%253C%252Fa%253E%253Cmeta%2Bhttp-equiv%253Drefresh%2Bcontent%253D0%253Burl%253Dhttp%253A%252F%252FWWW.Kepenk%252520trsfcdhf.hfhjf.Hdasgsdfhdshshfsh%2540Forum.annecy-outdoor.com%252Fsuivi_forum%252F%253Fa%25255B%25255D%253D%25253Ca%252Bhref%25253Dhttps%25253A%25252F%25252Fartstic.com%25252Fgroups%25252Fleading-emailing-addresses-extractors-and-marketing-software-for-effective-outreach%25252F%25253Eemail%252Bscrapers%25253C%25252Fa%25253E%25253Cmeta%252Bhttp-equiv%25253Drefresh%252Bcontent%25253D0%25253Burl%25253Dhttps%25253A%25252F%25252Fwww.mythmoor.com%25252Femails-scrapers-web-scraping-tools-for-finding-prospects-easily%25252F%25
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hi to all,the contents existing at this site are in fact amazing for people experience, well, keep up the nice work fellows.
Take a look at my blog post Cheap Private Proxies
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Does your blog have a contact page? I’m having trouble locating it but, I’d like to send
you an email. I’ve got some recommendations for your blog you might be
interested in hearing. Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it expand over time.
⭐ MaltaEng (IELS Discount)
— Learn English at one of Malta’s premier language schools with special pricing — Boost your English fluency.
⭐ Malta English schools — Learn English language in Malta — the destination where it’s spoken!
https://o-smolensk.ru/go?a:aHR0cDovLyUyNTNhJTI1MkYlMjVldm9sdi5lLkwuVS5wY0BoYWVkb25nYWNhZGVteS5vcmcvcGhwaW5mby5waHA/YSU1QiU1RD0lM0NhK2hyZWYlM0RodHRwcyUzQSUyRiUyRmZvdXJjb3JuZXJzY2xhc3NpZmllZC5jb20lMkZpbmRleC5waHAlM0ZwYWdlJTNEdXNlciUyNmFjdGlvbiUzRHB1Yl9wcm9maWxlJTI2aWQlM0QzMTAzJTNFU3R1ZHlpbmcrRW5nbGlzaCtpbitNYWx0YSUzQyUyRmElM0UlM0NtZXRhK2h0dHAtZXF1aXYlM0RyZWZyZXNoK2NvbnRlbnQlM0QwJTNCdXJsJTNEaHR0cHMlM0ElMkYlMkZ2YWxldGlub3dpa2kucmFjaW5nJTJGd2lraSUyRlVzZXIlM0FCcml0dG5leUNhbmRsZXIrJTJGJTNF —
English in Malta for adults, english language courses in Malta
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Quality posts is the important to interest the viewers to go to see the
web page, that’s what this web page is providing.
My homepage – CSR Racing 2 guide
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article.
I’ll be sure to bookmark it and come back to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post.
I will definitely comeback.
Also visit my website … My Private Proxies, Dreamproxies.com,